forked from toolshed/abra
chore: make deps, go mod vendor
This commit is contained in:
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
@ -14,16 +14,13 @@ issues:
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
# - dupl
|
||||
- exhaustive
|
||||
# - exhaustivestruct
|
||||
- goconst
|
||||
- godot
|
||||
- godox
|
||||
- gomnd
|
||||
- mnd
|
||||
- gomoddirectives
|
||||
- goprintffuncname
|
||||
# - lll
|
||||
- misspell
|
||||
- nakedret
|
||||
- nestif
|
||||
@ -34,13 +31,10 @@ linters:
|
||||
|
||||
# disable default linters, they are already enabled in .golangci.yml
|
||||
disable:
|
||||
- deadcode
|
||||
- errcheck
|
||||
- gosimple
|
||||
- govet
|
||||
- ineffassign
|
||||
- staticcheck
|
||||
- structcheck
|
||||
- typecheck
|
||||
- unused
|
||||
- varcheck
|
||||
|
||||
2
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
2
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
@ -15,12 +15,10 @@ issues:
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
- bodyclose
|
||||
- exportloopref
|
||||
- gofumpt
|
||||
- goimports
|
||||
- gosec
|
||||
- nilerr
|
||||
- predeclared
|
||||
- revive
|
||||
- rowserrcheck
|
||||
- sqlclosecheck
|
||||
|
||||
5
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
5
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
includes:
|
||||
- from_url:
|
||||
url: charmbracelet/meta/main/goreleaser-lib.yaml
|
||||
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://goreleaser.com/static/schema-pro.json
|
||||
|
||||
308
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
308
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Style definitions for nice terminal layouts. Built with TUIs in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
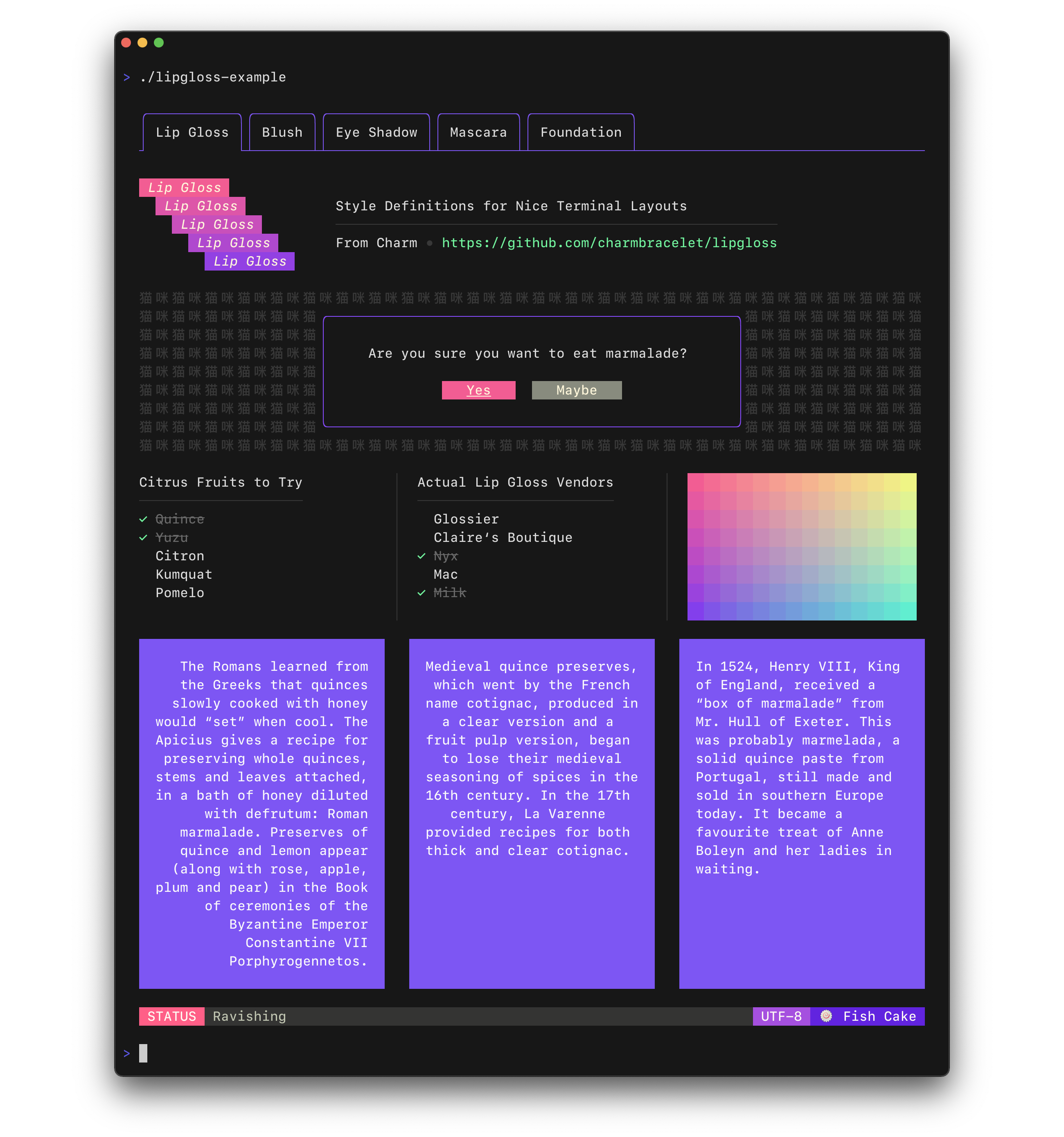
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss takes an expressive, declarative approach to terminal rendering.
|
||||
Users familiar with CSS will feel at home with Lip Gloss.
|
||||
@ -77,11 +77,11 @@ appropriate color will be chosen at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Colors
|
||||
|
||||
CompleteColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
CompleteColor specifies exact values for True Color, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
profiles.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteColor{True: "#0000FF", ANSI256: "86", ANSI: "5"}
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteColor{TrueColor: "#0000FF", ANSI256: "86", ANSI: "5"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic color degradation will not be performed in this case and it will be
|
||||
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ based on the color specified.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Adaptive Colors
|
||||
|
||||
You can use CompleteColor with AdaptiveColor to specify the exact values for
|
||||
You can use `CompleteColor` with `AdaptiveColor` to specify the exact values for
|
||||
light and dark backgrounds without automatic color degradation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
@ -402,7 +402,7 @@ block := lipgloss.Place(30, 80, lipgloss.Right, lipgloss.Bottom, fancyStyledPara
|
||||
|
||||
You can also style the whitespace. For details, see [the docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Tables
|
||||
## Rendering Tables
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a table rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -455,114 +455,9 @@ fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
|
||||
For more on tables see [the docs](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc) and [examples](https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree/master/examples/table).
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Trees
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a tree rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a new tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New("root", "child 1", "child 2", tree.New("child 3", "child 3.1"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
|
||||
// root
|
||||
// ├── child 1
|
||||
// ├── child 2
|
||||
// └── child 3
|
||||
// └── child 3.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
|
||||
Trees can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style1 := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
style2 := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("10")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
|
||||
t := tree.New().
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("Nyx").
|
||||
Items("Qux", "Quux").
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(style2),
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(style1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="Tree example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/5a875269-f6d6-43fa-9916-5d8360e66964"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
You may also define custom enumerator implementations:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New().
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("Nyx").
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Qux",
|
||||
"Quux",
|
||||
),
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(func(tree.Data, int) (string, string) {
|
||||
return "->", "->"
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="Tree example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/811e8b39-124f-48bb-b3dd-e015a65b1065"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Building
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build trees incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New("")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
t.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Lists
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a list rendering sub-package.
|
||||
Implementation-wise, lists are still trees.
|
||||
The `list` package provides many common `Enumerator` implementations, as well as
|
||||
some syntactic sugar.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/list"
|
||||
@ -584,77 +479,190 @@ fmt.Println(l)
|
||||
// • C
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lists have the ability to nest.
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New(
|
||||
"A", list.New("Artichoke"),
|
||||
"B", list.New("Baking Flour", "Bananas", "Barley", "Bean Sprouts"),
|
||||
"C", list.New("Cashew Apple", "Cashews", "Coconut Milk", "Curry Paste", "Currywurst"),
|
||||
"D", list.New("Dill", "Dragonfruit", "Dried Shrimp"),
|
||||
"E", list.New("Eggs"),
|
||||
"F", list.New("Fish Cake", "Furikake"),
|
||||
"J", list.New("Jicama"),
|
||||
"K", list.New("Kohlrabi"),
|
||||
"L", list.New("Leeks", "Lentils", "Licorice Root"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(l)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="image" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/0dc9f440-0748-4151-a3b0-7dcf29dfcdb0">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Lists can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
enumeratorStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
itemStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("10")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
itemStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("212")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
|
||||
l := list.New(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
"Nyx",
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(list.Roman).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(enumeratorStyle).
|
||||
ItemStyle(itemStyle)
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
"Nyx",
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(list.Roman).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(enumeratorStyle).
|
||||
ItemStyle(itemStyle)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="List example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/8f5e5e0b-7bf9-4e3b-a8ba-3af10825320e"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="List example" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/360494f1-57fb-4e13-bc19-0006efe01561">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the predefined enumerators (`Arabic`, `Alphabet`, `Roman`, `Bullet`, `Tree`),
|
||||
you may also define your own custom enumerator:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var DuckDuckGooseEnumerator Enumerator = func(l *List, i int) string {
|
||||
if l.At(i) == "Goose" {
|
||||
return "Honk →"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use it in a list:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New("Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Goose", "Duck", "Duck")
|
||||
l.Enumerator(DuckDuckGooseEnumerator)
|
||||
|
||||
func DuckDuckGooseEnumerator(l list.Items, i int) string {
|
||||
if l.At(i).Value() == "Goose" {
|
||||
return "Honk →"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l = l.Enumerator(DuckDuckGooseEnumerator)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="image"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/44e37a5b-5124-4f49-a332-1756a355002e"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<img width="600" alt="image" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/42545625/157aaf30-140d-4948-9bb4-dfba46e5b87e">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Building
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build trees incrementally:
|
||||
If you need, you can also build lists incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New()
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
l.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
l.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Trees
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a tree rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a new tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.Root(".").
|
||||
Child("A", "B", "C")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
|
||||
// .
|
||||
// ├── A
|
||||
// ├── B
|
||||
// └── C
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Trees have the ability to nest.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.Root(".").
|
||||
Child("macOS").
|
||||
Child(
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("Linux").
|
||||
Child("NixOS").
|
||||
Child("Arch Linux (btw)").
|
||||
Child("Void Linux"),
|
||||
).
|
||||
Child(
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("BSD").
|
||||
Child("FreeBSD").
|
||||
Child("OpenBSD"),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="663" alt="Tree Example (simple)" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/5ef14eb8-a5d4-4f94-8834-e15d1e714f89">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Trees can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
enumeratorStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("63")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
rootStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("35"))
|
||||
itemStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("212"))
|
||||
|
||||
t := tree.
|
||||
Root("⁜ Makeup").
|
||||
Child(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Fenty Beauty",
|
||||
tree.New().Child(
|
||||
"Gloss Bomb Universal Lip Luminizer",
|
||||
"Hot Cheeks Velour Blushlighter",
|
||||
),
|
||||
"Nyx",
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(tree.RoundedEnumerator).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(enumeratorStyle).
|
||||
RootStyle(rootStyle).
|
||||
ItemStyle(itemStyle)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="663" alt="Tree Example (makeup)" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/06d12d87-744a-4c89-bd98-45de9094a97e">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The predefined enumerators for trees are `DefaultEnumerator` and `RoundedEnumerator`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build trees incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New()
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
t.Child("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
@ -726,6 +734,12 @@ the stylesheet-based Markdown renderer.
|
||||
|
||||
[glamour]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/glamour
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
See [contributing][contribute].
|
||||
|
||||
[contribute]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/contribute
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
We’d love to hear your thoughts on this project. Feel free to drop us a note!
|
||||
|
||||
10
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
10
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
@ -307,9 +307,7 @@ func (s Style) Render(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
te = te.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Reverse()
|
||||
te = te.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if blink {
|
||||
@ -355,6 +353,8 @@ func (s Style) Render(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
|
||||
// Potentially convert tabs to spaces
|
||||
str = s.maybeConvertTabs(str)
|
||||
// carriage returns can cause strange behaviour when rendering.
|
||||
str = strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\r\n", "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
// Strip newlines in single line mode
|
||||
if inline {
|
||||
@ -564,14 +564,14 @@ func pad(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int { //nolint:unparam
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int { //nolint:unparam,predeclared
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int { //nolint:predeclared
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
131
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/table.go
generated
vendored
131
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/table.go
generated
vendored
@ -7,6 +7,10 @@ import (
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// HeaderRow denotes the header's row index used when rendering headers. Use
|
||||
// this value when looking to customize header styles in StyleFunc.
|
||||
const HeaderRow int = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// StyleFunc is the style function that determines the style of a Cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It takes the row and column of the cell as an input and determines the
|
||||
@ -53,9 +57,10 @@ type Table struct {
|
||||
headers []string
|
||||
data Data
|
||||
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
offset int
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
useManualHeight bool
|
||||
offset int
|
||||
|
||||
// widths tracks the width of each column.
|
||||
widths []int
|
||||
@ -84,7 +89,7 @@ func New() *Table {
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearRows clears the table rows.
|
||||
func (t *Table) ClearRows() *Table {
|
||||
t.data = nil
|
||||
t.data = NewStringData()
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -199,6 +204,7 @@ func (t *Table) Width(w int) *Table {
|
||||
// Height sets the table height.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Height(h int) *Table {
|
||||
t.height = h
|
||||
t.useManualHeight = true
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -210,15 +216,13 @@ func (t *Table) Offset(o int) *Table {
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the table as a string.
|
||||
func (t *Table) String() string {
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
hasHeaders := len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
hasRows := t.data != nil && t.data.Rows() > 0
|
||||
|
||||
if !hasHeaders && !hasRows {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
// Add empty cells to the headers, until it's the same length as the longest
|
||||
// row (only if there are at headers in the first place).
|
||||
if hasHeaders {
|
||||
@ -235,15 +239,15 @@ func (t *Table) String() string {
|
||||
// the StyleFunc after the headers and rows. Update the widths for a final
|
||||
// time.
|
||||
for i, cell := range t.headers {
|
||||
t.widths[i] = max(t.widths[i], lipgloss.Width(t.style(0, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
t.heights[0] = max(t.heights[0], lipgloss.Height(t.style(0, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
t.widths[i] = max(t.widths[i], lipgloss.Width(t.style(HeaderRow, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
t.heights[0] = max(t.heights[0], lipgloss.Height(t.style(HeaderRow, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for r := 0; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < t.data.Columns(); i++ {
|
||||
cell := t.data.At(r, i)
|
||||
|
||||
rendered := t.style(r+1, i).Render(cell)
|
||||
rendered := t.style(r, i).Render(cell)
|
||||
t.heights[r+btoi(hasHeaders)] = max(t.heights[r+btoi(hasHeaders)], lipgloss.Height(rendered))
|
||||
t.widths[i] = max(t.widths[i], lipgloss.Width(rendered))
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -342,27 +346,51 @@ func (t *Table) String() string {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var sb strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
if t.borderTop {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructTopBorder())
|
||||
s.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
sb.WriteString(t.constructTopBorder())
|
||||
sb.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if hasHeaders {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructHeaders())
|
||||
s.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for r := t.offset; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructRow(r))
|
||||
sb.WriteString(t.constructHeaders())
|
||||
sb.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var bottom string
|
||||
if t.borderBottom {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructBottomBorder())
|
||||
bottom = t.constructBottomBorder()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If there are no data rows render nothing.
|
||||
if t.data.Rows() > 0 {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case t.useManualHeight:
|
||||
// The height of the top border. Subtract 1 for the newline.
|
||||
topHeight := lipgloss.Height(sb.String()) - 1
|
||||
availableLines := t.height - (topHeight + lipgloss.Height(bottom))
|
||||
|
||||
// if the height is larger than the number of rows, use the number
|
||||
// of rows.
|
||||
if availableLines > t.data.Rows() {
|
||||
availableLines = t.data.Rows()
|
||||
}
|
||||
sb.WriteString(t.constructRows(availableLines))
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
for r := t.offset; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
sb.WriteString(t.constructRow(r, false))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sb.WriteString(bottom)
|
||||
|
||||
return lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
MaxHeight(t.computeHeight()).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.width).Render(s.String())
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.width).
|
||||
Render(sb.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// computeWidth computes the width of the table in it's current configuration.
|
||||
@ -376,7 +404,7 @@ func (t *Table) computeWidth() int {
|
||||
|
||||
// computeHeight computes the height of the table in it's current configuration.
|
||||
func (t *Table) computeHeight() int {
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
hasHeaders := len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
return sum(t.heights) - 1 + btoi(hasHeaders) +
|
||||
btoi(t.borderTop) + btoi(t.borderBottom) +
|
||||
btoi(t.borderHeader) + t.data.Rows()*btoi(t.borderRow)
|
||||
@ -433,7 +461,7 @@ func (t *Table) constructHeaders() string {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Left))
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, header := range t.headers {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.style(0, i).
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.style(HeaderRow, i).
|
||||
MaxHeight(1).
|
||||
Width(t.widths[i]).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.widths[i]).
|
||||
@ -466,13 +494,49 @@ func (t *Table) constructHeaders() string {
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructRows(availableLines int) string {
|
||||
var sb strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
// The number of rows to render after removing the offset.
|
||||
offsetRowCount := t.data.Rows() - t.offset
|
||||
|
||||
// The number of rows to render. We always render at least one row.
|
||||
rowsToRender := availableLines
|
||||
rowsToRender = max(rowsToRender, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
// Check if we need to render an overflow row.
|
||||
needsOverflow := rowsToRender < offsetRowCount
|
||||
|
||||
// only use the offset as the starting value if there is overflow.
|
||||
rowIdx := t.offset
|
||||
if !needsOverflow {
|
||||
// if there is no overflow, just render to the height of the table
|
||||
// check there's enough content to fill the table
|
||||
rowIdx = t.data.Rows() - rowsToRender
|
||||
}
|
||||
for rowsToRender > 0 && rowIdx < t.data.Rows() {
|
||||
// Whenever the height is too small to render all rows, the bottom row will be an overflow row (ellipsis).
|
||||
isOverflow := needsOverflow && rowsToRender == 1
|
||||
|
||||
sb.WriteString(t.constructRow(rowIdx, isOverflow))
|
||||
|
||||
rowIdx++
|
||||
rowsToRender--
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sb.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// constructRow constructs the row for the table given an index and row data
|
||||
// based on the current configuration.
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructRow(index int) string {
|
||||
// based on the current configuration. If isOverflow is true, the row is
|
||||
// rendered as an overflow row (using ellipsis).
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructRow(index int, isOverflow bool) string {
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
hasHeaders := len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
height := t.heights[index+btoi(hasHeaders)]
|
||||
if isOverflow {
|
||||
height = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cells []string
|
||||
left := strings.Repeat(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Left)+"\n", height)
|
||||
@ -481,14 +545,21 @@ func (t *Table) constructRow(index int) string {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for c := 0; c < t.data.Columns(); c++ {
|
||||
cell := t.data.At(index, c)
|
||||
cellWidth := t.widths[c]
|
||||
|
||||
cells = append(cells, t.style(index+1, c).
|
||||
Height(height).
|
||||
cell := "…"
|
||||
if !isOverflow {
|
||||
cell = t.data.At(index, c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cellStyle := t.style(index, c)
|
||||
cells = append(cells, cellStyle.
|
||||
// Account for the margins in the cell sizing.
|
||||
Height(height-cellStyle.GetVerticalMargins()).
|
||||
MaxHeight(height).
|
||||
Width(t.widths[c]).
|
||||
Width(t.widths[c]-cellStyle.GetHorizontalMargins()).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.widths[c]).
|
||||
Render(ansi.Truncate(cell, t.widths[c]*height, "…")))
|
||||
Render(ansi.Truncate(cell, cellWidth*height, "…")))
|
||||
|
||||
if c < t.data.Columns()-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
cells = append(cells, left)
|
||||
|
||||
4
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/util.go
generated
vendored
4
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/util.go
generated
vendored
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ func btoi(b bool) int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// max returns the greater of two integers.
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int { //nolint:predeclared
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// min returns the greater of two integers.
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int { //nolint:predeclared
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
114
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
114
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,9 +1,73 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Colorizer is a [color.Color] interface that can be formatted as a string.
|
||||
type Colorizer interface {
|
||||
color.Color
|
||||
fmt.Stringer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HexColorizer is a [color.Color] that can be formatted as a hex string.
|
||||
type HexColorizer struct{ color.Color }
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Colorizer = HexColorizer{}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the color as a hex string. If the color is nil, an empty
|
||||
// string is returned.
|
||||
func (h HexColorizer) String() string {
|
||||
if h.Color == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := h.RGBA()
|
||||
// Get the lower 8 bits
|
||||
r &= 0xff
|
||||
g &= 0xff
|
||||
b &= 0xff
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("#%02x%02x%02x", uint8(r), uint8(g), uint8(b)) //nolint:gosec
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// XRGBColorizer is a [color.Color] that can be formatted as an XParseColor
|
||||
// rgb: string.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://linux.die.net/man/3/xparsecolor
|
||||
type XRGBColorizer struct{ color.Color }
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Colorizer = XRGBColorizer{}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the color as an XParseColor rgb: string. If the color is nil,
|
||||
// an empty string is returned.
|
||||
func (x XRGBColorizer) String() string {
|
||||
if x.Color == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := x.RGBA()
|
||||
// Get the lower 8 bits
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("rgb:%04x/%04x/%04x", r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// XRGBAColorizer is a [color.Color] that can be formatted as an XParseColor
|
||||
// rgba: string.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://linux.die.net/man/3/xparsecolor
|
||||
type XRGBAColorizer struct{ color.Color }
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Colorizer = XRGBAColorizer{}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the color as an XParseColor rgba: string. If the color is nil,
|
||||
// an empty string is returned.
|
||||
func (x XRGBAColorizer) String() string {
|
||||
if x.Color == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b, a := x.RGBA()
|
||||
// Get the lower 8 bits
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("rgba:%04x/%04x/%04x/%04x", r, g, b, a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForegroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -14,7 +78,16 @@ import (
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetForegroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]10;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case Colorizer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
case fmt.Stringer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s = HexColorizer{c}.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]10;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestForegroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
@ -23,6 +96,12 @@ func SetForegroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestForegroundColor = "\x1b]10;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetForegroundColor is a sequence that resets the default terminal
|
||||
// foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const ResetForegroundColor = "\x1b]110\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBackgroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -33,7 +112,16 @@ const RequestForegroundColor = "\x1b]10;?\x07"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetBackgroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]11;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case Colorizer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
case fmt.Stringer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s = HexColorizer{c}.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]11;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestBackgroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
@ -42,6 +130,12 @@ func SetBackgroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestBackgroundColor = "\x1b]11;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetBackgroundColor is a sequence that resets the default terminal
|
||||
// background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const ResetBackgroundColor = "\x1b]111\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCursorColor returns a sequence that sets the terminal cursor color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 12 ; color ST
|
||||
@ -51,7 +145,16 @@ const RequestBackgroundColor = "\x1b]11;?\x07"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetCursorColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]12;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case Colorizer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
case fmt.Stringer:
|
||||
s = c.String()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
s = HexColorizer{c}.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]12;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorColor is a sequence that requests the current terminal cursor
|
||||
@ -59,3 +162,8 @@ func SetCursorColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestCursorColor = "\x1b]12;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetCursorColor is a sequence that resets the terminal cursor color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const ResetCursorColor = "\x1b]112\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
@ -69,4 +69,11 @@ const (
|
||||
RS = 0x1E
|
||||
// US is the unit separator character (Caret: ^_).
|
||||
US = 0x1F
|
||||
|
||||
// LS0 is the locking shift 0 character.
|
||||
// This is an alias for [SI].
|
||||
LS0 = SI
|
||||
// LS1 is the locking shift 1 character.
|
||||
// This is an alias for [SO].
|
||||
LS1 = SO
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
55
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/charset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
55
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/charset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// SelectCharacterSet sets the G-set character designator to the specified
|
||||
// character set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC Ps Pd
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Ps is the G-set character designator, and Pd is the identifier.
|
||||
// For 94-character sets, the designator can be one of:
|
||||
// - ( G0
|
||||
// - ) G1
|
||||
// - * G2
|
||||
// - + G3
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For 96-character sets, the designator can be one of:
|
||||
// - - G1
|
||||
// - . G2
|
||||
// - / G3
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Some common 94-character sets are:
|
||||
// - 0 DEC Special Drawing Set
|
||||
// - A United Kingdom (UK)
|
||||
// - B United States (USASCII)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC ( B Select character set G0 = United States (USASCII)
|
||||
// ESC ( 0 Select character set G0 = Special Character and Line Drawing Set
|
||||
// ESC ) 0 Select character set G1 = Special Character and Line Drawing Set
|
||||
// ESC * A Select character set G2 = United Kingdom (UK)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCS.html
|
||||
func SelectCharacterSet(gset byte, charset byte) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b" + string(gset) + string(charset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SCS is an alias for SelectCharacterSet.
|
||||
func SCS(gset byte, charset byte) string {
|
||||
return SelectCharacterSet(gset, charset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Locking Shift 1 Right (LS1R) shifts G1 into GR character set.
|
||||
const LS1R = "\x1b~"
|
||||
|
||||
// Locking Shift 2 (LS2) shifts G2 into GL character set.
|
||||
const LS2 = "\x1bn"
|
||||
|
||||
// Locking Shift 2 Right (LS2R) shifts G2 into GR character set.
|
||||
const LS2R = "\x1b}"
|
||||
|
||||
// Locking Shift 3 (LS3) shifts G3 into GL character set.
|
||||
const LS3 = "\x1bo"
|
||||
|
||||
// Locking Shift 3 Right (LS3R) shifts G3 into GR character set.
|
||||
const LS3R = "\x1b|"
|
||||
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
@ -3,8 +3,6 @@ package ansi
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CsiSequence represents a control sequence introducer (CSI) sequence.
|
||||
@ -23,7 +21,7 @@ type CsiSequence struct {
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
Params []Parameter
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
// The command is a 32-bit integer containing the CSI command byte in the
|
||||
@ -35,17 +33,25 @@ type CsiSequence struct {
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'u' | '?' << 8
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
Cmd Command
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = CsiSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return CsiSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]Parameter(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Marker()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
@ -54,51 +60,22 @@ func (s CsiSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Intermediate()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Command()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return CsiSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
// Param is a helper that returns the parameter at the given index and falls
|
||||
// back to the default value if the parameter is missing. If the index is out
|
||||
// of bounds, it returns the default value and false.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Param(i, def int) (int, bool) {
|
||||
if i < 0 || i >= len(s.Params) {
|
||||
return def, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.Params[i].Param(def), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
@ -114,23 +91,25 @@ func (s CsiSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
for i, p := range s.Params {
|
||||
param := p.Param(-1)
|
||||
if param >= 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
if p.HasMore() {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
if cmd := s.Command(); cmd != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(cmd))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
105
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
105
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,12 +1,61 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestNameVersion (XTVERSION) is a control sequence that requests the
|
||||
// terminal's name and version. It responds with a DSR sequence identifying the
|
||||
// terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 0 q
|
||||
// DCS > | text ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-PC-Style-Function-Keys
|
||||
const (
|
||||
RequestNameVersion = "\x1b[>0q"
|
||||
XTVERSION = RequestNameVersion
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestXTVersion is a control sequence that requests the terminal's XTVERSION. It responds with a DSR sequence identifying the version.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > Ps q
|
||||
// DCS > | text ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-PC-Style-Function-Keys
|
||||
const RequestXTVersion = "\x1b[>0q"
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [RequestNameVersion] instead.
|
||||
const RequestXTVersion = RequestNameVersion
|
||||
|
||||
// PrimaryDeviceAttributes (DA1) is a control sequence that reports the
|
||||
// terminal's primary device attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI c
|
||||
// CSI 0 c
|
||||
// CSI ? Ps ; ... c
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If no attributes are given, or if the attribute is 0, this function returns
|
||||
// the request sequence. Otherwise, it returns the response sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA1.html
|
||||
func PrimaryDeviceAttributes(attrs ...int) string {
|
||||
if len(attrs) == 0 {
|
||||
return "\x1b[c"
|
||||
} else if len(attrs) == 1 && attrs[0] == 0 {
|
||||
return "\x1b[0c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
as := make([]string, len(attrs))
|
||||
for i, a := range attrs {
|
||||
as[i] = strconv.Itoa(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[?" + strings.Join(as, ";") + "c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DA1 is an alias for [PrimaryDeviceAttributes].
|
||||
func DA1(attrs ...int) string {
|
||||
return PrimaryDeviceAttributes(attrs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes is a control sequence that requests the
|
||||
// terminal's primary device attributes (DA1).
|
||||
@ -15,3 +64,57 @@ const RequestXTVersion = "\x1b[>0q"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA1.html
|
||||
const RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes = "\x1b[c"
|
||||
|
||||
// SecondaryDeviceAttributes (DA2) is a control sequence that reports the
|
||||
// terminal's secondary device attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > c
|
||||
// CSI > 0 c
|
||||
// CSI > Ps ; ... c
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA2.html
|
||||
func SecondaryDeviceAttributes(attrs ...int) string {
|
||||
if len(attrs) == 0 {
|
||||
return "\x1b[>c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
as := make([]string, len(attrs))
|
||||
for i, a := range attrs {
|
||||
as[i] = strconv.Itoa(a)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + strings.Join(as, ";") + "c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DA2 is an alias for [SecondaryDeviceAttributes].
|
||||
func DA2(attrs ...int) string {
|
||||
return SecondaryDeviceAttributes(attrs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TertiaryDeviceAttributes (DA3) is a control sequence that reports the
|
||||
// terminal's tertiary device attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI = c
|
||||
// CSI = 0 c
|
||||
// DCS ! | Text ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Text is the unit ID for the terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If no unit ID is given, or if the unit ID is 0, this function returns the
|
||||
// request sequence. Otherwise, it returns the response sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA3.html
|
||||
func TertiaryDeviceAttributes(unitID string) string {
|
||||
switch unitID {
|
||||
case "":
|
||||
return "\x1b[=c"
|
||||
case "0":
|
||||
return "\x1b[=0c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1bP!|" + unitID + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DA3 is an alias for [TertiaryDeviceAttributes].
|
||||
func DA3(unitID string) string {
|
||||
return TertiaryDeviceAttributes(unitID)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
473
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
473
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
@ -8,7 +8,10 @@ import "strconv"
|
||||
// ESC 7
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSC.html
|
||||
const SaveCursor = "\x1b7"
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SaveCursor = "\x1b7"
|
||||
DECSC = SaveCursor
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursor (DECRC) is an escape sequence that restores the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
@ -16,10 +19,13 @@ const SaveCursor = "\x1b7"
|
||||
// ESC 8
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRC.html
|
||||
const RestoreCursor = "\x1b8"
|
||||
const (
|
||||
RestoreCursor = "\x1b8"
|
||||
DECRC = RestoreCursor
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorPosition (CPR) is an escape sequence that requests the current
|
||||
// cursor position.
|
||||
// RequestCursorPosition is an escape sequence that requests the current cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI 6 n
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -60,9 +66,18 @@ func CursorUp(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "A"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUU is an alias for [CursorUp].
|
||||
func CUU(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorUp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUU1 is a sequence for moving the cursor up one cell.
|
||||
const CUU1 = "\x1b[A"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorUp1 is a sequence for moving the cursor up one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorUp(1).
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CUU1] instead.
|
||||
const CursorUp1 = "\x1b[A"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown (CUD) returns a sequence for moving the cursor down n cells.
|
||||
@ -78,17 +93,26 @@ func CursorDown(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "B"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUD is an alias for [CursorDown].
|
||||
func CUD(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorDown(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUD1 is a sequence for moving the cursor down one cell.
|
||||
const CUD1 = "\x1b[B"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown1 is a sequence for moving the cursor down one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorDown(1).
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CUD1] instead.
|
||||
const CursorDown1 = "\x1b[B"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight (CUF) returns a sequence for moving the cursor right n cells.
|
||||
// CursorForward (CUF) returns a sequence for moving the cursor right n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n C
|
||||
// # CSI n C
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUF.html
|
||||
func CursorRight(n int) string {
|
||||
func CursorForward(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
@ -96,17 +120,36 @@ func CursorRight(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "C"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUF is an alias for [CursorForward].
|
||||
func CUF(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorForward(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUF1 is a sequence for moving the cursor right one cell.
|
||||
const CUF1 = "\x1b[C"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight (CUF) returns a sequence for moving the cursor right n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n C
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUF.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorForward] instead.
|
||||
func CursorRight(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorForward(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight1 is a sequence for moving the cursor right one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorRight(1).
|
||||
const CursorRight1 = "\x1b[C"
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CUF1] instead.
|
||||
const CursorRight1 = CUF1
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft (CUB) returns a sequence for moving the cursor left n cells.
|
||||
// CursorBackward (CUB) returns a sequence for moving the cursor left n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n D
|
||||
// # CSI n D
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUB.html
|
||||
func CursorLeft(n int) string {
|
||||
func CursorBackward(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
@ -114,10 +157,29 @@ func CursorLeft(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "D"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUB is an alias for [CursorBackward].
|
||||
func CUB(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorBackward(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUB1 is a sequence for moving the cursor left one cell.
|
||||
const CUB1 = "\x1b[D"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft (CUB) returns a sequence for moving the cursor left n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n D
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUB.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorBackward] instead.
|
||||
func CursorLeft(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorBackward(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft1 is a sequence for moving the cursor left one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorLeft(1).
|
||||
const CursorLeft1 = "\x1b[D"
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CUB1] instead.
|
||||
const CursorLeft1 = CUB1
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorNextLine (CNL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the next line n times.
|
||||
@ -133,6 +195,11 @@ func CursorNextLine(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "E"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CNL is an alias for [CursorNextLine].
|
||||
func CNL(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorNextLine(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorPreviousLine (CPL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the previous line n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -147,25 +214,264 @@ func CursorPreviousLine(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "F"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursor (CUP) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the given row
|
||||
// and column.
|
||||
// CPL is an alias for [CursorPreviousLine].
|
||||
func CPL(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorPreviousLine(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorHorizontalAbsolute (CHA) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to
|
||||
// the given column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n G
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CHA.html
|
||||
func CursorHorizontalAbsolute(col int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if col > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "G"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CHA is an alias for [CursorHorizontalAbsolute].
|
||||
func CHA(col int) string {
|
||||
return CursorHorizontalAbsolute(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorPosition (CUP) returns a sequence for setting the cursor to the
|
||||
// given row and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1,1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUP.html
|
||||
func MoveCursor(row, col int) string {
|
||||
if row < 0 {
|
||||
row = 0
|
||||
func CursorPosition(col, row int) string {
|
||||
if row <= 0 && col <= 0 {
|
||||
return HomeCursorPosition
|
||||
}
|
||||
if col < 0 {
|
||||
col = 0
|
||||
|
||||
var r, c string
|
||||
if row > 0 {
|
||||
r = strconv.Itoa(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(row) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(col) + "H"
|
||||
if col > 0 {
|
||||
c = strconv.Itoa(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + r + ";" + c + "H"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CUP is an alias for [CursorPosition].
|
||||
func CUP(col, row int) string {
|
||||
return CursorPosition(col, row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorHomePosition is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left
|
||||
// corner of the scrolling region. This is equivalent to `CursorPosition(1, 1)`.
|
||||
const CursorHomePosition = "\x1b[H"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCursorPosition (CUP) returns a sequence for setting the cursor to the
|
||||
// given row and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUP.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorPosition] instead.
|
||||
func SetCursorPosition(col, row int) string {
|
||||
if row <= 0 && col <= 0 {
|
||||
return HomeCursorPosition
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var r, c string
|
||||
if row > 0 {
|
||||
r = strconv.Itoa(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if col > 0 {
|
||||
c = strconv.Itoa(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + r + ";" + c + "H"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HomeCursorPosition is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left
|
||||
// corner of the scrolling region. This is equivalent to `SetCursorPosition(1, 1)`.
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorHomePosition] instead.
|
||||
const HomeCursorPosition = CursorHomePosition
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursor (CUP) returns a sequence for setting the cursor to the
|
||||
// given row and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUP.html
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorPosition] instead.
|
||||
func MoveCursor(col, row int) string {
|
||||
return SetCursorPosition(col, row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorOrigin is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left corner of
|
||||
// the display. This is equivalent to `SetCursorPosition(1, 1)`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorHomePosition] instead.
|
||||
const CursorOrigin = "\x1b[1;1H"
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursorOrigin is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left
|
||||
// corner of the screen. This is equivalent to MoveCursor(1, 1).
|
||||
const MoveCursorOrigin = "\x1b[1;1H"
|
||||
// corner of the display. This is equivalent to `SetCursorPosition(1, 1)`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [CursorHomePosition] instead.
|
||||
const MoveCursorOrigin = CursorOrigin
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorHorizontalForwardTab (CHT) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to
|
||||
// the next tab stop n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n I
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CHT.html
|
||||
func CursorHorizontalForwardTab(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "I"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CHT is an alias for [CursorHorizontalForwardTab].
|
||||
func CHT(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorHorizontalForwardTab(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseCharacter (ECH) returns a sequence for erasing n characters and moving
|
||||
// the cursor to the right. This doesn't affect other cell attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n X
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/ECH.html
|
||||
func EraseCharacter(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "X"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ECH is an alias for [EraseCharacter].
|
||||
func ECH(n int) string {
|
||||
return EraseCharacter(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorBackwardTab (CBT) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// previous tab stop n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n Z
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CBT.html
|
||||
func CursorBackwardTab(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CBT is an alias for [CursorBackwardTab].
|
||||
func CBT(n int) string {
|
||||
return CursorBackwardTab(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VerticalPositionAbsolute (VPA) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to
|
||||
// the given row.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n d
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/VPA.html
|
||||
func VerticalPositionAbsolute(row int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if row > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "d"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VPA is an alias for [VerticalPositionAbsolute].
|
||||
func VPA(row int) string {
|
||||
return VerticalPositionAbsolute(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VerticalPositionRelative (VPR) returns a sequence for moving the cursor down
|
||||
// n rows relative to the current position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n e
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/VPR.html
|
||||
func VerticalPositionRelative(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "e"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// VPR is an alias for [VerticalPositionRelative].
|
||||
func VPR(n int) string {
|
||||
return VerticalPositionRelative(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HorizontalVerticalPosition (HVP) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to
|
||||
// the given row and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1,1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m f
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This has the same effect as [CursorPosition].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/HVP.html
|
||||
func HorizontalVerticalPosition(col, row int) string {
|
||||
var r, c string
|
||||
if row > 0 {
|
||||
r = strconv.Itoa(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if col > 0 {
|
||||
c = strconv.Itoa(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + r + ";" + c + "f"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HVP is an alias for [HorizontalVerticalPosition].
|
||||
func HVP(col, row int) string {
|
||||
return HorizontalVerticalPosition(col, row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HorizontalVerticalHomePosition is a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// upper left corner of the scrolling region. This is equivalent to
|
||||
// `HorizontalVerticalPosition(1, 1)`.
|
||||
const HorizontalVerticalHomePosition = "\x1b[f"
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCurrentCursorPosition (SCOSC) is a sequence for saving the current cursor
|
||||
// position for SCO console mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI s
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like [DECSC], except the page number where the cursor is located
|
||||
// is not saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCOSC.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SaveCurrentCursorPosition = "\x1b[s"
|
||||
SCOSC = SaveCurrentCursorPosition
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCursorPosition (SCP or SCOSC) is a sequence for saving the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
@ -176,8 +482,23 @@ const MoveCursorOrigin = "\x1b[1;1H"
|
||||
// not saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCOSC.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SaveCurrentCursorPosition] instead.
|
||||
const SaveCursorPosition = "\x1b[s"
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCurrentCursorPosition (SCORC) is a sequence for restoring the current
|
||||
// cursor position for SCO console mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like [DECRC], except the page number where the cursor was saved is
|
||||
// not restored.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCORC.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
RestoreCurrentCursorPosition = "\x1b[u"
|
||||
SCORC = RestoreCurrentCursorPosition
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursorPosition (RCP or SCORC) is a sequence for restoring the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -187,4 +508,112 @@ const SaveCursorPosition = "\x1b[s"
|
||||
// cursor was saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCORC.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [RestoreCurrentCursorPosition] instead.
|
||||
const RestoreCursorPosition = "\x1b[u"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCursorStyle (DECSCUSR) returns a sequence for changing the cursor style.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Ps SP q
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Ps is the cursor style:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Blinking block
|
||||
// 1: Blinking block (default)
|
||||
// 2: Steady block
|
||||
// 3: Blinking underline
|
||||
// 4: Steady underline
|
||||
// 5: Blinking bar (xterm)
|
||||
// 6: Steady bar (xterm)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSCUSR.html
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h4-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character-lparen-s-rparen:CSI-Ps-SP-q.1D81
|
||||
func SetCursorStyle(style int) string {
|
||||
if style < 0 {
|
||||
style = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(style) + " q"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECSCUSR is an alias for [SetCursorStyle].
|
||||
func DECSCUSR(style int) string {
|
||||
return SetCursorStyle(style)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPointerShape returns a sequence for changing the mouse pointer cursor
|
||||
// shape. Use "default" for the default pointer shape.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 22 ; Pt ST
|
||||
// OSC 22 ; Pt BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pt is the pointer shape name. The name can be anything that the
|
||||
// operating system can understand. Some common names are:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - copy
|
||||
// - crosshair
|
||||
// - default
|
||||
// - ew-resize
|
||||
// - n-resize
|
||||
// - text
|
||||
// - wait
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetPointerShape(shape string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]22;" + shape + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReverseIndex (RI) is an escape sequence for moving the cursor up one line in
|
||||
// the same column. If the cursor is at the top margin, the screen scrolls
|
||||
// down.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This has the same effect as [RI].
|
||||
const ReverseIndex = "\x1bM"
|
||||
|
||||
// HorizontalPositionAbsolute (HPA) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to
|
||||
// the given column. This has the same effect as [CUP].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n `
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/HPA.html
|
||||
func HorizontalPositionAbsolute(col int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if col > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "`"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HPA is an alias for [HorizontalPositionAbsolute].
|
||||
func HPA(col int) string {
|
||||
return HorizontalPositionAbsolute(col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HorizontalPositionRelative (HPR) returns a sequence for moving the cursor
|
||||
// right n columns relative to the current position. This has the same effect
|
||||
// as [CUP].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n a
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/HPR.html
|
||||
func HorizontalPositionRelative(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "a"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HPR is an alias for [HorizontalPositionRelative].
|
||||
func HPR(n int) string {
|
||||
return HorizontalPositionRelative(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Index (IND) is an escape sequence for moving the cursor down one line in the
|
||||
// same column. If the cursor is at the bottom margin, the screen scrolls up.
|
||||
// This has the same effect as [IND].
|
||||
const Index = "\x1bD"
|
||||
|
||||
26
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cwd.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
26
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cwd.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"net/url"
|
||||
"path"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NotifyWorkingDirectory returns a sequence that notifies the terminal
|
||||
// of the current working directory.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 7 ; Pt BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pt is a URL in the format "file://[host]/[path]".
|
||||
// Set host to "localhost" if this is a path on the local computer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://wezfurlong.org/wezterm/shell-integration.html#osc-7-escape-sequence-to-set-the-working-directory
|
||||
// See: https://iterm2.com/documentation-escape-codes.html#:~:text=RemoteHost%20and%20CurrentDir%3A-,OSC%207,-%3B%20%5BPs%5D%20ST
|
||||
func NotifyWorkingDirectory(host string, paths ...string) string {
|
||||
path := path.Join(paths...)
|
||||
u := &url.URL{
|
||||
Scheme: "file",
|
||||
Host: host,
|
||||
Path: path,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]7;" + u.String() + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
85
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
85
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
@ -3,8 +3,7 @@ package ansi
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DcsSequence represents a Device Control String (DCS) escape sequence.
|
||||
@ -22,7 +21,7 @@ type DcsSequence struct {
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
Params []Parameter
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the string raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is the data between the final byte and the escape sequence terminator.
|
||||
@ -38,17 +37,31 @@ type DcsSequence struct {
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'r' | '>' << 8 | '$' << 16
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
Cmd Command
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = DcsSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return DcsSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]Parameter(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Split returns a slice of data split by the semicolon.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Split() []string {
|
||||
return strings.Split(string(s.Data), ";")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Marker()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
@ -57,52 +70,22 @@ func (s DcsSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Intermediate()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
return s.Cmd.Command()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return DcsSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
// Param is a helper that returns the parameter at the given index and falls
|
||||
// back to the default value if the parameter is missing. If the index is out
|
||||
// of bounds, it returns the default value and false.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Param(i, def int) (int, bool) {
|
||||
if i < 0 || i >= len(s.Params) {
|
||||
return def, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.Params[i].Param(def), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
@ -118,23 +101,25 @@ func (s DcsSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
if param >= -1 {
|
||||
for i, p := range s.Params {
|
||||
param := p.Param(-1)
|
||||
if param >= 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
if p.HasMore() {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
if cmd := s.Command(); cmd != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(cmd))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteByte(ESC)
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\\')
|
||||
|
||||
9
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/focus.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
9
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/focus.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// Focus is an escape sequence to notify the terminal that it has focus.
|
||||
// This is used with [FocusEventMode].
|
||||
const Focus = "\x1b[I"
|
||||
|
||||
// Blur is an escape sequence to notify the terminal that it has lost focus.
|
||||
// This is used with [FocusEventMode].
|
||||
const Blur = "\x1b[O"
|
||||
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/keypad.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/keypad.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// Keypad Application Mode (DECKPAM) is a mode that determines whether the
|
||||
// keypad sends application sequences or ANSI sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This works like enabling [DECNKM].
|
||||
// Use [NumericKeypadMode] to set the numeric keypad mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC =
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECKPAM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KeypadApplicationMode = "\x1b="
|
||||
DECKPAM = KeypadApplicationMode
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Keypad Numeric Mode (DECKPNM) is a mode that determines whether the keypad
|
||||
// sends application sequences or ANSI sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This works the same as disabling [DECNKM].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC >
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECKPNM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KeypadNumericMode = "\x1b>"
|
||||
DECKPNM = KeypadNumericMode
|
||||
)
|
||||
36
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
36
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
@ -8,11 +8,11 @@ const (
|
||||
KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes = 1 << iota
|
||||
KittyReportEventTypes
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAllKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAllKeysAsEscapeCodes
|
||||
KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
|
||||
KittyAllFlags = KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes | KittyReportEventTypes |
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys | KittyReportAllKeys | KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys | KittyReportAllKeysAsEscapeCodes | KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestKittyKeyboard is a sequence to request the terminal Kitty keyboard
|
||||
@ -21,9 +21,41 @@ const (
|
||||
// See: https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/
|
||||
const RequestKittyKeyboard = "\x1b[?u"
|
||||
|
||||
// KittyKeyboard returns a sequence to request keyboard enhancements from the terminal.
|
||||
// The flags argument is a bitmask of the Kitty keyboard protocol flags. While
|
||||
// mode specifies how the flags should be interpreted.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Possible values for flags mask:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1: Disambiguate escape codes
|
||||
// 2: Report event types
|
||||
// 4: Report alternate keys
|
||||
// 8: Report all keys as escape codes
|
||||
// 16: Report associated text
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Possible values for mode:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1: Set given flags and unset all others
|
||||
// 2: Set given flags and keep existing flags unchanged
|
||||
// 3: Unset given flags and keep existing flags unchanged
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
func KittyKeyboard(flags, mode int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[=" + strconv.Itoa(flags) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(mode) + "u"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PushKittyKeyboard returns a sequence to push the given flags to the terminal
|
||||
// Kitty Keyboard stack.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Possible values for flags mask:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Disable all features
|
||||
// 1: Disambiguate escape codes
|
||||
// 2: Report event types
|
||||
// 4: Report alternate keys
|
||||
// 8: Report all keys as escape codes
|
||||
// 16: Report associated text
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > flags u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
|
||||
660
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
660
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,100 +1,672 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// This file define uses multiple sequences to set (SM), reset (RM), and request
|
||||
// (DECRQM) different ANSI and DEC modes.
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ModeSetting represents a mode setting.
|
||||
type ModeSetting byte
|
||||
|
||||
// ModeSetting constants.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ModeNotRecognized ModeSetting = iota
|
||||
ModeSet
|
||||
ModeReset
|
||||
ModePermanentlySet
|
||||
ModePermanentlyReset
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// IsNotRecognized returns true if the mode is not recognized.
|
||||
func (m ModeSetting) IsNotRecognized() bool {
|
||||
return m == ModeNotRecognized
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsSet returns true if the mode is set or permanently set.
|
||||
func (m ModeSetting) IsSet() bool {
|
||||
return m == ModeSet || m == ModePermanentlySet
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsReset returns true if the mode is reset or permanently reset.
|
||||
func (m ModeSetting) IsReset() bool {
|
||||
return m == ModeReset || m == ModePermanentlyReset
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsPermanentlySet returns true if the mode is permanently set.
|
||||
func (m ModeSetting) IsPermanentlySet() bool {
|
||||
return m == ModePermanentlySet
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IsPermanentlyReset returns true if the mode is permanently reset.
|
||||
func (m ModeSetting) IsPermanentlyReset() bool {
|
||||
return m == ModePermanentlyReset
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode represents an interface for terminal modes.
|
||||
// Modes can be set, reset, and requested.
|
||||
type Mode interface {
|
||||
Mode() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetMode (SM) returns a sequence to set a mode.
|
||||
// The mode arguments are a list of modes to set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/RM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRQM.html
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal then responds to the request with a Report Mode function
|
||||
// (DECRPM) in the format:
|
||||
// If one of the modes is a [DECMode], the sequence will use the DEC format.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pa ; Ps ; $ y
|
||||
// CSI Pd ; ... ; Pd h
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pa ; Ps $ y
|
||||
// CSI ? Pd ; ... ; Pd h
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SM.html
|
||||
func SetMode(modes ...Mode) string {
|
||||
return setMode(false, modes...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SM is an alias for [SetMode].
|
||||
func SM(modes ...Mode) string {
|
||||
return SetMode(modes...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetMode (RM) returns a sequence to reset a mode.
|
||||
// The mode arguments are a list of modes to reset.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If one of the modes is a [DECMode], the sequence will use the DEC format.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pd ; ... ; Pd l
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pd ; ... ; Pd l
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/RM.html
|
||||
func ResetMode(modes ...Mode) string {
|
||||
return setMode(true, modes...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RM is an alias for [ResetMode].
|
||||
func RM(modes ...Mode) string {
|
||||
return ResetMode(modes...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func setMode(reset bool, modes ...Mode) string {
|
||||
if len(modes) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
cmd := "h"
|
||||
if reset {
|
||||
cmd = "l"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
seq := "\x1b["
|
||||
if len(modes) == 1 {
|
||||
switch modes[0].(type) {
|
||||
case DECMode:
|
||||
seq += "?"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return seq + strconv.Itoa(modes[0].Mode()) + cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var dec bool
|
||||
list := make([]string, len(modes))
|
||||
for i, m := range modes {
|
||||
list[i] = strconv.Itoa(m.Mode())
|
||||
switch m.(type) {
|
||||
case DECMode:
|
||||
dec = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if dec {
|
||||
seq += "?"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return seq + strings.Join(list, ";") + cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestMode (DECRQM) returns a sequence to request a mode from the terminal.
|
||||
// The terminal responds with a report mode function [DECRPM].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pa $ p
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pa $ p
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRQM.html
|
||||
func RequestMode(m Mode) string {
|
||||
seq := "\x1b["
|
||||
switch m.(type) {
|
||||
case DECMode:
|
||||
seq += "?"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return seq + strconv.Itoa(m.Mode()) + "$p"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECRQM is an alias for [RequestMode].
|
||||
func DECRQM(m Mode) string {
|
||||
return RequestMode(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ReportMode (DECRPM) returns a sequence that the terminal sends to the host
|
||||
// in response to a mode request [DECRQM].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pa ; Ps ; $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pa ; Ps $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pa is the mode number, and Ps is the mode value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Not recognized
|
||||
// 1: Set
|
||||
// 2: Reset
|
||||
// 3: Permanent set
|
||||
// 4: Permanent reset
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRPM.html
|
||||
func ReportMode(mode Mode, value ModeSetting) string {
|
||||
if value > 4 {
|
||||
value = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch mode.(type) {
|
||||
case DECMode:
|
||||
return "\x1b[?" + strconv.Itoa(mode.Mode()) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(int(value)) + "$y"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(mode.Mode()) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(int(value)) + "$y"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Application Cursor Keys (DECCKM) is a mode that determines whether the
|
||||
// cursor keys send ANSI cursor sequences or application sequences.
|
||||
// DECRPM is an alias for [ReportMode].
|
||||
func DECRPM(mode Mode, value ModeSetting) string {
|
||||
return ReportMode(mode, value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSIMode represents an ANSI terminal mode.
|
||||
type ANSIMode int //nolint:revive
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode returns the ANSI mode as an integer.
|
||||
func (m ANSIMode) Mode() int {
|
||||
return int(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECMode represents a private DEC terminal mode.
|
||||
type DECMode int
|
||||
|
||||
// Mode returns the DEC mode as an integer.
|
||||
func (m DECMode) Mode() int {
|
||||
return int(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Keyboard Action Mode (KAM) is a mode that controls locking of the keyboard.
|
||||
// When the keyboard is locked, it cannot send data to the terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/KAM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KeyboardActionMode = ANSIMode(2)
|
||||
KAM = KeyboardActionMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetKeyboardActionMode = "\x1b[2h"
|
||||
ResetKeyboardActionMode = "\x1b[2l"
|
||||
RequestKeyboardActionMode = "\x1b[2$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Insert/Replace Mode (IRM) is a mode that determines whether characters are
|
||||
// inserted or replaced when typed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When enabled, characters are inserted at the cursor position pushing the
|
||||
// characters to the right. When disabled, characters replace the character at
|
||||
// the cursor position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/IRM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
InsertReplaceMode = ANSIMode(4)
|
||||
IRM = InsertReplaceMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetInsertReplaceMode = "\x1b[4h"
|
||||
ResetInsertReplaceMode = "\x1b[4l"
|
||||
RequestInsertReplaceMode = "\x1b[4$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Send Receive Mode (SRM) or Local Echo Mode is a mode that determines whether
|
||||
// the terminal echoes characters back to the host. When enabled, the terminal
|
||||
// sends characters to the host as they are typed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SRM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SendReceiveMode = ANSIMode(12)
|
||||
LocalEchoMode = SendReceiveMode
|
||||
SRM = SendReceiveMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetSendReceiveMode = "\x1b[12h"
|
||||
ResetSendReceiveMode = "\x1b[12l"
|
||||
RequestSendReceiveMode = "\x1b[12$p"
|
||||
|
||||
SetLocalEchoMode = "\x1b[12h"
|
||||
ResetLocalEchoMode = "\x1b[12l"
|
||||
RequestLocalEchoMode = "\x1b[12$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Line Feed/New Line Mode (LNM) is a mode that determines whether the terminal
|
||||
// interprets the line feed character as a new line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// When enabled, the terminal interprets the line feed character as a new line.
|
||||
// When disabled, the terminal interprets the line feed character as a line feed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A new line moves the cursor to the first position of the next line.
|
||||
// A line feed moves the cursor down one line without changing the column
|
||||
// scrolling the screen if necessary.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/LNM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
LineFeedNewLineMode = ANSIMode(20)
|
||||
LNM = LineFeedNewLineMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetLineFeedNewLineMode = "\x1b[20h"
|
||||
ResetLineFeedNewLineMode = "\x1b[20l"
|
||||
RequestLineFeedNewLineMode = "\x1b[20$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cursor Keys Mode (DECCKM) is a mode that determines whether the cursor keys
|
||||
// send ANSI cursor sequences or application sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECCKM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
CursorKeysMode = DECMode(1)
|
||||
DECCKM = CursorKeysMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetCursorKeysMode = "\x1b[?1h"
|
||||
ResetCursorKeysMode = "\x1b[?1l"
|
||||
RequestCursorKeysMode = "\x1b[?1$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetCursorKeysMode] and [ResetCursorKeysMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1h"
|
||||
DisableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1l"
|
||||
RequestCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Origin Mode (DECOM) is a mode that determines whether the cursor moves to the
|
||||
// home position or the margin position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECOM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
OriginMode = DECMode(6)
|
||||
DECOM = OriginMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetOriginMode = "\x1b[?6h"
|
||||
ResetOriginMode = "\x1b[?6l"
|
||||
RequestOriginMode = "\x1b[?6$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Auto Wrap Mode (DECAWM) is a mode that determines whether the cursor wraps
|
||||
// to the next line when it reaches the right margin.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECAWM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AutoWrapMode = DECMode(7)
|
||||
DECAWM = AutoWrapMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetAutoWrapMode = "\x1b[?7h"
|
||||
ResetAutoWrapMode = "\x1b[?7l"
|
||||
RequestAutoWrapMode = "\x1b[?7$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// X10 Mouse Mode is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on button
|
||||
// presses.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal responds with the following encoding:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI M CbCxCy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Cb is the button-1, where it can be 1, 2, or 3.
|
||||
// Cx and Cy are the x and y coordinates of the mouse event.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
X10MouseMode = DECMode(9)
|
||||
|
||||
SetX10MouseMode = "\x1b[?9h"
|
||||
ResetX10MouseMode = "\x1b[?9l"
|
||||
RequestX10MouseMode = "\x1b[?9$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Text Cursor Enable Mode (DECTCEM) is a mode that shows/hides the cursor.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECTCEM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ShowCursor = "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
HideCursor = "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
TextCursorEnableMode = DECMode(25)
|
||||
DECTCEM = TextCursorEnableMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetTextCursorEnableMode = "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
ResetTextCursorEnableMode = "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
RequestTextCursorEnableMode = "\x1b[?25$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// These are aliases for [SetTextCursorEnableMode] and [ResetTextCursorEnableMode].
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ShowCursor = SetTextCursorEnableMode
|
||||
HideCursor = ResetTextCursorEnableMode
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Text Cursor Enable Mode (DECTCEM) is a mode that shows/hides the cursor.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECTCEM.html
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetTextCursorEnableMode] and [ResetTextCursorEnableMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
CursorEnableMode = DECMode(25)
|
||||
RequestCursorVisibility = "\x1b[?25$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Numeric Keypad Mode (DECNKM) is a mode that determines whether the keypad
|
||||
// sends application sequences or numeric sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This works like [DECKPAM] and [DECKPNM], but uses different sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECNKM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NumericKeypadMode = DECMode(66)
|
||||
DECNKM = NumericKeypadMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetNumericKeypadMode = "\x1b[?66h"
|
||||
ResetNumericKeypadMode = "\x1b[?66l"
|
||||
RequestNumericKeypadMode = "\x1b[?66$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Backarrow Key Mode (DECBKM) is a mode that determines whether the backspace
|
||||
// key sends a backspace or delete character. Disabled by default.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECBKM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
BackarrowKeyMode = DECMode(67)
|
||||
DECBKM = BackarrowKeyMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetBackarrowKeyMode = "\x1b[?67h"
|
||||
ResetBackarrowKeyMode = "\x1b[?67l"
|
||||
RequestBackarrowKeyMode = "\x1b[?67$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Left Right Margin Mode (DECLRMM) is a mode that determines whether the left
|
||||
// and right margins can be set with [DECSLRM].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECLRMM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
LeftRightMarginMode = DECMode(69)
|
||||
DECLRMM = LeftRightMarginMode
|
||||
|
||||
SetLeftRightMarginMode = "\x1b[?69h"
|
||||
ResetLeftRightMarginMode = "\x1b[?69l"
|
||||
RequestLeftRightMarginMode = "\x1b[?69$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Normal Mouse Mode is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button presses and releases. It will also report modifier keys, wheel
|
||||
// events, and extra buttons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It uses the same encoding as [X10MouseMode] with a few differences:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NormalMouseMode = DECMode(1000)
|
||||
|
||||
SetNormalMouseMode = "\x1b[?1000h"
|
||||
ResetNormalMouseMode = "\x1b[?1000l"
|
||||
RequestNormalMouseMode = "\x1b[?1000$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press and release.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [NormalMouseMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseMode = DECMode(1000)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableMouse = "\x1b[?1000h"
|
||||
DisableMouse = "\x1b[?1000l"
|
||||
RequestMouse = "\x1b[?1000$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Highlight Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports
|
||||
// on button presses, releases, and highlighted cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It uses the same encoding as [NormalMouseMode] with a few differences:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// On highlight events, the terminal responds with the following encoding:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI t CxCy
|
||||
// CSI T CxCyCxCyCxCy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where the parameters are startx, starty, endx, endy, mousex, and mousey.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
HighlightMouseMode = DECMode(1001)
|
||||
|
||||
SetHighlightMouseMode = "\x1b[?1001h"
|
||||
ResetHighlightMouseMode = "\x1b[?1001l"
|
||||
RequestHighlightMouseMode = "\x1b[?1001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Hilite Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button presses, releases, and highlighted cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [HighlightMouseMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseHiliteMode = DECMode(1001)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001h"
|
||||
DisableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001l"
|
||||
RequestMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Button Event Mouse Tracking is essentially the same as [NormalMouseMode],
|
||||
// but it also reports button-motion events when a button is pressed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ButtonEventMouseMode = DECMode(1002)
|
||||
|
||||
SetButtonEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1002h"
|
||||
ResetButtonEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1002l"
|
||||
RequestButtonEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1002$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cell Motion Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse
|
||||
// reports on button press, release, and motion events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [ButtonEventMouseMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseCellMotionMode = DECMode(1002)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002h"
|
||||
DisableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002l"
|
||||
RequestMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Any Event Mouse Tracking is the same as [ButtonEventMouseMode], except that
|
||||
// all motion events are reported even if no mouse buttons are pressed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AnyEventMouseMode = DECMode(1003)
|
||||
|
||||
SetAnyEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1003h"
|
||||
ResetAnyEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1003l"
|
||||
RequestAnyEventMouseMode = "\x1b[?1003$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// All Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press, release, motion, and highlight events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [AnyEventMouseMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseAllMotionMode = DECMode(1003)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003h"
|
||||
DisableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003l"
|
||||
RequestMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR Mouse Extension is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports events
|
||||
// formatted with SGR parameters.
|
||||
// Focus Event Mode is a mode that determines whether the terminal reports focus
|
||||
// and blur events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal sends the following encoding:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI I // Focus In
|
||||
// CSI O // Focus Out
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Focus-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
FocusEventMode = DECMode(1004)
|
||||
|
||||
SetFocusEventMode = "\x1b[?1004h"
|
||||
ResetFocusEventMode = "\x1b[?1004l"
|
||||
RequestFocusEventMode = "\x1b[?1004$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetFocusEventMode], [ResetFocusEventMode], and
|
||||
// [RequestFocusEventMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ReportFocusMode = DECMode(1004)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableReportFocus = "\x1b[?1004h"
|
||||
DisableReportFocus = "\x1b[?1004l"
|
||||
RequestReportFocus = "\x1b[?1004$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR Extended Mouse Mode is a mode that changes the mouse tracking encoding
|
||||
// to use SGR parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal responds with the following encoding:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI < Cb ; Cx ; Cy M
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Cb is the same as [NormalMouseMode], and Cx and Cy are the x and y.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SgrExtMouseMode = DECMode(1006)
|
||||
|
||||
SetSgrExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1006h"
|
||||
ResetSgrExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1006l"
|
||||
RequestSgrExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1006$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SgrExtMouseMode] [SetSgrExtMouseMode],
|
||||
// [ResetSgrExtMouseMode], and [RequestSgrExtMouseMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MouseSgrExtMode = DECMode(1006)
|
||||
EnableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006h"
|
||||
DisableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006l"
|
||||
RequestMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// UTF-8 Extended Mouse Mode is a mode that changes the mouse tracking encoding
|
||||
// to use UTF-8 parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Utf8ExtMouseMode = DECMode(1005)
|
||||
|
||||
SetUtf8ExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1005h"
|
||||
ResetUtf8ExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1005l"
|
||||
RequestUtf8ExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1005$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// URXVT Extended Mouse Mode is a mode that changes the mouse tracking encoding
|
||||
// to use an alternate encoding.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
UrxvtExtMouseMode = DECMode(1015)
|
||||
|
||||
SetUrxvtExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1015h"
|
||||
ResetUrxvtExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1015l"
|
||||
RequestUrxvtExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1015$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR Pixel Extended Mouse Mode is a mode that changes the mouse tracking
|
||||
// encoding to use SGR parameters with pixel coordinates.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is similar to [SgrExtMouseMode], but also reports pixel coordinates.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SgrPixelExtMouseMode = DECMode(1016)
|
||||
|
||||
SetSgrPixelExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1016h"
|
||||
ResetSgrPixelExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1016l"
|
||||
RequestSgrPixelExtMouseMode = "\x1b[?1016$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Alternate Screen Mode is a mode that determines whether the alternate screen
|
||||
// buffer is active. When this mode is enabled, the alternate screen buffer is
|
||||
// cleared.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AltScreenMode = DECMode(1047)
|
||||
|
||||
SetAltScreenMode = "\x1b[?1047h"
|
||||
ResetAltScreenMode = "\x1b[?1047l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenMode = "\x1b[?1047$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Save Cursor Mode is a mode that saves the cursor position.
|
||||
// This is equivalent to [SaveCursor] and [RestoreCursor].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SaveCursorMode = DECMode(1048)
|
||||
|
||||
SetSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1048h"
|
||||
ResetSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1048l"
|
||||
RequestSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1048$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Alternate Screen Save Cursor Mode is a mode that saves the cursor position as in
|
||||
// [SaveCursorMode], switches to the alternate screen buffer as in [AltScreenMode],
|
||||
// and clears the screen on switch.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AltScreenSaveCursorMode = DECMode(1049)
|
||||
|
||||
SetAltScreenSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1049h"
|
||||
ResetAltScreenSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1049l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenSaveCursorMode = "\x1b[?1049$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Alternate Screen Buffer is a mode that determines whether the alternate screen
|
||||
// buffer is active.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [AltScreenSaveCursorMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
AltScreenBufferMode = DECMode(1049)
|
||||
|
||||
SetAltScreenBufferMode = "\x1b[?1049h"
|
||||
ResetAltScreenBufferMode = "\x1b[?1049l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenBufferMode = "\x1b[?1049$p"
|
||||
|
||||
EnableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049h"
|
||||
DisableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049$p"
|
||||
@ -105,6 +677,16 @@ const (
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://cirw.in/blog/bracketed-paste
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Bracketed-Paste-Mode
|
||||
const (
|
||||
BracketedPasteMode = DECMode(2004)
|
||||
|
||||
SetBracketedPasteMode = "\x1b[?2004h"
|
||||
ResetBracketedPasteMode = "\x1b[?2004l"
|
||||
RequestBracketedPasteMode = "\x1b[?2004$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetBracketedPasteMode], [ResetBracketedPasteMode], and
|
||||
// [RequestBracketedPasteMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004h"
|
||||
DisableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004l"
|
||||
@ -116,15 +698,59 @@ const (
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/christianparpart/d8a62cc1ab659194337d73e399004036
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SynchronizedOutputMode = DECMode(2026)
|
||||
|
||||
SetSynchronizedOutputMode = "\x1b[?2026h"
|
||||
ResetSynchronizedOutputMode = "\x1b[?2026l"
|
||||
RequestSynchronizedOutputMode = "\x1b[?2026$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SynchronizedOutputMode], [SetSynchronizedOutputMode], and
|
||||
// [ResetSynchronizedOutputMode], and [RequestSynchronizedOutputMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SyncdOutputMode = DECMode(2026)
|
||||
|
||||
EnableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026h"
|
||||
DisableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026l"
|
||||
RequestSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Grapheme Clustering Mode is a mode that determines whether the terminal
|
||||
// should look for grapheme clusters instead of single runes in the rendered
|
||||
// text. This makes the terminal properly render combining characters such as
|
||||
// emojis.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/contour-terminal/terminal-unicode-core
|
||||
const (
|
||||
GraphemeClusteringMode = DECMode(2027)
|
||||
|
||||
SetGraphemeClusteringMode = "\x1b[?2027h"
|
||||
ResetGraphemeClusteringMode = "\x1b[?2027l"
|
||||
RequestGraphemeClusteringMode = "\x1b[?2027$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetGraphemeClusteringMode], [ResetGraphemeClusteringMode], and
|
||||
// [RequestGraphemeClusteringMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableGraphemeClustering = "\x1b[?2027h"
|
||||
DisableGraphemeClustering = "\x1b[?2027l"
|
||||
RequestGraphemeClustering = "\x1b[?2027$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Win32Input is a mode that determines whether input is processed by the
|
||||
// Win32 console and Conpty.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/microsoft/terminal/blob/main/doc/specs/%234999%20-%20Improved%20keyboard%20handling%20in%20Conpty.md
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Win32InputMode = DECMode(9001)
|
||||
|
||||
SetWin32InputMode = "\x1b[?9001h"
|
||||
ResetWin32InputMode = "\x1b[?9001l"
|
||||
RequestWin32InputMode = "\x1b[?9001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetWin32InputMode], [ResetWin32InputMode], and
|
||||
// [RequestWin32InputMode] instead.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001h"
|
||||
DisableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001l"
|
||||
|
||||
36
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mouse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
36
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mouse.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseX10 returns an escape sequence representing a mouse event in X10 mode.
|
||||
// Note that this requires the terminal support X10 mouse modes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI M Cb Cx Cy
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#Mouse%20Tracking
|
||||
func MouseX10(b byte, x, y int) string {
|
||||
const x10Offset = 32
|
||||
return "\x1b[M" + string(b+x10Offset) + string(byte(x)+x10Offset+1) + string(byte(y)+x10Offset+1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MouseSgr returns an escape sequence representing a mouse event in SGR mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI < Cb ; Cx ; Cy M
|
||||
// CSI < Cb ; Cx ; Cy m (release)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#Mouse%20Tracking
|
||||
func MouseSgr(b byte, x, y int, release bool) string {
|
||||
s := "M"
|
||||
if release {
|
||||
s = "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
if x < 0 {
|
||||
x = -x
|
||||
}
|
||||
if y < 0 {
|
||||
y = -y
|
||||
}
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("\x1b[<%d;%d;%d%s", b, x+1, y+1, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/notification.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
13
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/notification.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// Notify sends a desktop notification using iTerm's OSC 9.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 9 ; Mc ST
|
||||
// OSC 9 ; Mc BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Mc is the notification body.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://iterm2.com/documentation-escape-codes.html
|
||||
func Notify(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]9;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
@ -27,25 +27,26 @@ type OscSequence struct {
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = OscSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return s.Cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Params returns the parameters of the OSC sequence split by ';'.
|
||||
// The first element is the identifier command.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Params() []string {
|
||||
return strings.Split(string(s.Data), ";")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (o OscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return OscSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), o.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: o.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Split returns a slice of data split by the semicolon with the first element
|
||||
// being the identifier command.
|
||||
func (o OscSequence) Split() []string {
|
||||
return strings.Split(string(o.Data), ";")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the OSC command. This is always gonna be a positive integer
|
||||
// that identifies the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (o OscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return o.Cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
// To be more compatible with different terminal, this will always return a
|
||||
// 7-bit formatted sequence, terminated by BEL.
|
||||
|
||||
386
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
386
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@ package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
"unsafe"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -19,128 +20,200 @@ type ParserDispatcher func(Sequence)
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:generate go run ./gen.go
|
||||
type Parser struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// the dispatch function to call when a sequence is complete
|
||||
dispatcher ParserDispatcher
|
||||
|
||||
// params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// These parameters used when constructing CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// These data used when constructing OSC, DCS, SOS, PM, and APC sequences.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// DataLen keeps track of the length of the data buffer.
|
||||
// If DataLen is -1, the data buffer is unlimited and will grow as needed.
|
||||
// Otherwise, DataLen is limited by the size of the Data buffer.
|
||||
DataLen int
|
||||
// dataLen keeps track of the length of the data buffer.
|
||||
// If dataLen is -1, the data buffer is unlimited and will grow as needed.
|
||||
// Otherwise, dataLen is limited by the size of the data buffer.
|
||||
dataLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// ParamsLen keeps track of the number of parameters.
|
||||
// This is limited by the size of the Params buffer.
|
||||
ParamsLen int
|
||||
// paramsLen keeps track of the number of parameters.
|
||||
// This is limited by the size of the params buffer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is also used when collecting UTF-8 runes to keep track of the
|
||||
// number of rune bytes collected.
|
||||
paramsLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command along with the private marker and
|
||||
// cmd contains the raw command along with the private marker and
|
||||
// intermediate bytes of the sequence.
|
||||
// The first lower byte contains the command byte, the next byte contains
|
||||
// the private marker, and the next byte contains the intermediate byte.
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is also used when collecting UTF-8 runes treating it as a slice of
|
||||
// 4 bytes.
|
||||
cmd int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneLen keeps track of the number of bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneBuf contains the bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneBuf [utf8.MaxRune]byte
|
||||
|
||||
// State is the current state of the parser.
|
||||
State byte
|
||||
// state is the current state of the parser.
|
||||
state byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewParser returns a new parser with the given sizes allocated.
|
||||
// If dataSize is zero, the underlying data buffer will be unlimited and will
|
||||
// NewParser returns a new parser with an optional [ParserDispatcher].
|
||||
// The [Parser] uses a default size of 32 for the parameters and 64KB for the
|
||||
// data buffer. Use [Parser.SetParamsSize] and [Parser.SetDataSize] to set the
|
||||
// size of the parameters and data buffer respectively.
|
||||
func NewParser(d ParserDispatcher) *Parser {
|
||||
p := new(Parser)
|
||||
p.SetDispatcher(d)
|
||||
p.SetParamsSize(parser.MaxParamsSize)
|
||||
p.SetDataSize(1024 * 64) // 64KB data buffer
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDispatcher sets the dispatcher function to call when a sequence is
|
||||
// complete.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) SetDispatcher(d ParserDispatcher) {
|
||||
p.dispatcher = d
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetParamsSize sets the size of the parameters buffer.
|
||||
// This is used when constructing CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) SetParamsSize(size int) {
|
||||
p.params = make([]int, size)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDataSize sets the size of the data buffer.
|
||||
// This is used when constructing OSC, DCS, SOS, PM, and APC sequences.
|
||||
// If size is less than or equal to 0, the data buffer is unlimited and will
|
||||
// grow as needed.
|
||||
func NewParser(paramsSize, dataSize int) *Parser {
|
||||
s := &Parser{
|
||||
Params: make([]int, paramsSize),
|
||||
Data: make([]byte, dataSize),
|
||||
func (p *Parser) SetDataSize(size int) {
|
||||
if size <= 0 {
|
||||
size = 0
|
||||
p.dataLen = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dataSize <= 0 {
|
||||
s.DataLen = -1
|
||||
p.data = make([]byte, size)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Params returns the list of parsed packed parameters.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Params() []Parameter {
|
||||
return unsafe.Slice((*Parameter)(unsafe.Pointer(&p.params[0])), p.paramsLen)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index and falls back to the default
|
||||
// value if the parameter is missing. If the index is out of bounds, it returns
|
||||
// the default value and false.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Param(i, def int) (int, bool) {
|
||||
if i < 0 || i >= p.paramsLen {
|
||||
return def, false
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
return Parameter(p.params[i]).Param(def), true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd returns the packed command of the last dispatched sequence.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Cmd() Command {
|
||||
return Command(p.cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rune returns the last dispatched sequence as a rune.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Rune() rune {
|
||||
rw := utf8ByteLen(byte(p.cmd & 0xff))
|
||||
if rw == -1 {
|
||||
return utf8.RuneError
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune((*[utf8.UTFMax]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(&p.cmd))[:rw])
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Data returns the raw data of the last dispatched sequence.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Data() []byte {
|
||||
return p.data[:p.dataLen]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset resets the parser to its initial state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Reset() {
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
p.state = parser.GroundState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clear clears the parser parameters and command.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) clear() {
|
||||
if len(p.Params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.Params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
if len(p.params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.ParamsLen = 0
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// State returns the current state of the parser.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) State() parser.State {
|
||||
return p.state
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StateName returns the name of the current state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) StateName() string {
|
||||
return parser.StateNames[p.State]
|
||||
return parser.StateNames[p.state]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses the given dispatcher and byte buffer.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Parse(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b []byte) {
|
||||
// Deprecated: Loop over the buffer and call [Parser.Advance] instead.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Parse(b []byte) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b); i++ {
|
||||
p.Advance(dispatcher, b[i], i < len(b)-1)
|
||||
p.Advance(b[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Advance advances the parser with the given dispatcher and byte.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Advance(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
// Advance advances the parser using the given byte. It returns the action
|
||||
// performed by the parser.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Advance(b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
switch p.state {
|
||||
case parser.Utf8State:
|
||||
// We handle UTF-8 here.
|
||||
return p.advanceUtf8(dispatcher, b)
|
||||
return p.advanceUtf8(b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return p.advance(dispatcher, b, more)
|
||||
return p.advance(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) collectRune(b byte) {
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < utf8.UTFMax {
|
||||
p.RuneBuf[p.RuneLen] = b
|
||||
p.RuneLen++
|
||||
if p.paramsLen >= utf8.UTFMax {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
shift := p.paramsLen * 8
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << shift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b) << shift
|
||||
p.paramsLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) dispatch(s Sequence) {
|
||||
if p.dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
p.dispatcher(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advanceUtf8(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advanceUtf8(b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
// Collect UTF-8 rune bytes.
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
rw := utf8ByteLen(p.RuneBuf[0])
|
||||
rw := utf8ByteLen(byte(p.cmd & 0xff))
|
||||
if rw == -1 {
|
||||
// We panic here because the first byte comes from the state machine,
|
||||
// if this panics, it means there is a bug in the state machine!
|
||||
panic("invalid rune") // unreachable
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < rw {
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
if p.paramsLen < rw {
|
||||
return parser.CollectAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We have enough bytes to decode the rune
|
||||
bts := p.RuneBuf[:rw]
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(bts)
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
// We have enough bytes to decode the rune using unsafe
|
||||
p.dispatch(Rune(p.Rune()))
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
p.state = parser.GroundState
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
return parser.PrintAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advance(d ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(p.State, b)
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advance(b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(p.state, b)
|
||||
|
||||
// We need to clear the parser state if the state changes from EscapeState.
|
||||
// This is because when we enter the EscapeState, we don't get a chance to
|
||||
@ -148,60 +221,53 @@ func (p *Parser) advance(d ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
// ST (\x1b\\ or \x9c), we dispatch the current sequence and transition to
|
||||
// EscapeState. However, the parser state is not cleared in this case and
|
||||
// we need to clear it here before dispatching the esc sequence.
|
||||
if p.State != state {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ClearAction, b)
|
||||
if p.state != state {
|
||||
if p.state == parser.EscapeState {
|
||||
p.performAction(parser.ClearAction, state, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if action == parser.PutAction &&
|
||||
p.State == parser.DcsEntryState && state == parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
p.state == parser.DcsEntryState && state == parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// XXX: This is a special case where we need to start collecting
|
||||
// non-string parameterized data i.e. doesn't follow the ECMA-48 §
|
||||
// 5.4.1 string parameters format.
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.StartAction, 0)
|
||||
p.performAction(parser.StartAction, state, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle special cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case b == ESC && p.State == parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
case b == ESC && p.state == parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
// Two ESCs in a row
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
if !more {
|
||||
// Two ESCs at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case b == ESC && !more:
|
||||
// Last byte is an ESC
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'P' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC P (DCS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'X' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC X (SOS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '[' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC [ (CSI) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == ']' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ] (OSC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '^' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ^ (PM) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '_' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC _ (APC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
p.performAction(parser.ExecuteAction, state, b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, action, b)
|
||||
p.performAction(action, state, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = state
|
||||
p.state = state
|
||||
|
||||
return action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) performAction(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, action parser.Action, b byte) {
|
||||
func (p *Parser) parseStringCmd() {
|
||||
// Try to parse the command
|
||||
datalen := len(p.data)
|
||||
if p.dataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
datalen = p.dataLen
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < datalen; i++ {
|
||||
d := p.data[i]
|
||||
if d < '0' || d > '9' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.cmd *= 10
|
||||
p.cmd += int(d - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) performAction(action parser.Action, state parser.State, b byte) {
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.IgnoreAction:
|
||||
break
|
||||
@ -210,127 +276,117 @@ func (p *Parser) performAction(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, action parser.Action
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b) > 1 {
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
} else if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.dispatch(Rune(b))
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(ControlCode(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.dispatch(ControlCode(b))
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.MarkerAction:
|
||||
// Collect private marker
|
||||
// we only store the last marker
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.CollectAction:
|
||||
// Collect intermediate bytes
|
||||
// we only store the last intermediate byte
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
// Reset the UTF-8 counter
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// Collect intermediate bytes
|
||||
// we only store the last intermediate byte
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ParamAction:
|
||||
// Collect parameters
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen >= len(p.Params) {
|
||||
if p.paramsLen >= len(p.params) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b >= '0' && b <= '9' {
|
||||
if p.Params[p.ParamsLen] == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = 0
|
||||
if p.params[p.paramsLen] == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] *= 10
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] += int(b - '0')
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] *= 10
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] += int(b - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ':' {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] |= parser.HasMoreFlag
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] |= parser.HasMoreFlag
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ';' || b == ':' {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params) {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
p.paramsLen++
|
||||
if p.paramsLen < len(p.params) {
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.StartAction:
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = make([]byte, 0)
|
||||
if p.dataLen < 0 && p.data != nil {
|
||||
p.data = p.data[:0]
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.DataLen = 0
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.State >= parser.DcsEntryState && p.State <= parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
if p.state >= parser.DcsEntryState && p.state <= parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// Collect the command byte for DCS
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.Cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
p.cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PutAction:
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
switch p.state {
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
if b == ';' && p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
// Try to parse the command
|
||||
datalen := len(p.Data)
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
datalen = p.DataLen
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < datalen; i++ {
|
||||
d := p.Data[i]
|
||||
if d < '0' || d > '9' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.Cmd *= 10
|
||||
p.Cmd += int(d - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b == ';' && p.cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.parseStringCmd()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = append(p.Data, b)
|
||||
if p.dataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.data = append(p.data, b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if p.DataLen < len(p.Data) {
|
||||
p.Data[p.DataLen] = b
|
||||
p.DataLen++
|
||||
if p.dataLen < len(p.data) {
|
||||
p.data[p.dataLen] = b
|
||||
p.dataLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.DispatchAction:
|
||||
// Increment the last parameter
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen > 0 && p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params)-1 ||
|
||||
p.ParamsLen == 0 && len(p.Params) > 0 && p.Params[0] != parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
if p.paramsLen > 0 && p.paramsLen < len(p.params)-1 ||
|
||||
p.paramsLen == 0 && len(p.params) > 0 && p.params[0] != parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.paramsLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if dispatcher == nil {
|
||||
if p.state == parser.OscStringState && p.cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
// Ensure we have a command for OSC
|
||||
p.parseStringCmd()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.dispatcher == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var seq Sequence
|
||||
data := p.Data
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
data = data[:p.DataLen]
|
||||
data := p.data
|
||||
if p.dataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
data = data[:p.dataLen]
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
switch p.state {
|
||||
case parser.CsiEntryState, parser.CsiParamState, parser.CsiIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = CsiSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen]}
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = CsiSequence{Cmd: Command(p.cmd), Params: p.Params()}
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState, parser.EscapeIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = EscSequence(p.Cmd)
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = EscSequence(p.cmd)
|
||||
case parser.DcsEntryState, parser.DcsParamState, parser.DcsIntermediateState, parser.DcsStringState:
|
||||
seq = DcsSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen], Data: data}
|
||||
seq = DcsSequence{Cmd: Command(p.cmd), Params: p.Params(), Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
seq = OscSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Data: data}
|
||||
seq = OscSequence{Cmd: p.cmd, Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.SosStringState:
|
||||
seq = SosSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.PmStringState:
|
||||
@ -339,7 +395,7 @@ func (p *Parser) performAction(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, action parser.Action
|
||||
seq = ApcSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dispatcher(seq)
|
||||
p.dispatch(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
16
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
16
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
@ -81,6 +81,9 @@ func r(start, end byte) []byte {
|
||||
// - We don't ignore 0x3A (':') when building Csi and Dcs parameters and
|
||||
// instead use it to denote sub-parameters.
|
||||
// - Support dispatching SosPmApc sequences.
|
||||
// - The DEL (0x7F) character is executed in the Ground state.
|
||||
// - The DEL (0x7F) character is collected in the DcsPassthrough string state.
|
||||
// - The ST C1 control character (0x9C) is executed and not ignored.
|
||||
func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
table := NewTransitionTable(DefaultTableSize)
|
||||
table.SetDefault(NoneAction, GroundState)
|
||||
@ -91,7 +94,7 @@ func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1a, 0x99, 0x9a}, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0x8F, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x90, 0x97, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Escape
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, state, ClearAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> SosStringState
|
||||
@ -107,16 +110,17 @@ func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
// Anywhere -> OscString
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9D, state, StartAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Utf8
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xC2, 0xDF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 2 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xE0, 0xEF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 3 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xF0, 0xF4, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 4 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xC2, 0xDF, state, CollectAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 2 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xE0, 0xEF, state, CollectAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 3 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xF0, 0xF4, state, CollectAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 4 byte sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7F, GroundState, PrintAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7E, GroundState, PrintAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// EscapeIntermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
@ -209,7 +213,7 @@ func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7E, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsStringState, IgnoreAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0xFF, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState) // Allow Utf8 characters by extending the printable range from 0x7F to 0xFF
|
||||
// ST, CAN, SUB, and ESC terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, DcsStringState, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
|
||||
461
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser_decode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
461
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser_decode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,461 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// State represents the state of the ANSI escape sequence parser used by
|
||||
// [DecodeSequence].
|
||||
type State = byte
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSI escape sequence states used by [DecodeSequence].
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NormalState State = iota
|
||||
MarkerState
|
||||
ParamsState
|
||||
IntermedState
|
||||
EscapeState
|
||||
StringState
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DecodeSequence decodes the first ANSI escape sequence or a printable
|
||||
// grapheme from the given data. It returns the sequence slice, the number of
|
||||
// bytes read, the cell width for each sequence, and the new state.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The cell width will always be 0 for control and escape sequences, 1 for
|
||||
// ASCII printable characters, and the number of cells other Unicode characters
|
||||
// occupy. It uses the uniseg package to calculate the width of Unicode
|
||||
// graphemes and characters. This means it will always do grapheme clustering
|
||||
// (mode 2027).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Passing a non-nil [*Parser] as the last argument will allow the decoder to
|
||||
// collect sequence parameters, data, and commands. The parser cmd will have
|
||||
// the packed command value that contains intermediate and marker characters.
|
||||
// In the case of a OSC sequence, the cmd will be the OSC command number. Use
|
||||
// [Command] and [Parameter] types to unpack command intermediates and markers as well
|
||||
// as parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Zero [Command] means the CSI, DCS, or ESC sequence is invalid. Moreover, checking the
|
||||
// validity of other data sequences, OSC, DCS, etc, will require checking for
|
||||
// the returned sequence terminator bytes such as ST (ESC \\) and BEL).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// We store the command byte in [Command] in the most significant byte, the
|
||||
// marker byte in the next byte, and the intermediate byte in the least
|
||||
// significant byte. This is done to avoid using a struct to store the command
|
||||
// and its intermediates and markers. The command byte is always the least
|
||||
// significant byte i.e. [Cmd & 0xff]. Use the [Command] type to unpack the
|
||||
// command, intermediate, and marker bytes. Note that we only collect the last
|
||||
// marker character and intermediate byte.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The [p.Params] slice will contain the parameters of the sequence. Any
|
||||
// sub-parameter will have the [parser.HasMoreFlag] set. Use the [Parameter] type
|
||||
// to unpack the parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var state byte // the initial state is always zero [NormalState]
|
||||
// p := NewParser(32, 1024) // create a new parser with a 32 params buffer and 1024 data buffer (optional)
|
||||
// input := []byte("\x1b[31mHello, World!\x1b[0m")
|
||||
// for len(input) > 0 {
|
||||
// seq, width, n, newState := DecodeSequence(input, state, p)
|
||||
// log.Printf("seq: %q, width: %d", seq, width)
|
||||
// state = newState
|
||||
// input = input[n:]
|
||||
// }
|
||||
func DecodeSequence[T string | []byte](b T, state byte, p *Parser) (seq T, width int, n int, newState byte) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b); i++ {
|
||||
c := b[i]
|
||||
|
||||
switch state {
|
||||
case NormalState:
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case ESC:
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
if len(p.params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = EscapeState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case CSI, DCS:
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
if len(p.params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = MarkerState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case OSC, APC, SOS, PM:
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = StringState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if c > US && c < DEL {
|
||||
// ASCII printable characters
|
||||
return b[i : i+1], 1, 1, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c <= US || c == DEL || c < 0xC0 {
|
||||
// C0 & C1 control characters & DEL
|
||||
return b[i : i+1], 0, 1, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if utf8.RuneStart(c) {
|
||||
seq, _, width, _ = FirstGraphemeCluster(b, -1)
|
||||
i += len(seq)
|
||||
return b[:i], width, i, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Invalid UTF-8 sequence
|
||||
return b[:i], 0, i, NormalState
|
||||
case MarkerState:
|
||||
if c >= '<' && c <= '?' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
// We only collect the last marker character.
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(c) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
state = ParamsState
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case ParamsState:
|
||||
if c >= '0' && c <= '9' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
if p.params[p.paramsLen] == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] *= 10
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] += int(c - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c == ':' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] |= parser.HasMoreFlag
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c == ';' || c == ':' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.paramsLen++
|
||||
if p.paramsLen < len(p.params) {
|
||||
p.params[p.paramsLen] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
state = IntermedState
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case IntermedState:
|
||||
if c >= ' ' && c <= '/' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(c) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
// Increment the last parameter
|
||||
if p.paramsLen > 0 && p.paramsLen < len(p.params)-1 ||
|
||||
p.paramsLen == 0 && len(p.params) > 0 && p.params[0] != parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.paramsLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c >= '@' && c <= '~' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if HasDcsPrefix(b) {
|
||||
// Continue to collect DCS data
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = StringState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b[:i+1], 0, i + 1, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Invalid CSI/DCS sequence
|
||||
return b[:i], 0, i, NormalState
|
||||
case EscapeState:
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case '[', 'P':
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
if len(p.params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.paramsLen = 0
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = MarkerState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case ']', 'X', '^', '_':
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
state = StringState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c >= ' ' && c <= '/' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(c) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
continue
|
||||
} else if c >= '0' && c <= '~' {
|
||||
if p != nil {
|
||||
p.cmd &^= 0xff
|
||||
p.cmd |= int(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b[:i+1], 0, i + 1, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Invalid escape sequence
|
||||
return b[:i], 0, i, NormalState
|
||||
case StringState:
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case BEL:
|
||||
if HasOscPrefix(b) {
|
||||
parseOscCmd(p)
|
||||
return b[:i+1], 0, i + 1, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
case CAN, SUB:
|
||||
if HasOscPrefix(b) {
|
||||
// Ensure we parse the OSC command number
|
||||
parseOscCmd(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cancel the sequence
|
||||
return b[:i], 0, i, NormalState
|
||||
case ST:
|
||||
if HasOscPrefix(b) {
|
||||
// Ensure we parse the OSC command number
|
||||
parseOscCmd(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b[:i+1], 0, i + 1, NormalState
|
||||
case ESC:
|
||||
if HasStPrefix(b[i:]) {
|
||||
if HasOscPrefix(b) {
|
||||
// Ensure we parse the OSC command number
|
||||
parseOscCmd(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// End of string 7-bit (ST)
|
||||
return b[:i+2], 0, i + 2, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Otherwise, cancel the sequence
|
||||
return b[:i], 0, i, NormalState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p != nil && p.dataLen < len(p.data) {
|
||||
p.data[p.dataLen] = c
|
||||
p.dataLen++
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse the OSC command number
|
||||
if c == ';' && HasOscPrefix(b) {
|
||||
parseOscCmd(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b, 0, len(b), state
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func parseOscCmd(p *Parser) {
|
||||
if p == nil || p.cmd != parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
for j := 0; j < p.dataLen; j++ {
|
||||
d := p.data[j]
|
||||
if d < '0' || d > '9' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.cmd *= 10
|
||||
p.cmd += int(d - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Equal returns true if the given byte slices are equal.
|
||||
func Equal[T string | []byte](a, b T) bool {
|
||||
return string(a) == string(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has prefix.
|
||||
func HasPrefix[T string | []byte](b, prefix T) bool {
|
||||
return len(b) >= len(prefix) && Equal(b[0:len(prefix)], prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasSuffix returns true if the given byte slice has suffix.
|
||||
func HasSuffix[T string | []byte](b, suffix T) bool {
|
||||
return len(b) >= len(suffix) && Equal(b[len(b)-len(suffix):], suffix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasCsiPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has a CSI prefix.
|
||||
func HasCsiPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == CSI) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == '[')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasOscPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has an OSC prefix.
|
||||
func HasOscPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == OSC) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == ']')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasApcPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has an APC prefix.
|
||||
func HasApcPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == APC) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == '_')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasDcsPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has a DCS prefix.
|
||||
func HasDcsPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == DCS) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == 'P')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasSosPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has a SOS prefix.
|
||||
func HasSosPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == SOS) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == 'X')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasPmPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has a PM prefix.
|
||||
func HasPmPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == PM) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == '^')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasStPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has a ST prefix.
|
||||
func HasStPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return (len(b) > 0 && b[0] == ST) ||
|
||||
(len(b) > 1 && b[0] == ESC && b[1] == '\\')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasEscPrefix returns true if the given byte slice has an ESC prefix.
|
||||
func HasEscPrefix[T string | []byte](b T) bool {
|
||||
return len(b) > 0 && b[0] == ESC
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FirstGraphemeCluster returns the first grapheme cluster in the given string or byte slice.
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar function that wraps
|
||||
// uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString and uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster.
|
||||
func FirstGraphemeCluster[T string | []byte](b T, state int) (T, T, int, int) {
|
||||
switch b := any(b).(type) {
|
||||
case string:
|
||||
cluster, rest, width, newState := uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(b, state)
|
||||
return T(cluster), T(rest), width, newState
|
||||
case []byte:
|
||||
cluster, rest, width, newState := uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b, state)
|
||||
return T(cluster), T(rest), width, newState
|
||||
}
|
||||
panic("unreachable")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command represents a sequence command. This is used to pack/unpack a sequence
|
||||
// command with its intermediate and marker characters. Those are commonly
|
||||
// found in CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
type Command int
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the unpacked marker byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (c Command) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(int(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the unpacked intermediate byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (c Command) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(int(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the unpacked command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (c Command) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(int(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd returns a packed [Command] with the given command, marker, and
|
||||
// intermediate.
|
||||
// The first byte is the command, the next shift is the marker, and the next
|
||||
// shift is the intermediate.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Even though this function takes integers, it only uses the lower 8 bits of
|
||||
// each integer.
|
||||
func Cmd(marker, inter, cmd int) (c Command) {
|
||||
c = Command(cmd & parser.CommandMask)
|
||||
c |= Command(marker&parser.CommandMask) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
c |= Command(inter&parser.CommandMask) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parameter represents a sequence parameter. Sequence parameters with
|
||||
// sub-parameters are packed with the HasMoreFlag set. This is used to unpack
|
||||
// the parameters from a CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
type Parameter int
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the unpacked parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns the default value if the parameter is missing.
|
||||
func (s Parameter) Param(def int) int {
|
||||
p := int(s) & parser.ParamMask
|
||||
if p == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
return def
|
||||
}
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore unpacks the HasMoreFlag from the parameter.
|
||||
func (s Parameter) HasMore() bool {
|
||||
return s&parser.HasMoreFlag != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns a packed [Parameter] with the given parameter and whether this
|
||||
// parameter has following sub-parameters.
|
||||
func Param(p int, hasMore bool) (s Parameter) {
|
||||
s = Parameter(p & parser.ParamMask)
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
s |= Parameter(parser.HasMoreFlag)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser_sync.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser_sync.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var parserPool = sync.Pool{
|
||||
New: func() any {
|
||||
p := NewParser(nil)
|
||||
p.SetParamsSize(parser.MaxParamsSize)
|
||||
p.SetDataSize(1024 * 1024 * 4) // 4MB of data buffer
|
||||
return p
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetParser returns a parser from a sync pool.
|
||||
func GetParser() *Parser {
|
||||
return parserPool.Get().(*Parser)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PutParser returns a parser to a sync pool. The parser is reset
|
||||
// automatically.
|
||||
func PutParser(p *Parser) {
|
||||
p.Reset()
|
||||
p.dataLen = 0
|
||||
parserPool.Put(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/paste.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/paste.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// BracketedPasteStart is the control sequence to enable bracketed paste mode.
|
||||
const BracketedPasteStart = "\x1b[200~"
|
||||
|
||||
// BracketedPasteEnd is the control sequence to disable bracketed paste mode.
|
||||
const BracketedPasteEnd = "\x1b[201~"
|
||||
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/reset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/reset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetInitialState (RIS) resets the terminal to its initial state.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC c
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/RIS.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ResetInitialState = "\x1bc"
|
||||
RIS = ResetInitialState
|
||||
)
|
||||
317
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
317
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,30 +1,44 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay (ED) clears the screen or parts of the screen. Possible values:
|
||||
// EraseDisplay (ED) clears the display or parts of the display. A screen is
|
||||
// the shown part of the terminal display excluding the scrollback buffer.
|
||||
// Possible values:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Clear from cursor to end of screen.
|
||||
// 1: Clear from cursor to beginning of the screen.
|
||||
// 2: Clear entire screen (and moves cursor to upper left on DOS).
|
||||
// 3: Clear entire screen and delete all lines saved in the scrollback buffer.
|
||||
// 3: Clear entire display which delete all lines saved in the scrollback buffer (xterm).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> J
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/ED.html
|
||||
func EraseDisplay(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "J"
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "J"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ED is an alias for [EraseDisplay].
|
||||
func ED(n int) string {
|
||||
return EraseDisplay(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseDisplay function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseDisplayRight = "\x1b[0J"
|
||||
EraseDisplayLeft = "\x1b[1J"
|
||||
EraseEntireDisplay = "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
EraseScreenBelow = "\x1b[J"
|
||||
EraseScreenAbove = "\x1b[1J"
|
||||
EraseEntireScreen = "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
EraseEntireDisplay = "\x1b[3J"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine (EL) clears the current line or parts of the line. Possible values:
|
||||
@ -39,16 +53,22 @@ const (
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/EL.html
|
||||
func EraseLine(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "K"
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "K"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EL is an alias for [EraseLine].
|
||||
func EL(n int) string {
|
||||
return EraseLine(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseLine function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseLineRight = "\x1b[0K"
|
||||
EraseLineRight = "\x1b[K"
|
||||
EraseLineLeft = "\x1b[1K"
|
||||
EraseEntireLine = "\x1b[2K"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -56,7 +76,7 @@ const (
|
||||
// ScrollUp (SU) scrolls the screen up n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// bottom of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> S
|
||||
// CSI Pn S
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SU.html
|
||||
func ScrollUp(n int) string {
|
||||
@ -67,10 +87,20 @@ func ScrollUp(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "S"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PanDown is an alias for [ScrollUp].
|
||||
func PanDown(n int) string {
|
||||
return ScrollUp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SU is an alias for [ScrollUp].
|
||||
func SU(n int) string {
|
||||
return ScrollUp(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollDown (SD) scrolls the screen down n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// top of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> T
|
||||
// CSI Pn T
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SD.html
|
||||
func ScrollDown(n int) string {
|
||||
@ -81,10 +111,20 @@ func ScrollDown(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "T"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PanUp is an alias for [ScrollDown].
|
||||
func PanUp(n int) string {
|
||||
return ScrollDown(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SD is an alias for [ScrollDown].
|
||||
func SD(n int) string {
|
||||
return ScrollDown(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InsertLine (IL) inserts n blank lines at the current cursor position.
|
||||
// Existing lines are moved down.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> L
|
||||
// CSI Pn L
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/IL.html
|
||||
func InsertLine(n int) string {
|
||||
@ -95,10 +135,15 @@ func InsertLine(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "L"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// IL is an alias for [InsertLine].
|
||||
func IL(n int) string {
|
||||
return InsertLine(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeleteLine (DL) deletes n lines at the current cursor position. Existing
|
||||
// lines are moved up.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> M
|
||||
// CSI Pn M
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DL.html
|
||||
func DeleteLine(n int) string {
|
||||
@ -109,12 +154,66 @@ func DeleteLine(n int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "M"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DL is an alias for [DeleteLine].
|
||||
func DL(n int) string {
|
||||
return DeleteLine(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTopBottomMargins (DECSTBM) sets the top and bottom margins for the scrolling
|
||||
// region. The default is the entire screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1 and the bottom of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pt ; Pb r
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSTBM.html
|
||||
func SetTopBottomMargins(top, bot int) string {
|
||||
var t, b string
|
||||
if top > 0 {
|
||||
t = strconv.Itoa(top)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bot > 0 {
|
||||
b = strconv.Itoa(bot)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + t + ";" + b + "r"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECSTBM is an alias for [SetTopBottomMargins].
|
||||
func DECSTBM(top, bot int) string {
|
||||
return SetTopBottomMargins(top, bot)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetLeftRightMargins (DECSLRM) sets the left and right margins for the scrolling
|
||||
// region.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1 and the right of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pl ; Pr s
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSLRM.html
|
||||
func SetLeftRightMargins(left, right int) string {
|
||||
var l, r string
|
||||
if left > 0 {
|
||||
l = strconv.Itoa(left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if right > 0 {
|
||||
r = strconv.Itoa(right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + l + ";" + r + "s"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECSLRM is an alias for [SetLeftRightMargins].
|
||||
func DECSLRM(left, right int) string {
|
||||
return SetLeftRightMargins(left, right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetScrollingRegion (DECSTBM) sets the top and bottom margins for the scrolling
|
||||
// region. The default is the entire screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <top> ; <bottom> r
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSTBM.html
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetTopBottomMargins] instead.
|
||||
func SetScrollingRegion(t, b int) string {
|
||||
if t < 0 {
|
||||
t = 0
|
||||
@ -124,3 +223,187 @@ func SetScrollingRegion(t, b int) string {
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(t) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(b) + "r"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InsertCharacter (ICH) inserts n blank characters at the current cursor
|
||||
// position. Existing characters move to the right. Characters moved past the
|
||||
// right margin are lost. ICH has no effect outside the scrolling margins.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pn @
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/ICH.html
|
||||
func InsertCharacter(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "@"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ICH is an alias for [InsertCharacter].
|
||||
func ICH(n int) string {
|
||||
return InsertCharacter(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeleteCharacter (DCH) deletes n characters at the current cursor position.
|
||||
// As the characters are deleted, the remaining characters move to the left and
|
||||
// the cursor remains at the same position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pn P
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DCH.html
|
||||
func DeleteCharacter(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "P"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DCH is an alias for [DeleteCharacter].
|
||||
func DCH(n int) string {
|
||||
return DeleteCharacter(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTabEvery8Columns (DECST8C) sets the tab stops at every 8 columns.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? 5 W
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECST8C.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SetTabEvery8Columns = "\x1b[?5W"
|
||||
DECST8C = SetTabEvery8Columns
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// HorizontalTabSet (HTS) sets a horizontal tab stop at the current cursor
|
||||
// column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to [HTS].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/HTS.html
|
||||
const HorizontalTabSet = "\x1bH"
|
||||
|
||||
// TabClear (TBC) clears tab stops.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Possible values:
|
||||
// 0: Clear tab stop at the current column. (default)
|
||||
// 3: Clear all tab stops.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pn g
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/TBC.html
|
||||
func TabClear(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "g"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TBC is an alias for [TabClear].
|
||||
func TBC(n int) string {
|
||||
return TabClear(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPresentationStateReport (DECRQPSR) requests the terminal to send a
|
||||
// report of the presentation state. This includes the cursor information [DECCIR],
|
||||
// and tab stop [DECTABSR] reports.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Possible values:
|
||||
// 0: Error, request ignored.
|
||||
// 1: Cursor information report [DECCIR].
|
||||
// 2: Tab stop report [DECTABSR].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Ps $ w
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRQPSR.html
|
||||
func RequestPresentationStateReport(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "$w"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECRQPSR is an alias for [RequestPresentationStateReport].
|
||||
func DECRQPSR(n int) string {
|
||||
return RequestPresentationStateReport(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TabStopReport (DECTABSR) is the response to a tab stop report request.
|
||||
// It reports the tab stops set in the terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The response is a list of tab stops separated by a slash (/) character.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS 2 $ u D ... D ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where D is a decimal number representing a tab stop.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECTABSR.html
|
||||
func TabStopReport(stops ...int) string {
|
||||
var s []string
|
||||
for _, v := range stops {
|
||||
s = append(s, strconv.Itoa(v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1bP2$u" + strings.Join(s, "/") + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECTABSR is an alias for [TabStopReport].
|
||||
func DECTABSR(stops ...int) string {
|
||||
return TabStopReport(stops...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorInformationReport (DECCIR) is the response to a cursor information
|
||||
// report request. It reports the cursor position, visual attributes, and
|
||||
// character protection attributes. It also reports the status of origin mode
|
||||
// [DECOM] and the current active character set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The response is a list of values separated by a semicolon (;) character.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS 1 $ u D ... D ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where D is a decimal number representing a value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECCIR.html
|
||||
func CursorInformationReport(values ...int) string {
|
||||
var s []string
|
||||
for _, v := range values {
|
||||
s = append(s, strconv.Itoa(v))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1bP1$u" + strings.Join(s, ";") + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECCIR is an alias for [CursorInformationReport].
|
||||
func DECCIR(values ...int) string {
|
||||
return CursorInformationReport(values...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RepeatPreviousCharacter (REP) repeats the previous character n times.
|
||||
// This is identical to typing the same character n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pn b
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: ECMA-48 § 8.3.103
|
||||
func RepeatPreviousCharacter(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "b"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// REP is an alias for [RepeatPreviousCharacter].
|
||||
func REP(n int) string {
|
||||
return RepeatPreviousCharacter(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
94
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
94
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
@ -8,12 +8,19 @@ import (
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence represents an ANSI sequence. This can be a control sequence, escape
|
||||
// sequence, a printable character, etc.
|
||||
// A Sequence can be one of the following types:
|
||||
// - [Rune]
|
||||
// - [ControlCode]
|
||||
// - [Grapheme]
|
||||
// - [EscSequence]
|
||||
// - [CsiSequence]
|
||||
// - [OscSequence]
|
||||
// - [DcsSequence]
|
||||
// - [SosSequence]
|
||||
// - [PmSequence]
|
||||
// - [ApcSequence]
|
||||
type Sequence interface {
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
String() string
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
Bytes() []byte
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the sequence.
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the sequence.
|
||||
Clone() Sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,21 +29,24 @@ type Rune rune
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = Rune(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return []byte(string(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) String() string {
|
||||
return string(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the rune.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Grapheme represents a grapheme cluster.
|
||||
type Grapheme struct {
|
||||
Cluster string
|
||||
Width int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = Grapheme{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the grapheme.
|
||||
func (g Grapheme) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return g
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ControlCode represents a control code character. This is a character that
|
||||
// is not printable and is used to control the terminal. This would be a
|
||||
// character in the C0 or C1 set in the range of 0x00-0x1F and 0x80-0x9F.
|
||||
@ -54,13 +64,13 @@ func (c ControlCode) String() string {
|
||||
return string(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the control code.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EscSequence represents an escape sequence.
|
||||
type EscSequence int
|
||||
type EscSequence Command
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = EscSequence(0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,7 +81,9 @@ func (e EscSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
if i := parser.Intermediate(int(e)); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(e.Command()))
|
||||
if cmd := e.Command(); cmd != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(cmd))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,19 +97,19 @@ func (e EscSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return e.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return e
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(int(e))
|
||||
return Command(e).Command()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(int(e))
|
||||
return Command(e).Intermediate()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SosSequence represents a SOS sequence.
|
||||
@ -106,12 +118,7 @@ type SosSequence struct {
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &SosSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return SosSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
var _ Sequence = SosSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
@ -132,18 +139,20 @@ func (s SosSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the SOS sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return SosSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PmSequence represents a PM sequence.
|
||||
type PmSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &PmSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return PmSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
var _ Sequence = PmSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
@ -165,17 +174,26 @@ func (s PmSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the PM sequence.
|
||||
func (p PmSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return PmSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), p.Data...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApcSequence represents an APC sequence.
|
||||
type ApcSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &ApcSequence{}
|
||||
var _ Sequence = ApcSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return ApcSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
// Clone returns a deep copy of the APC sequence.
|
||||
func (a ApcSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return ApcSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), a.Data...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
95
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sgr.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
95
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sgr.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// Select Graphic Rendition (SGR) is a command that sets display attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Ps ; Ps ... m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SGR.html
|
||||
func SelectGraphicRendition(ps ...Attr) string {
|
||||
if len(ps) == 0 {
|
||||
return ResetStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var s Style
|
||||
for _, p := range ps {
|
||||
attr, ok := attrStrings[p]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
s = append(s, attr)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if p < 0 {
|
||||
p = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
s = append(s, strconv.Itoa(p))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR is an alias for [SelectGraphicRendition].
|
||||
func SGR(ps ...Attr) string {
|
||||
return SelectGraphicRendition(ps...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var attrStrings = map[int]string{
|
||||
ResetAttr: "0",
|
||||
BoldAttr: "1",
|
||||
FaintAttr: "2",
|
||||
ItalicAttr: "3",
|
||||
UnderlineAttr: "4",
|
||||
SlowBlinkAttr: "5",
|
||||
RapidBlinkAttr: "6",
|
||||
ReverseAttr: "7",
|
||||
ConcealAttr: "8",
|
||||
StrikethroughAttr: "9",
|
||||
NoBoldAttr: "21",
|
||||
NormalIntensityAttr: "22",
|
||||
NoItalicAttr: "23",
|
||||
NoUnderlineAttr: "24",
|
||||
NoBlinkAttr: "25",
|
||||
NoReverseAttr: "27",
|
||||
NoConcealAttr: "28",
|
||||
NoStrikethroughAttr: "29",
|
||||
BlackForegroundColorAttr: "30",
|
||||
RedForegroundColorAttr: "31",
|
||||
GreenForegroundColorAttr: "32",
|
||||
YellowForegroundColorAttr: "33",
|
||||
BlueForegroundColorAttr: "34",
|
||||
MagentaForegroundColorAttr: "35",
|
||||
CyanForegroundColorAttr: "36",
|
||||
WhiteForegroundColorAttr: "37",
|
||||
ExtendedForegroundColorAttr: "38",
|
||||
DefaultForegroundColorAttr: "39",
|
||||
BlackBackgroundColorAttr: "40",
|
||||
RedBackgroundColorAttr: "41",
|
||||
GreenBackgroundColorAttr: "42",
|
||||
YellowBackgroundColorAttr: "43",
|
||||
BlueBackgroundColorAttr: "44",
|
||||
MagentaBackgroundColorAttr: "45",
|
||||
CyanBackgroundColorAttr: "46",
|
||||
WhiteBackgroundColorAttr: "47",
|
||||
ExtendedBackgroundColorAttr: "48",
|
||||
DefaultBackgroundColorAttr: "49",
|
||||
ExtendedUnderlineColorAttr: "58",
|
||||
DefaultUnderlineColorAttr: "59",
|
||||
BrightBlackForegroundColorAttr: "90",
|
||||
BrightRedForegroundColorAttr: "91",
|
||||
BrightGreenForegroundColorAttr: "92",
|
||||
BrightYellowForegroundColorAttr: "93",
|
||||
BrightBlueForegroundColorAttr: "94",
|
||||
BrightMagentaForegroundColorAttr: "95",
|
||||
BrightCyanForegroundColorAttr: "96",
|
||||
BrightWhiteForegroundColorAttr: "97",
|
||||
BrightBlackBackgroundColorAttr: "100",
|
||||
BrightRedBackgroundColorAttr: "101",
|
||||
BrightGreenBackgroundColorAttr: "102",
|
||||
BrightYellowBackgroundColorAttr: "103",
|
||||
BrightBlueBackgroundColorAttr: "104",
|
||||
BrightMagentaBackgroundColorAttr: "105",
|
||||
BrightCyanBackgroundColorAttr: "106",
|
||||
BrightWhiteBackgroundColorAttr: "107",
|
||||
}
|
||||
115
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/status.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
115
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/status.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Status represents a terminal status report.
|
||||
type Status interface {
|
||||
// Status returns the status report identifier.
|
||||
Status() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSIStatus represents an ANSI terminal status report.
|
||||
type ANSIStatus int //nolint:revive
|
||||
|
||||
// Status returns the status report identifier.
|
||||
func (s ANSIStatus) Status() int {
|
||||
return int(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECStatus represents a DEC terminal status report.
|
||||
type DECStatus int
|
||||
|
||||
// Status returns the status report identifier.
|
||||
func (s DECStatus) Status() int {
|
||||
return int(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeviceStatusReport (DSR) is a control sequence that reports the terminal's
|
||||
// status.
|
||||
// The terminal responds with a DSR sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Ps n
|
||||
// CSI ? Ps n
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If one of the statuses is a [DECStatus], the sequence will use the DEC
|
||||
// format.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See also https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DSR.html
|
||||
func DeviceStatusReport(statues ...Status) string {
|
||||
var dec bool
|
||||
list := make([]string, len(statues))
|
||||
seq := "\x1b["
|
||||
for i, status := range statues {
|
||||
list[i] = strconv.Itoa(status.Status())
|
||||
switch status.(type) {
|
||||
case DECStatus:
|
||||
dec = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dec {
|
||||
seq += "?"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return seq + strings.Join(list, ";") + "n"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DSR is an alias for [DeviceStatusReport].
|
||||
func DSR(status Status) string {
|
||||
return DeviceStatusReport(status)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorPositionReport (CPR) is a control sequence that reports the cursor's
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pl ; Pc R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number and Pc is the column number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See also https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CPR.html
|
||||
func CursorPositionReport(line, column int) string {
|
||||
if line < 1 {
|
||||
line = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if column < 1 {
|
||||
column = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(line) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(column) + "R"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CPR is an alias for [CursorPositionReport].
|
||||
func CPR(line, column int) string {
|
||||
return CursorPositionReport(line, column)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExtendedCursorPositionReport (DECXCPR) is a control sequence that reports the
|
||||
// cursor's position along with the page number (optional).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pl ; Pc R
|
||||
// CSI ? Pl ; Pc ; Pv R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number, Pc is the column number, and Pv is the page
|
||||
// number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the page number is zero or negative, the returned sequence won't include
|
||||
// the page number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See also https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECXCPR.html
|
||||
func ExtendedCursorPositionReport(line, column, page int) string {
|
||||
if line < 1 {
|
||||
line = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if column < 1 {
|
||||
column = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
if page < 1 {
|
||||
return "\x1b[?" + strconv.Itoa(line) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(column) + "R"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[?" + strconv.Itoa(line) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(column) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(page) + "R"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DECXCPR is an alias for [ExtendedCursorPositionReport].
|
||||
func DECXCPR(line, column, page int) string {
|
||||
return ExtendedCursorPositionReport(line, column, page)
|
||||
}
|
||||
355
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
355
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
@ -12,10 +12,10 @@ import (
|
||||
const ResetStyle = "\x1b[m"
|
||||
|
||||
// Attr is a SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attribute.
|
||||
type Attr = string
|
||||
type Attr = int
|
||||
|
||||
// Style represents an ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style.
|
||||
type Style []Attr
|
||||
type Style []string
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style sequence for
|
||||
// the given style.
|
||||
@ -36,186 +36,357 @@ func (s Style) Styled(str string) string {
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset appends the reset style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reset() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ResetAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, resetAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bold appends the bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Bold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BoldAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, boldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Faint appends the faint style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Faint() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, FaintAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, faintAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Italic appends the italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Italic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ItalicAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, italicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Underline appends the underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Underline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, underlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineStyle appends the underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineStyle(u UnderlineStyle) Style {
|
||||
switch u {
|
||||
case NoUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return s.NoUnderline()
|
||||
case SingleUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return s.Underline()
|
||||
case DoubleUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return append(s, doubleUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
case CurlyUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return append(s, curlyUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
case DottedUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return append(s, dottedUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
case DashedUnderlineStyle:
|
||||
return append(s, dashedUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DoubleUnderline appends the double underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
// This is a convenience method for UnderlineStyle(DoubleUnderlineStyle).
|
||||
func (s Style) DoubleUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DoubleUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return s.UnderlineStyle(DoubleUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CurlyUnderline appends the curly underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
// This is a convenience method for UnderlineStyle(CurlyUnderlineStyle).
|
||||
func (s Style) CurlyUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, CurlyUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return s.UnderlineStyle(CurlyUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DottedUnderline appends the dotted underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
// This is a convenience method for UnderlineStyle(DottedUnderlineStyle).
|
||||
func (s Style) DottedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DottedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return s.UnderlineStyle(DottedUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DashedUnderline appends the dashed underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
// This is a convenience method for UnderlineStyle(DashedUnderlineStyle).
|
||||
func (s Style) DashedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DashedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return s.UnderlineStyle(DashedUnderlineStyle)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SlowBlink appends the slow blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) SlowBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, SlowBlinkAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, slowBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RapidBlink appends the rapid blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) RapidBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, RapidBlinkAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, rapidBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse appends the reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ReverseAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, reverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Conceal appends the conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Conceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ConcealAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, concealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Strikethrough appends the strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Strikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, StrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, strikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBold appends the no bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBoldAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noBoldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NormalIntensity appends the normal intensity style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NormalIntensity() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NormalIntensityAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, normalIntensityAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoItalic appends the no italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoItalic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoItalicAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noItalicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoUnderline appends the no underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBlink appends the no blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBlinkAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoReverse appends the no reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoReverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoReverseAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noReverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoConceal appends the no conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoConceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoConcealAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noConcealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoStrikethrough appends the no strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoStrikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoStrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, noStrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultForegroundColor appends the default foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultForegroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultForegroundColorAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, defaultForegroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultBackgroundColor appends the default background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultBackgroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultBackgroundColorAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, defaultBackgroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultUnderlineColor appends the default underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultUnderlineColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultUnderlineColorAttr)
|
||||
return append(s, defaultUnderlineColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColor appends the foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) ForegroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ForegroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
return append(s, foregroundColorString(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColor appends the background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) BackgroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BackgroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
return append(s, backgroundColorString(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColor appends the underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineColorAttr(c))
|
||||
return append(s, underlineColorString(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineStyle represents an ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) underline
|
||||
// style.
|
||||
type UnderlineStyle = int
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
doubleUnderlineStyle = "4:2"
|
||||
curlyUnderlineStyle = "4:3"
|
||||
dottedUnderlineStyle = "4:4"
|
||||
dashedUnderlineStyle = "4:5"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// NoUnderlineStyle is the default underline style.
|
||||
NoUnderlineStyle UnderlineStyle = iota
|
||||
// SingleUnderlineStyle is a single underline style.
|
||||
SingleUnderlineStyle
|
||||
// DoubleUnderlineStyle is a double underline style.
|
||||
DoubleUnderlineStyle
|
||||
// CurlyUnderlineStyle is a curly underline style.
|
||||
CurlyUnderlineStyle
|
||||
// DottedUnderlineStyle is a dotted underline style.
|
||||
DottedUnderlineStyle
|
||||
// DashedUnderlineStyle is a dashed underline style.
|
||||
DashedUnderlineStyle
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attributes.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ResetAttr Attr = "0"
|
||||
BoldAttr Attr = "1"
|
||||
FaintAttr Attr = "2"
|
||||
ItalicAttr Attr = "3"
|
||||
UnderlineAttr Attr = "4"
|
||||
DoubleUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:2"
|
||||
CurlyUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:3"
|
||||
DottedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:4"
|
||||
DashedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:5"
|
||||
SlowBlinkAttr Attr = "5"
|
||||
RapidBlinkAttr Attr = "6"
|
||||
ReverseAttr Attr = "7"
|
||||
ConcealAttr Attr = "8"
|
||||
StrikethroughAttr Attr = "9"
|
||||
NoBoldAttr Attr = "21" // Some terminals treat this as double underline.
|
||||
NormalIntensityAttr Attr = "22"
|
||||
NoItalicAttr Attr = "23"
|
||||
NoUnderlineAttr Attr = "24"
|
||||
NoBlinkAttr Attr = "25"
|
||||
NoReverseAttr Attr = "27"
|
||||
NoConcealAttr Attr = "28"
|
||||
NoStrikethroughAttr Attr = "29"
|
||||
DefaultForegroundColorAttr Attr = "39"
|
||||
DefaultBackgroundColorAttr Attr = "49"
|
||||
DefaultUnderlineColorAttr Attr = "59"
|
||||
ResetAttr Attr = 0
|
||||
BoldAttr Attr = 1
|
||||
FaintAttr Attr = 2
|
||||
ItalicAttr Attr = 3
|
||||
UnderlineAttr Attr = 4
|
||||
SlowBlinkAttr Attr = 5
|
||||
RapidBlinkAttr Attr = 6
|
||||
ReverseAttr Attr = 7
|
||||
ConcealAttr Attr = 8
|
||||
StrikethroughAttr Attr = 9
|
||||
NoBoldAttr Attr = 21 // Some terminals treat this as double underline.
|
||||
NormalIntensityAttr Attr = 22
|
||||
NoItalicAttr Attr = 23
|
||||
NoUnderlineAttr Attr = 24
|
||||
NoBlinkAttr Attr = 25
|
||||
NoReverseAttr Attr = 27
|
||||
NoConcealAttr Attr = 28
|
||||
NoStrikethroughAttr Attr = 29
|
||||
BlackForegroundColorAttr Attr = 30
|
||||
RedForegroundColorAttr Attr = 31
|
||||
GreenForegroundColorAttr Attr = 32
|
||||
YellowForegroundColorAttr Attr = 33
|
||||
BlueForegroundColorAttr Attr = 34
|
||||
MagentaForegroundColorAttr Attr = 35
|
||||
CyanForegroundColorAttr Attr = 36
|
||||
WhiteForegroundColorAttr Attr = 37
|
||||
ExtendedForegroundColorAttr Attr = 38
|
||||
DefaultForegroundColorAttr Attr = 39
|
||||
BlackBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 40
|
||||
RedBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 41
|
||||
GreenBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 42
|
||||
YellowBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 43
|
||||
BlueBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 44
|
||||
MagentaBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 45
|
||||
CyanBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 46
|
||||
WhiteBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 47
|
||||
ExtendedBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 48
|
||||
DefaultBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 49
|
||||
ExtendedUnderlineColorAttr Attr = 58
|
||||
DefaultUnderlineColorAttr Attr = 59
|
||||
BrightBlackForegroundColorAttr Attr = 90
|
||||
BrightRedForegroundColorAttr Attr = 91
|
||||
BrightGreenForegroundColorAttr Attr = 92
|
||||
BrightYellowForegroundColorAttr Attr = 93
|
||||
BrightBlueForegroundColorAttr Attr = 94
|
||||
BrightMagentaForegroundColorAttr Attr = 95
|
||||
BrightCyanForegroundColorAttr Attr = 96
|
||||
BrightWhiteForegroundColorAttr Attr = 97
|
||||
BrightBlackBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 100
|
||||
BrightRedBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 101
|
||||
BrightGreenBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 102
|
||||
BrightYellowBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 103
|
||||
BrightBlueBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 104
|
||||
BrightMagentaBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 105
|
||||
BrightCyanBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 106
|
||||
BrightWhiteBackgroundColorAttr Attr = 107
|
||||
|
||||
RGBColorIntroducerAttr Attr = 2
|
||||
ExtendedColorIntroducerAttr Attr = 5
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given foreground
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
resetAttr = "0"
|
||||
boldAttr = "1"
|
||||
faintAttr = "2"
|
||||
italicAttr = "3"
|
||||
underlineAttr = "4"
|
||||
slowBlinkAttr = "5"
|
||||
rapidBlinkAttr = "6"
|
||||
reverseAttr = "7"
|
||||
concealAttr = "8"
|
||||
strikethroughAttr = "9"
|
||||
noBoldAttr = "21"
|
||||
normalIntensityAttr = "22"
|
||||
noItalicAttr = "23"
|
||||
noUnderlineAttr = "24"
|
||||
noBlinkAttr = "25"
|
||||
noReverseAttr = "27"
|
||||
noConcealAttr = "28"
|
||||
noStrikethroughAttr = "29"
|
||||
blackForegroundColorAttr = "30"
|
||||
redForegroundColorAttr = "31"
|
||||
greenForegroundColorAttr = "32"
|
||||
yellowForegroundColorAttr = "33"
|
||||
blueForegroundColorAttr = "34"
|
||||
magentaForegroundColorAttr = "35"
|
||||
cyanForegroundColorAttr = "36"
|
||||
whiteForegroundColorAttr = "37"
|
||||
extendedForegroundColorAttr = "38"
|
||||
defaultForegroundColorAttr = "39"
|
||||
blackBackgroundColorAttr = "40"
|
||||
redBackgroundColorAttr = "41"
|
||||
greenBackgroundColorAttr = "42"
|
||||
yellowBackgroundColorAttr = "43"
|
||||
blueBackgroundColorAttr = "44"
|
||||
magentaBackgroundColorAttr = "45"
|
||||
cyanBackgroundColorAttr = "46"
|
||||
whiteBackgroundColorAttr = "47"
|
||||
extendedBackgroundColorAttr = "48"
|
||||
defaultBackgroundColorAttr = "49"
|
||||
extendedUnderlineColorAttr = "58"
|
||||
defaultUnderlineColorAttr = "59"
|
||||
brightBlackForegroundColorAttr = "90"
|
||||
brightRedForegroundColorAttr = "91"
|
||||
brightGreenForegroundColorAttr = "92"
|
||||
brightYellowForegroundColorAttr = "93"
|
||||
brightBlueForegroundColorAttr = "94"
|
||||
brightMagentaForegroundColorAttr = "95"
|
||||
brightCyanForegroundColorAttr = "96"
|
||||
brightWhiteForegroundColorAttr = "97"
|
||||
brightBlackBackgroundColorAttr = "100"
|
||||
brightRedBackgroundColorAttr = "101"
|
||||
brightGreenBackgroundColorAttr = "102"
|
||||
brightYellowBackgroundColorAttr = "103"
|
||||
brightBlueBackgroundColorAttr = "104"
|
||||
brightMagentaBackgroundColorAttr = "105"
|
||||
brightCyanBackgroundColorAttr = "106"
|
||||
brightWhiteBackgroundColorAttr = "107"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// foregroundColorString returns the style SGR attribute for the given
|
||||
// foreground color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func ForegroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
func foregroundColorString(c Color) string {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "3<n>" or "9<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "3" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else if c < 16 {
|
||||
return "9" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case Black:
|
||||
return blackForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Red:
|
||||
return redForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Green:
|
||||
return greenForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Yellow:
|
||||
return yellowForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Blue:
|
||||
return blueForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Magenta:
|
||||
return magentaForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Cyan:
|
||||
return cyanForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case White:
|
||||
return whiteForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightBlack:
|
||||
return brightBlackForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightRed:
|
||||
return brightRedForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightGreen:
|
||||
return brightGreenForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightYellow:
|
||||
return brightYellowForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightBlue:
|
||||
return brightBlueForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightMagenta:
|
||||
return brightMagentaForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightCyan:
|
||||
return brightCyanForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightWhite:
|
||||
return brightWhiteForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
@ -230,21 +401,50 @@ func ForegroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
return defaultForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given background
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// backgroundColorString returns the style SGR attribute for the given
|
||||
// background color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func BackgroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
func backgroundColorString(c Color) string {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "4<n>" or "10<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "4" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return "10" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
switch c {
|
||||
case Black:
|
||||
return blackBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Red:
|
||||
return redBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Green:
|
||||
return greenBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Yellow:
|
||||
return yellowBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Blue:
|
||||
return blueBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Magenta:
|
||||
return magentaBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case Cyan:
|
||||
return cyanBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case White:
|
||||
return whiteBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightBlack:
|
||||
return brightBlackBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightRed:
|
||||
return brightRedBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightGreen:
|
||||
return brightGreenBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightYellow:
|
||||
return brightYellowBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightBlue:
|
||||
return brightBlueBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightMagenta:
|
||||
return brightMagentaBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightCyan:
|
||||
return brightCyanBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
case BrightWhite:
|
||||
return brightWhiteBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
@ -259,13 +459,13 @@ func BackgroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
return defaultBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given underline
|
||||
// underlineColorString returns the style SGR attribute for the given underline
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func UnderlineColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
func underlineColorString(c Color) string {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
// NOTE: we can't use 3-bit and 4-bit ANSI color codes with underline
|
||||
// color, use 256-color instead.
|
||||
@ -285,12 +485,5 @@ func UnderlineColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultUnderlineColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func shift(v uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
if v > 0xff {
|
||||
return v >> 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
return defaultUnderlineColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
12
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
12
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ import (
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/terminfo.5.html
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func RequestTermcap(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
func XTGETTCAP(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(caps) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -29,3 +29,13 @@ func RequestTermcap(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
|
||||
return s + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestTermcap is an alias for [XTGETTCAP].
|
||||
func RequestTermcap(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
return XTGETTCAP(caps...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestTerminfo is an alias for [XTGETTCAP].
|
||||
func RequestTerminfo(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
return XTGETTCAP(caps...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
@ -26,7 +26,6 @@ func Truncate(s string, length int, tail string) string {
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth := 0
|
||||
ignoring := false
|
||||
gstate := -1
|
||||
pstate := parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b := []byte(s)
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
@ -38,44 +37,40 @@ func Truncate(s string, length int, tail string) string {
|
||||
// collect ANSI escape codes until we reach the end of string.
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, _ = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], -1)
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
// increment the index by the length of the cluster
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
// increment the index by the length of the cluster
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
// Are we ignoring? Skip to the next byte
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
for _, r := range cluster {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gstate = -1 // reset grapheme state otherwise, width calculation might be off
|
||||
// Done collecting, now we're back in the ground state.
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
// Are we ignoring? Skip to the next byte
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
// Done collecting, now we're back in the ground state.
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth >= length && !ignoring {
|
||||
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
@ -3,6 +3,10 @@ package ansi
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/lucasb-eyer/go-colorful"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// colorToHexString returns a hex string representation of a color.
|
||||
@ -27,3 +31,62 @@ func colorToHexString(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
func rgbToHex(r, g, b uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
return r<<16 + g<<8 + b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type shiftable interface {
|
||||
~uint | ~uint16 | ~uint32 | ~uint64
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func shift[T shiftable](x T) T {
|
||||
if x > 0xff {
|
||||
x >>= 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return x
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// XParseColor is a helper function that parses a string into a color.Color. It
|
||||
// provides a similar interface to the XParseColor function in Xlib. It
|
||||
// supports the following formats:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - #RGB
|
||||
// - #RRGGBB
|
||||
// - rgb:RRRR/GGGG/BBBB
|
||||
// - rgba:RRRR/GGGG/BBBB/AAAA
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If the string is not a valid color, nil is returned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://linux.die.net/man/3/xparsecolor
|
||||
func XParseColor(s string) color.Color {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(s, "#"):
|
||||
c, err := colorful.Hex(s)
|
||||
if err != nil {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return c
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(s, "rgb:"):
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(s[4:], "/")
|
||||
if len(parts) != 3 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[0], 16, 32)
|
||||
g, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[1], 16, 32)
|
||||
b, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[2], 16, 32)
|
||||
|
||||
return color.RGBA{uint8(shift(r)), uint8(shift(g)), uint8(shift(b)), 255} //nolint:gosec
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(s, "rgba:"):
|
||||
parts := strings.Split(s[5:], "/")
|
||||
if len(parts) != 4 {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[0], 16, 32)
|
||||
g, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[1], 16, 32)
|
||||
b, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[2], 16, 32)
|
||||
a, _ := strconv.ParseUint(parts[3], 16, 32)
|
||||
|
||||
return color.RGBA{uint8(shift(r)), uint8(shift(g)), uint8(shift(b)), uint8(shift(a))} //nolint:gosec
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/width.go
generated
vendored
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/width.go
generated
vendored
@ -19,13 +19,7 @@ func Strip(s string) string {
|
||||
// This implements a subset of the Parser to only collect runes and
|
||||
// printable characters.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
var state, action byte
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
state, action = parser.Table.Transition(pstate, s[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case pstate == parser.Utf8State:
|
||||
if pstate == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
// During this state, collect rw bytes to form a valid rune in the
|
||||
// buffer. After getting all the rune bytes into the buffer,
|
||||
// transition to GroundState and reset the counters.
|
||||
@ -37,16 +31,19 @@ func Strip(s string) string {
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
ri = 0
|
||||
rw = 0
|
||||
case action == parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
if w := utf8ByteLen(s[i]); w > 1 {
|
||||
rw = w
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, s[i])
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.CollectAction:
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
rw = utf8ByteLen(s[i])
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(s[i])
|
||||
ri++
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case action == parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction, parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
// collects printable ASCII and non-printable characters
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(s[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -71,7 +68,6 @@ func StringWidth(s string) int {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
cluster string
|
||||
width int
|
||||
@ -79,16 +75,16 @@ func StringWidth(s string) int {
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, s[i])
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(s[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
cluster, _, w, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(s[i:], gstate)
|
||||
width += w
|
||||
i += len(cluster) - 1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
cluster, _, w, _ = uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(s[i:], -1)
|
||||
width += w
|
||||
i += len(cluster) - 1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if action == parser.PrintAction {
|
||||
width++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
186
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/wrap.go
generated
vendored
186
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/wrap.go
generated
vendored
@ -27,7 +27,6 @@ func Hardwrap(s string, limit int, preserveSpace bool) string {
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int
|
||||
forceNewline bool
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -40,33 +39,30 @@ func Hardwrap(s string, limit int, preserveSpace bool) string {
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, _ = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], -1)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !preserveSpace && curWidth == 0 && len(cluster) <= 4 {
|
||||
// Skip spaces at the beginning of a line
|
||||
if r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster); r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) {
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !preserveSpace && curWidth == 0 && len(cluster) <= 4 {
|
||||
// Skip spaces at the beginning of a line
|
||||
if r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster); r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) {
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
gstate = -1 // reset grapheme state otherwise, width calculation might be off
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction, parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
if b[i] == '\n' {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
forceNewline = false
|
||||
@ -87,7 +83,9 @@ func Hardwrap(s string, limit int, preserveSpace bool) string {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
if action == parser.PrintAction {
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -122,7 +120,6 @@ func Wordwrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
space bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int
|
||||
wordLen int
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -154,37 +151,35 @@ func Wordwrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, _ = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], -1)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
if r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
} else if bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints) {
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len()+wordLen > limit &&
|
||||
wordLen < limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
if r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
} else if bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints) {
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len()+wordLen > limit &&
|
||||
wordLen < limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction, parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
r := rune(b[i])
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r == '\n':
|
||||
@ -251,9 +246,8 @@ func Wrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
word bytes.Buffer
|
||||
space bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int // written width of the line
|
||||
wordLen int // word buffer len without ANSI escape codes
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
curWidth int // written width of the line
|
||||
wordLen int // word buffer len without ANSI escape codes
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -285,49 +279,46 @@ func Wrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
if state == parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, _ = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], -1)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp: // nbsp is a non-breaking space
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
case bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints):
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
// Hardwrap the word if it's too long
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp: // nbsp is a non-breaking space
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
case bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints):
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
// Hardwrap the word if it's too long
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction, parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
switch r := rune(b[i]); {
|
||||
case r == '\n':
|
||||
if wordLen == 0 {
|
||||
@ -360,6 +351,9 @@ func Wrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if curWidth == limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
word.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
wordLen++
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
100
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/xterm.go
generated
vendored
100
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/xterm.go
generated
vendored
@ -1,11 +1,108 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// KeyModifierOptions (XTMODKEYS) sets/resets xterm key modifier options.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > Pp m
|
||||
// CSI > Pp ; Pv m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If Pv is omitted, the resource is reset to its initial value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
func KeyModifierOptions(p int, vs ...int) string {
|
||||
var pp, pv string
|
||||
if p > 0 {
|
||||
pp = strconv.Itoa(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if len(vs) == 0 {
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + strconv.Itoa(p) + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
v := vs[0]
|
||||
if v > 0 {
|
||||
pv = strconv.Itoa(v)
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + pp + ";" + pv + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + pp + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// XTMODKEYS is an alias for [KeyModifierOptions].
|
||||
func XTMODKEYS(p int, vs ...int) string {
|
||||
return KeyModifierOptions(p, vs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetKeyModifierOptions sets xterm key modifier options.
|
||||
// This is an alias for [KeyModifierOptions].
|
||||
func SetKeyModifierOptions(pp int, pv int) string {
|
||||
return KeyModifierOptions(pp, pv)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetKeyModifierOptions resets xterm key modifier options.
|
||||
// This is an alias for [KeyModifierOptions].
|
||||
func ResetKeyModifierOptions(pp int) string {
|
||||
return KeyModifierOptions(pp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// QueryKeyModifierOptions (XTQMODKEYS) requests xterm key modifier options.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Default is 0.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pp m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
func QueryKeyModifierOptions(pp int) string {
|
||||
var p string
|
||||
if pp > 0 {
|
||||
p = strconv.Itoa(pp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[?" + p + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// XTQMODKEYS is an alias for [QueryKeyModifierOptions].
|
||||
func XTQMODKEYS(pp int) string {
|
||||
return QueryKeyModifierOptions(pp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Modify Other Keys (modifyOtherKeys) is an xterm feature that allows the
|
||||
// terminal to modify the behavior of certain keys to send different escape
|
||||
// sequences when pressed.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SetModifyOtherKeys1 = "\x1b[>4;1m"
|
||||
SetModifyOtherKeys2 = "\x1b[>4;2m"
|
||||
ResetModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[>4m"
|
||||
QueryModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[?4m"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ModifyOtherKeys returns a sequence that sets XTerm modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
// The mode argument specifies the mode to set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Disable modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
// 1: Enable modifyOtherKeys mode 1.
|
||||
// 2: Enable modifyOtherKeys mode 2.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 4 ; mode m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetModifyOtherKeys1] or [SetModifyOtherKeys2] instead.
|
||||
func ModifyOtherKeys(mode int) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b[>4;" + strconv.Itoa(mode) + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableModifyOtherKeys disables the modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 4 ; 0 m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [ResetModifyOtherKeys] instead.
|
||||
const DisableModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[>4;0m"
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableModifyOtherKeys1 enables the modifyOtherKeys mode 1.
|
||||
@ -14,6 +111,7 @@ const DisableModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[>4;0m"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetModifyOtherKeys1] instead.
|
||||
const EnableModifyOtherKeys1 = "\x1b[>4;1m"
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableModifyOtherKeys2 enables the modifyOtherKeys mode 2.
|
||||
@ -22,6 +120,7 @@ const EnableModifyOtherKeys1 = "\x1b[>4;1m"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [SetModifyOtherKeys2] instead.
|
||||
const EnableModifyOtherKeys2 = "\x1b[>4;2m"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestModifyOtherKeys requests the modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
@ -30,4 +129,5 @@ const EnableModifyOtherKeys2 = "\x1b[>4;2m"
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
// Deprecated: use [QueryModifyOtherKeys] instead.
|
||||
const RequestModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[?4m"
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user