forked from toolshed/abra
chore: vendor
This commit is contained in:
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
1
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
ssh_example_ed25519*
|
||||
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
46
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci-soft.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
# - dupl
|
||||
- exhaustive
|
||||
# - exhaustivestruct
|
||||
- goconst
|
||||
- godot
|
||||
- godox
|
||||
- gomnd
|
||||
- gomoddirectives
|
||||
- goprintffuncname
|
||||
# - lll
|
||||
- misspell
|
||||
- nakedret
|
||||
- nestif
|
||||
- noctx
|
||||
- nolintlint
|
||||
- prealloc
|
||||
- wrapcheck
|
||||
|
||||
# disable default linters, they are already enabled in .golangci.yml
|
||||
disable:
|
||||
- deadcode
|
||||
- errcheck
|
||||
- gosimple
|
||||
- govet
|
||||
- ineffassign
|
||||
- staticcheck
|
||||
- structcheck
|
||||
- typecheck
|
||||
- unused
|
||||
- varcheck
|
||||
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
30
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
- bodyclose
|
||||
- exportloopref
|
||||
- gofumpt
|
||||
- goimports
|
||||
- gosec
|
||||
- nilerr
|
||||
- predeclared
|
||||
- revive
|
||||
- rowserrcheck
|
||||
- sqlclosecheck
|
||||
- tparallel
|
||||
- unconvert
|
||||
- unparam
|
||||
- whitespace
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2021-2023 Charmbracelet, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
751
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
751
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,751 @@
|
||||
# Lip Gloss
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://stuff.charm.sh/lipgloss/lipgloss-mascot-2k.png"><img width="340" alt="Lip Gloss title treatment" src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/25087/147cadb1-4254-43ec-ae6b-8d6ca7b029a1"></a><br>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/charmbracelet/lipgloss.svg" alt="Latest Release"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc"><img src="https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/gddo?status.svg" alt="GoDoc"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/actions"><img src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/workflows/build/badge.svg" alt="Build Status"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.phorm.ai/query?projectId=a0e324b6-b706-4546-b951-6671ea60c13f"><img src="https://stuff.charm.sh/misc/phorm-badge.svg" alt="phorm.ai"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Style definitions for nice terminal layouts. Built with TUIs in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
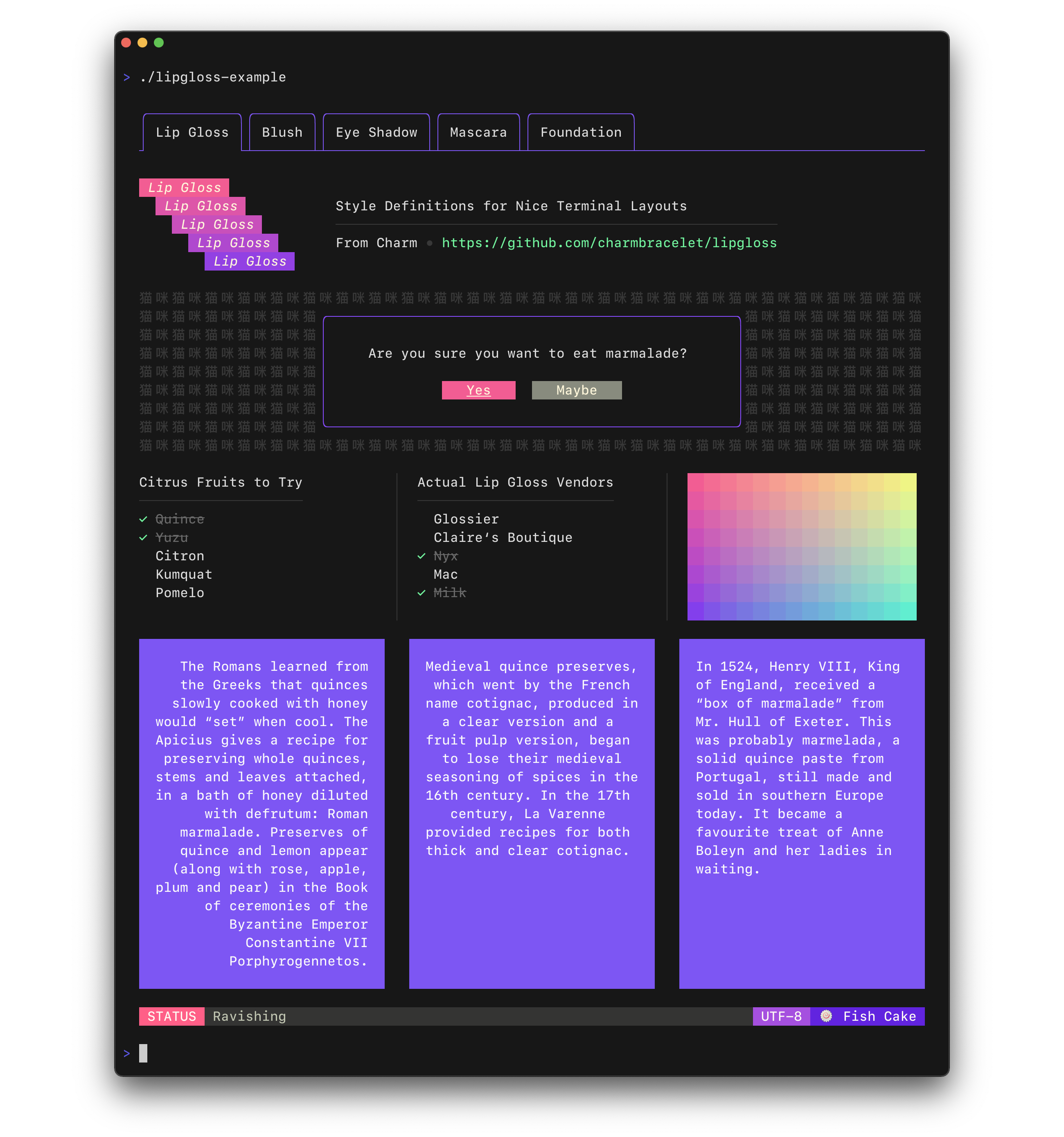
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss takes an expressive, declarative approach to terminal rendering.
|
||||
Users familiar with CSS will feel at home with Lip Gloss.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("#FAFAFA")).
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("#7D56F4")).
|
||||
PaddingTop(2).
|
||||
PaddingLeft(4).
|
||||
Width(22)
|
||||
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("Hello, kitty"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Colors
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss supports the following color profiles:
|
||||
|
||||
### ANSI 16 colors (4-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("5") // magenta
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("9") // red
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("12") // light blue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### ANSI 256 Colors (8-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("86") // aqua
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("201") // hot pink
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("202") // orange
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### True Color (16,777,216 colors; 24-bit)
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#0000FF") // good ol' 100% blue
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#04B575") // a green
|
||||
lipgloss.Color("#3C3C3C") // a dark gray
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...as well as a 1-bit ASCII profile, which is black and white only.
|
||||
|
||||
The terminal's color profile will be automatically detected, and colors outside
|
||||
the gamut of the current palette will be automatically coerced to their closest
|
||||
available value.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adaptive Colors
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify color options for light and dark backgrounds:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "236", Dark: "248"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The terminal's background color will automatically be detected and the
|
||||
appropriate color will be chosen at runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Colors
|
||||
|
||||
CompleteColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
profiles.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteColor{True: "#0000FF", ANSI256: "86", ANSI: "5"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic color degradation will not be performed in this case and it will be
|
||||
based on the color specified.
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete Adaptive Colors
|
||||
|
||||
You can use CompleteColor with AdaptiveColor to specify the exact values for
|
||||
light and dark backgrounds without automatic color degradation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
lipgloss.CompleteAdaptiveColor{
|
||||
Light: CompleteColor{TrueColor: "#d7ffae", ANSI256: "193", ANSI: "11"},
|
||||
Dark: CompleteColor{TrueColor: "#d75fee", ANSI256: "163", ANSI: "5"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inline Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss supports the usual ANSI text formatting options:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
Italic(true).
|
||||
Faint(true).
|
||||
Blink(true).
|
||||
Strikethrough(true).
|
||||
Underline(true).
|
||||
Reverse(true)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Block-Level Formatting
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss also supports rules for block-level formatting:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Padding
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
PaddingTop(2).
|
||||
PaddingRight(4).
|
||||
PaddingBottom(2).
|
||||
PaddingLeft(4)
|
||||
|
||||
// Margins
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
MarginTop(2).
|
||||
MarginRight(4).
|
||||
MarginBottom(2).
|
||||
MarginLeft(4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There is also shorthand syntax for margins and padding, which follows the same
|
||||
format as CSS:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// 2 cells on all sides
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Padding(2)
|
||||
|
||||
// 2 cells on the top and bottom, 4 cells on the left and right
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Margin(2, 4)
|
||||
|
||||
// 1 cell on the top, 4 cells on the sides, 2 cells on the bottom
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Padding(1, 4, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
// Clockwise, starting from the top: 2 cells on the top, 4 on the right, 3 on
|
||||
// the bottom, and 1 on the left
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().Margin(2, 4, 3, 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Aligning Text
|
||||
|
||||
You can align paragraphs of text to the left, right, or center.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Width(24).
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Left). // align it left
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Right). // no wait, align it right
|
||||
Align(lipgloss.Center) // just kidding, align it in the center
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Width and Height
|
||||
|
||||
Setting a minimum width and height is simple and straightforward.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString("What’s for lunch?").
|
||||
Width(24).
|
||||
Height(32).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Borders
|
||||
|
||||
Adding borders is easy:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Add a purple, rectangular border
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.NormalBorder()).
|
||||
BorderForeground(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a rounded, yellow-on-purple border to the top and left
|
||||
var anotherStyle = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.RoundedBorder()).
|
||||
BorderForeground(lipgloss.Color("228")).
|
||||
BorderBackground(lipgloss.Color("63")).
|
||||
BorderTop(true).
|
||||
BorderLeft(true)
|
||||
|
||||
// Make your own border
|
||||
var myCuteBorder = lipgloss.Border{
|
||||
Top: "._.:*:",
|
||||
Bottom: "._.:*:",
|
||||
Left: "|*",
|
||||
Right: "|*",
|
||||
TopLeft: "*",
|
||||
TopRight: "*",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "*",
|
||||
BottomRight: "*",
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are also shorthand functions for defining borders, which follow a similar
|
||||
pattern to the margin and padding shorthand functions.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Add a thick border to the top and bottom
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.ThickBorder(), true, false)
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a double border to the top and left sides. Rules are set clockwise
|
||||
// from top.
|
||||
lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.DoubleBorder(), true, false, false, true)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more on borders see [the docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
## Copying Styles
|
||||
|
||||
Just use assignment:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("219"))
|
||||
|
||||
copiedStyle := style // this is a true copy
|
||||
|
||||
wildStyle := style.Blink(true) // this is also true copy, with blink added
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since `Style` data structures contains only primitive types, assigning a style
|
||||
to another effectively creates a new copy of the style without mutating the
|
||||
original.
|
||||
|
||||
## Inheritance
|
||||
|
||||
Styles can inherit rules from other styles. When inheriting, only unset rules
|
||||
on the receiver are inherited.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var styleA = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("229")).
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("63"))
|
||||
|
||||
// Only the background color will be inherited here, because the foreground
|
||||
// color will have been already set:
|
||||
var styleB = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("201")).
|
||||
Inherit(styleA)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Unsetting Rules
|
||||
|
||||
All rules can be unset:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Bold(true). // make it bold
|
||||
UnsetBold(). // jk don't make it bold
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("227")). // yellow background
|
||||
UnsetBackground() // never mind
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When a rule is unset, it won't be inherited or copied.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforcing Rules
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes, such as when developing a component, you want to make sure style
|
||||
definitions respect their intended purpose in the UI. This is where `Inline`
|
||||
and `MaxWidth`, and `MaxHeight` come in:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Force rendering onto a single line, ignoring margins, padding, and borders.
|
||||
someStyle.Inline(true).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
|
||||
// Also limit rendering to five cells
|
||||
someStyle.Inline(true).MaxWidth(5).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
|
||||
// Limit rendering to a 5x5 cell block
|
||||
someStyle.MaxWidth(5).MaxHeight(5).Render("yadda yadda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tabs
|
||||
|
||||
The tab character (`\t`) is rendered differently in different terminals (often
|
||||
as 8 spaces, sometimes 4). Because of this inconsistency, Lip Gloss converts
|
||||
tabs to 4 spaces at render time. This behavior can be changed on a per-style
|
||||
basis, however:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle() // tabs will render as 4 spaces, the default
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(2) // render tabs as 2 spaces
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(0) // remove tabs entirely
|
||||
style = style.TabWidth(lipgloss.NoTabConversion) // leave tabs intact
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, you just call the `Render(string...)` method on a `lipgloss.Style`:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style := lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true).SetString("Hello,")
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("kitty.")) // Hello, kitty.
|
||||
fmt.Println(style.Render("puppy.")) // Hello, puppy.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But you could also use the Stringer interface:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().SetString("你好,猫咪。").Bold(true)
|
||||
fmt.Println(style) // 你好,猫咪。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Renderers
|
||||
|
||||
Custom renderers allow you to render to a specific outputs. This is
|
||||
particularly important when you want to render to different outputs and
|
||||
correctly detect the color profile and dark background status for each, such as
|
||||
in a server-client situation.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func myLittleHandler(sess ssh.Session) {
|
||||
// Create a renderer for the client.
|
||||
renderer := lipgloss.NewRenderer(sess)
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a new style on the renderer.
|
||||
style := renderer.NewStyle().Background(lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "63", Dark: "228"})
|
||||
|
||||
// Render. The color profile and dark background state will be correctly detected.
|
||||
io.WriteString(sess, style.Render("Heyyyyyyy"))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For an example on using a custom renderer over SSH with [Wish][wish] see the
|
||||
[SSH example][ssh-example].
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to pure styling, Lip Gloss also ships with some utilities to help
|
||||
assemble your layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Joining Paragraphs
|
||||
|
||||
Horizontally and vertically joining paragraphs is a cinch.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Horizontally join three paragraphs along their bottom edges
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Bottom, paragraphA, paragraphB, paragraphC)
|
||||
|
||||
// Vertically join two paragraphs along their center axes
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinVertical(lipgloss.Center, paragraphA, paragraphB)
|
||||
|
||||
// Horizontally join three paragraphs, with the shorter ones aligning 20%
|
||||
// from the top of the tallest
|
||||
lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(0.2, paragraphA, paragraphB, paragraphC)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Measuring Width and Height
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you’ll want to know the width and height of text blocks when building
|
||||
your layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Render a block of text.
|
||||
var style = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
Width(40).
|
||||
Padding(2)
|
||||
var block string = style.Render(someLongString)
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the actual, physical dimensions of the text block.
|
||||
width := lipgloss.Width(block)
|
||||
height := lipgloss.Height(block)
|
||||
|
||||
// Here's a shorthand function.
|
||||
w, h := lipgloss.Size(block)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Placing Text in Whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you’ll simply want to place a block of text in whitespace.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Center a paragraph horizontally in a space 80 cells wide. The height of
|
||||
// the block returned will be as tall as the input paragraph.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.PlaceHorizontal(80, lipgloss.Center, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place a paragraph at the bottom of a space 30 cells tall. The width of
|
||||
// the text block returned will be as wide as the input paragraph.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.PlaceVertical(30, lipgloss.Bottom, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place a paragraph in the bottom right corner of a 30x80 cell space.
|
||||
block := lipgloss.Place(30, 80, lipgloss.Right, lipgloss.Bottom, fancyStyledParagraph)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also style the whitespace. For details, see [the docs][docs].
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Tables
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a table rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define some rows of data.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
rows := [][]string{
|
||||
{"Chinese", "您好", "你好"},
|
||||
{"Japanese", "こんにちは", "やあ"},
|
||||
{"Arabic", "أهلين", "أهلا"},
|
||||
{"Russian", "Здравствуйте", "Привет"},
|
||||
{"Spanish", "Hola", "¿Qué tal?"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the table package to style and render the table.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := table.New().
|
||||
Border(lipgloss.NormalBorder()).
|
||||
BorderStyle(lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99"))).
|
||||
StyleFunc(func(row, col int) lipgloss.Style {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case row == 0:
|
||||
return HeaderStyle
|
||||
case row%2 == 0:
|
||||
return EvenRowStyle
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return OddRowStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
}).
|
||||
Headers("LANGUAGE", "FORMAL", "INFORMAL").
|
||||
Rows(rows...)
|
||||
|
||||
// You can also add tables row-by-row
|
||||
t.Row("English", "You look absolutely fabulous.", "How's it going?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the table.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For more on tables see [the docs](https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc) and [examples](https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree/master/examples/table).
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Trees
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a tree rendering sub-package.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/tree"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a new tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New("root", "child 1", "child 2", tree.New("child 3", "child 3.1"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(t)
|
||||
|
||||
// root
|
||||
// ├── child 1
|
||||
// ├── child 2
|
||||
// └── child 3
|
||||
// └── child 3.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
|
||||
Trees can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
style1 := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
style2 := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("10")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
|
||||
t := tree.New().
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("Nyx").
|
||||
Items("Qux", "Quux").
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(style2),
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(style1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="Tree example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/5a875269-f6d6-43fa-9916-5d8360e66964"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
You may also define custom enumerator implementations:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New().
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
tree.New().
|
||||
Root("Nyx").
|
||||
Items(
|
||||
"Qux",
|
||||
"Quux",
|
||||
),
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(func(tree.Data, int) (string, string) {
|
||||
return "->", "->"
|
||||
})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the tree.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="Tree example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/811e8b39-124f-48bb-b3dd-e015a65b1065"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Building
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build trees incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
t := tree.New("")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
t.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Lists
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss ships with a list rendering sub-package.
|
||||
Implementation-wise, lists are still trees.
|
||||
The `list` package provides many common `Enumerator` implementations, as well as
|
||||
some syntactic sugar.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/list"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a new list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New("A", "B", "C")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
fmt.Println(l)
|
||||
|
||||
// • A
|
||||
// • B
|
||||
// • C
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Customization
|
||||
|
||||
Lists can be customized via their enumeration function as well as using
|
||||
`lipgloss.Style`s.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
enumeratorStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("99")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
itemStyle := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("10")).MarginRight(1)
|
||||
|
||||
l := list.New(
|
||||
"Glossier",
|
||||
"Claire’s Boutique",
|
||||
"Nyx",
|
||||
"Mac",
|
||||
"Milk",
|
||||
).
|
||||
Enumerator(list.Roman).
|
||||
EnumeratorStyle(enumeratorStyle).
|
||||
ItemStyle(itemStyle)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="List example"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/8f5e5e0b-7bf9-4e3b-a8ba-3af10825320e"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
In addition to the predefined enumerators (`Arabic`, `Alphabet`, `Roman`, `Bullet`, `Tree`),
|
||||
you may also define your own custom enumerator:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
var DuckDuckGooseEnumerator Enumerator = func(l *List, i int) string {
|
||||
if l.At(i) == "Goose" {
|
||||
return "Honk →"
|
||||
}
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use it in a list:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New("Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Duck", "Goose", "Duck", "Duck")
|
||||
l.Enumerator(DuckDuckGooseEnumerator)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the list:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
alt="image"
|
||||
src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/assets/245435/44e37a5b-5124-4f49-a332-1756a355002e"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Building
|
||||
|
||||
If you need, you can also build trees incrementally:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
l := list.New()
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < repeat; i++ {
|
||||
l.Item("Lip Gloss")
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
Why are things misaligning? Why are borders at the wrong widths?
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<p>This is most likely due to your locale and encoding, particularly with
|
||||
regard to Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (for example, <code>zh_CN.UTF-8</code>
|
||||
or <code>ja_JP.UTF-8</code>). The most direct way to fix this is to set
|
||||
<code>RUNEWIDTH_EASTASIAN=0</code> in your environment.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>For details see <a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/issues/40">https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/issues/40.</a></p>
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>
|
||||
Why isn't Lip Gloss displaying colors?
|
||||
</summary>
|
||||
<p>Lip Gloss automatically degrades colors to the best available option in the
|
||||
given terminal, and if output's not a TTY it will remove color output entirely.
|
||||
This is common when running tests, CI, or when piping output elsewhere.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>If necessary, you can force a color profile in your tests with
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss#SetColorProfile"><code>SetColorProfile</code></a>.</p>
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
lipgloss.SetColorProfile(termenv.TrueColor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
_Note:_ this option limits the flexibility of your application and can cause
|
||||
ANSI escape codes to be output in cases where that might not be desired. Take
|
||||
careful note of your use case and environment before choosing to force a color
|
||||
profile.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## What about [Bubble Tea][tea]?
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss doesn’t replace Bubble Tea. Rather, it is an excellent Bubble Tea
|
||||
companion. It was designed to make assembling terminal user interface views as
|
||||
simple and fun as possible so that you can focus on building your application
|
||||
instead of concerning yourself with low-level layout details.
|
||||
|
||||
In simple terms, you can use Lip Gloss to help build your Bubble Tea views.
|
||||
|
||||
[tea]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/tea
|
||||
|
||||
## Under the Hood
|
||||
|
||||
Lip Gloss is built on the excellent [Termenv][termenv] and [Reflow][reflow]
|
||||
libraries which deal with color and ANSI-aware text operations, respectively.
|
||||
For many use cases Termenv and Reflow will be sufficient for your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
[termenv]: https://github.com/muesli/termenv
|
||||
[reflow]: https://github.com/muesli/reflow
|
||||
|
||||
## Rendering Markdown
|
||||
|
||||
For a more document-centric rendering solution with support for things like
|
||||
lists, tables, and syntax-highlighted code have a look at [Glamour][glamour],
|
||||
the stylesheet-based Markdown renderer.
|
||||
|
||||
[glamour]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/glamour
|
||||
|
||||
## Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
We’d love to hear your thoughts on this project. Feel free to drop us a note!
|
||||
|
||||
- [Twitter](https://twitter.com/charmcli)
|
||||
- [The Fediverse](https://mastodon.social/@charmcli)
|
||||
- [Discord](https://charm.sh/chat)
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
[MIT](https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/raw/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Part of [Charm](https://charm.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://charm.sh/"><img alt="The Charm logo" src="https://stuff.charm.sh/charm-badge.jpg" width="400"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Charm热爱开源 • Charm loves open source
|
||||
|
||||
[docs]: https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss?tab=doc
|
||||
[wish]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/wish
|
||||
[ssh-example]: examples/ssh
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/align.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/align.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Perform text alignment. If the string is multi-lined, we also make all lines
|
||||
// the same width by padding them with spaces. If a termenv style is passed,
|
||||
// use that to style the spaces added.
|
||||
func alignTextHorizontal(str string, pos Position, width int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
lines, widestLine := getLines(str)
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
lineWidth := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
|
||||
shortAmount := widestLine - lineWidth // difference from the widest line
|
||||
shortAmount += max(0, width-(shortAmount+lineWidth)) // difference from the total width, if set
|
||||
|
||||
if shortAmount > 0 {
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
s := strings.Repeat(" ", shortAmount)
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
s = style.Styled(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l = s + l
|
||||
case Center:
|
||||
// Note: remainder goes on the right.
|
||||
left := shortAmount / 2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
right := left + shortAmount%2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
|
||||
leftSpaces := strings.Repeat(" ", left)
|
||||
rightSpaces := strings.Repeat(" ", right)
|
||||
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
leftSpaces = style.Styled(leftSpaces)
|
||||
rightSpaces = style.Styled(rightSpaces)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l = leftSpaces + l + rightSpaces
|
||||
default: // Left
|
||||
s := strings.Repeat(" ", shortAmount)
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
s = style.Styled(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
l += s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func alignTextVertical(str string, pos Position, height int, _ *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
strHeight := strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
if height < strHeight {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos {
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
return str + strings.Repeat("\n", height-strHeight)
|
||||
case Center:
|
||||
topPadding, bottomPadding := (height-strHeight)/2, (height-strHeight)/2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
if strHeight+topPadding+bottomPadding > height {
|
||||
topPadding--
|
||||
} else if strHeight+topPadding+bottomPadding < height {
|
||||
bottomPadding++
|
||||
}
|
||||
return strings.Repeat("\n", topPadding) + str + strings.Repeat("\n", bottomPadding)
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
return strings.Repeat("\n", height-strHeight) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_unix.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
//go:build !windows
|
||||
// +build !windows
|
||||
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// enableLegacyWindowsANSI is only needed on Windows.
|
||||
func enableLegacyWindowsANSI() {}
|
||||
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
22
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/ansi_windows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
//go:build windows
|
||||
// +build windows
|
||||
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var enableANSI sync.Once
|
||||
|
||||
// enableANSIColors enables support for ANSI color sequences in the Windows
|
||||
// default console (cmd.exe and the PowerShell application). Note that this
|
||||
// only works with Windows 10. Also note that Windows Terminal supports colors
|
||||
// by default.
|
||||
func enableLegacyWindowsANSI() {
|
||||
enableANSI.Do(func() {
|
||||
_, _ = termenv.EnableWindowsANSIConsole()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
443
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/borders.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
443
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/borders.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,443 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Border contains a series of values which comprise the various parts of a
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
type Border struct {
|
||||
Top string
|
||||
Bottom string
|
||||
Left string
|
||||
Right string
|
||||
TopLeft string
|
||||
TopRight string
|
||||
BottomLeft string
|
||||
BottomRight string
|
||||
MiddleLeft string
|
||||
MiddleRight string
|
||||
Middle string
|
||||
MiddleTop string
|
||||
MiddleBottom string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTopSize returns the width of the top border. If borders contain runes of
|
||||
// varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on the top
|
||||
// edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetTopSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopLeft, b.Top, b.TopRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetRightSize returns the width of the right border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the right edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetRightSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopRight, b.Right, b.BottomRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBottomSize returns the width of the bottom border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the bottom edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetBottomSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.BottomLeft, b.Bottom, b.BottomRight)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetLeftSize returns the width of the left border. If borders contain runes
|
||||
// of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on the
|
||||
// left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (b Border) GetLeftSize() int {
|
||||
return getBorderEdgeWidth(b.TopLeft, b.Left, b.BottomLeft)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getBorderEdgeWidth(borderParts ...string) (maxWidth int) {
|
||||
for _, piece := range borderParts {
|
||||
w := maxRuneWidth(piece)
|
||||
if w > maxWidth {
|
||||
maxWidth = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return maxWidth
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
noBorder = Border{}
|
||||
|
||||
normalBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "─",
|
||||
Bottom: "─",
|
||||
Left: "│",
|
||||
Right: "│",
|
||||
TopLeft: "┌",
|
||||
TopRight: "┐",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "└",
|
||||
BottomRight: "┘",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "├",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┤",
|
||||
Middle: "┼",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┬",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┴",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
roundedBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "─",
|
||||
Bottom: "─",
|
||||
Left: "│",
|
||||
Right: "│",
|
||||
TopLeft: "╭",
|
||||
TopRight: "╮",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "╰",
|
||||
BottomRight: "╯",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "├",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┤",
|
||||
Middle: "┼",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┬",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┴",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
blockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "█",
|
||||
Bottom: "█",
|
||||
Left: "█",
|
||||
Right: "█",
|
||||
TopLeft: "█",
|
||||
TopRight: "█",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "█",
|
||||
BottomRight: "█",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
outerHalfBlockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "▀",
|
||||
Bottom: "▄",
|
||||
Left: "▌",
|
||||
Right: "▐",
|
||||
TopLeft: "▛",
|
||||
TopRight: "▜",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "▙",
|
||||
BottomRight: "▟",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
innerHalfBlockBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "▄",
|
||||
Bottom: "▀",
|
||||
Left: "▐",
|
||||
Right: "▌",
|
||||
TopLeft: "▗",
|
||||
TopRight: "▖",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "▝",
|
||||
BottomRight: "▘",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
thickBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "━",
|
||||
Bottom: "━",
|
||||
Left: "┃",
|
||||
Right: "┃",
|
||||
TopLeft: "┏",
|
||||
TopRight: "┓",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "┗",
|
||||
BottomRight: "┛",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "┣",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "┫",
|
||||
Middle: "╋",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "┳",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "┻",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
doubleBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: "═",
|
||||
Bottom: "═",
|
||||
Left: "║",
|
||||
Right: "║",
|
||||
TopLeft: "╔",
|
||||
TopRight: "╗",
|
||||
BottomLeft: "╚",
|
||||
BottomRight: "╝",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: "╠",
|
||||
MiddleRight: "╣",
|
||||
Middle: "╬",
|
||||
MiddleTop: "╦",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: "╩",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
hiddenBorder = Border{
|
||||
Top: " ",
|
||||
Bottom: " ",
|
||||
Left: " ",
|
||||
Right: " ",
|
||||
TopLeft: " ",
|
||||
TopRight: " ",
|
||||
BottomLeft: " ",
|
||||
BottomRight: " ",
|
||||
MiddleLeft: " ",
|
||||
MiddleRight: " ",
|
||||
Middle: " ",
|
||||
MiddleTop: " ",
|
||||
MiddleBottom: " ",
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// NormalBorder returns a standard-type border with a normal weight and 90
|
||||
// degree corners.
|
||||
func NormalBorder() Border {
|
||||
return normalBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RoundedBorder returns a border with rounded corners.
|
||||
func RoundedBorder() Border {
|
||||
return roundedBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BlockBorder returns a border that takes the whole block.
|
||||
func BlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return blockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// OuterHalfBlockBorder returns a half-block border that sits outside the frame.
|
||||
func OuterHalfBlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return outerHalfBlockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InnerHalfBlockBorder returns a half-block border that sits inside the frame.
|
||||
func InnerHalfBlockBorder() Border {
|
||||
return innerHalfBlockBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ThickBorder returns a border that's thicker than the one returned by
|
||||
// NormalBorder.
|
||||
func ThickBorder() Border {
|
||||
return thickBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DoubleBorder returns a border comprised of two thin strokes.
|
||||
func DoubleBorder() Border {
|
||||
return doubleBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HiddenBorder returns a border that renders as a series of single-cell
|
||||
// spaces. It's useful for cases when you want to remove a standard border but
|
||||
// maintain layout positioning. This said, you can still apply a background
|
||||
// color to a hidden border.
|
||||
func HiddenBorder() Border {
|
||||
return hiddenBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) applyBorder(str string) string {
|
||||
var (
|
||||
topSet = s.isSet(borderTopKey)
|
||||
rightSet = s.isSet(borderRightKey)
|
||||
bottomSet = s.isSet(borderBottomKey)
|
||||
leftSet = s.isSet(borderLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
border = s.getBorderStyle()
|
||||
hasTop = s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false)
|
||||
hasRight = s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false)
|
||||
hasBottom = s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false)
|
||||
hasLeft = s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
|
||||
topFG = s.getAsColor(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
rightFG = s.getAsColor(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
bottomFG = s.getAsColor(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
leftFG = s.getAsColor(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
|
||||
topBG = s.getAsColor(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
rightBG = s.getAsColor(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
bottomBG = s.getAsColor(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
leftBG = s.getAsColor(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// If a border is set and no sides have been specifically turned on or off
|
||||
// render borders on all sides.
|
||||
if border != noBorder && !(topSet || rightSet || bottomSet || leftSet) {
|
||||
hasTop = true
|
||||
hasRight = true
|
||||
hasBottom = true
|
||||
hasLeft = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If no border is set or all borders are been disabled, abort.
|
||||
if border == noBorder || (!hasTop && !hasRight && !hasBottom && !hasLeft) {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lines, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
|
||||
if hasLeft {
|
||||
if border.Left == "" {
|
||||
border.Left = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
width += maxRuneWidth(border.Left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if hasRight && border.Right == "" {
|
||||
border.Right = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// If corners should be rendered but are set with the empty string, fill them
|
||||
// with a single space.
|
||||
if hasTop && hasLeft && border.TopLeft == "" {
|
||||
border.TopLeft = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasTop && hasRight && border.TopRight == "" {
|
||||
border.TopRight = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom && hasLeft && border.BottomLeft == "" {
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom && hasRight && border.BottomRight == "" {
|
||||
border.BottomRight = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Figure out which corners we should actually be using based on which
|
||||
// sides are set to show.
|
||||
if hasTop {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case !hasLeft && !hasRight:
|
||||
border.TopLeft = ""
|
||||
border.TopRight = ""
|
||||
case !hasLeft:
|
||||
border.TopLeft = ""
|
||||
case !hasRight:
|
||||
border.TopRight = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if hasBottom {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case !hasLeft && !hasRight:
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = ""
|
||||
border.BottomRight = ""
|
||||
case !hasLeft:
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = ""
|
||||
case !hasRight:
|
||||
border.BottomRight = ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// For now, limit corners to one rune.
|
||||
border.TopLeft = getFirstRuneAsString(border.TopLeft)
|
||||
border.TopRight = getFirstRuneAsString(border.TopRight)
|
||||
border.BottomRight = getFirstRuneAsString(border.BottomRight)
|
||||
border.BottomLeft = getFirstRuneAsString(border.BottomLeft)
|
||||
|
||||
var out strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
// Render top
|
||||
if hasTop {
|
||||
top := renderHorizontalEdge(border.TopLeft, border.Top, border.TopRight, width)
|
||||
top = s.styleBorder(top, topFG, topBG)
|
||||
out.WriteString(top)
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
leftRunes := []rune(border.Left)
|
||||
leftIndex := 0
|
||||
|
||||
rightRunes := []rune(border.Right)
|
||||
rightIndex := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Render sides
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
if hasLeft {
|
||||
r := string(leftRunes[leftIndex])
|
||||
leftIndex++
|
||||
if leftIndex >= len(leftRunes) {
|
||||
leftIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(s.styleBorder(r, leftFG, leftBG))
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(l)
|
||||
if hasRight {
|
||||
r := string(rightRunes[rightIndex])
|
||||
rightIndex++
|
||||
if rightIndex >= len(rightRunes) {
|
||||
rightIndex = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(s.styleBorder(r, rightFG, rightBG))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render bottom
|
||||
if hasBottom {
|
||||
bottom := renderHorizontalEdge(border.BottomLeft, border.Bottom, border.BottomRight, width)
|
||||
bottom = s.styleBorder(bottom, bottomFG, bottomBG)
|
||||
out.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
out.WriteString(bottom)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render the horizontal (top or bottom) portion of a border.
|
||||
func renderHorizontalEdge(left, middle, right string, width int) string {
|
||||
if middle == "" {
|
||||
middle = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
leftWidth := ansi.StringWidth(left)
|
||||
rightWidth := ansi.StringWidth(right)
|
||||
|
||||
runes := []rune(middle)
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
|
||||
out := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
out.WriteString(left)
|
||||
for i := leftWidth + rightWidth; i < width+rightWidth; {
|
||||
out.WriteRune(runes[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
if j >= len(runes) {
|
||||
j = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += ansi.StringWidth(string(runes[j]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(right)
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply foreground and background styling to a border.
|
||||
func (s Style) styleBorder(border string, fg, bg TerminalColor) string {
|
||||
if fg == noColor && bg == noColor {
|
||||
return border
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
style := termenv.Style{}
|
||||
|
||||
if fg != noColor {
|
||||
style = style.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bg != noColor {
|
||||
style = style.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return style.Styled(border)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func maxRuneWidth(str string) int {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
|
||||
state := -1
|
||||
for len(str) > 0 {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
_, str, w, state = uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(str, state)
|
||||
if w > width {
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func getFirstRuneAsString(str string) string {
|
||||
if str == "" {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
r := []rune(str)
|
||||
return string(r[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
172
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
172
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// TerminalColor is a color intended to be rendered in the terminal.
|
||||
type TerminalColor interface {
|
||||
color(*Renderer) termenv.Color
|
||||
RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var noColor = NoColor{}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoColor is used to specify the absence of color styling. When this is active
|
||||
// foreground colors will be rendered with the terminal's default text color,
|
||||
// and background colors will not be drawn at all.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var style = someStyle.Background(lipgloss.NoColor{})
|
||||
type NoColor struct{}
|
||||
|
||||
func (NoColor) color(*Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return termenv.NoColor{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. Because we have to return
|
||||
// something, despite this color being the absence of color, we're returning
|
||||
// black with 100% opacity.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (n NoColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0xFFFF //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Color specifies a color by hex or ANSI value. For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ansiColor := lipgloss.Color("21")
|
||||
// hexColor := lipgloss.Color("#0000ff")
|
||||
type Color string
|
||||
|
||||
func (c Color) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return r.ColorProfile().Color(string(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (c Color) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(c.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSIColor is a color specified by an ANSI color value. It's merely syntactic
|
||||
// sugar for the more general Color function. Invalid colors will render as
|
||||
// black.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // These two statements are equivalent.
|
||||
// colorA := lipgloss.ANSIColor(21)
|
||||
// colorB := lipgloss.Color("21")
|
||||
type ANSIColor uint
|
||||
|
||||
func (ac ANSIColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
return Color(strconv.FormatUint(uint64(ac), 10)).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (ac ANSIColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
cf := Color(strconv.FormatUint(uint64(ac), 10))
|
||||
return cf.RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AdaptiveColor provides color options for light and dark backgrounds. The
|
||||
// appropriate color will be returned at runtime based on the darkness of the
|
||||
// terminal background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// color := lipgloss.AdaptiveColor{Light: "#0000ff", Dark: "#000099"}
|
||||
type AdaptiveColor struct {
|
||||
Light string
|
||||
Dark string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (ac AdaptiveColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
if r.HasDarkBackground() {
|
||||
return Color(ac.Dark).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Color(ac.Light).color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (ac AdaptiveColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(ac.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CompleteColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
// profiles. Automatic color degradation will not be performed.
|
||||
type CompleteColor struct {
|
||||
TrueColor string
|
||||
ANSI256 string
|
||||
ANSI string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (c CompleteColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
p := r.ColorProfile()
|
||||
switch p { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case termenv.TrueColor:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.TrueColor)
|
||||
case termenv.ANSI256:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.ANSI256)
|
||||
case termenv.ANSI:
|
||||
return p.Color(c.ANSI)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return termenv.NoColor{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
// CompleteAdaptiveColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (c CompleteColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(c.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CompleteAdaptiveColor specifies exact values for truecolor, ANSI256, and ANSI color
|
||||
// profiles, with separate options for light and dark backgrounds. Automatic
|
||||
// color degradation will not be performed.
|
||||
type CompleteAdaptiveColor struct {
|
||||
Light CompleteColor
|
||||
Dark CompleteColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (cac CompleteAdaptiveColor) color(r *Renderer) termenv.Color {
|
||||
if r.HasDarkBackground() {
|
||||
return cac.Dark.color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return cac.Light.color(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the RGBA value of this color. This satisfies the Go Color
|
||||
// interface. Note that on error we return black with 100% opacity, or:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Red: 0x0, Green: 0x0, Blue: 0x0, Alpha: 0xFFFF.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated.
|
||||
func (cac CompleteAdaptiveColor) RGBA() (r, g, b, a uint32) {
|
||||
return termenv.ConvertToRGB(cac.color(renderer)).RGBA()
|
||||
}
|
||||
542
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/get.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
542
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/get.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,542 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBold returns the style's bold value. If no value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBold() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(boldKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetItalic returns the style's italic value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetItalic() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(italicKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetUnderline returns the style's underline value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetUnderline() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(underlineKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetStrikethrough returns the style's strikethrough value. If no value is set false
|
||||
// is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetStrikethrough() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(strikethroughKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetReverse returns the style's reverse value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetReverse() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(reverseKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBlink returns the style's blink value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBlink() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(blinkKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetFaint returns the style's faint value. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetFaint() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(faintKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetForeground returns the style's foreground color. If no value is set
|
||||
// NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(foregroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBackground returns the style's background color. If no value is set
|
||||
// NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(backgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetWidth returns the style's width setting. If no width is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(widthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHeight returns the style's height setting. If no height is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHeight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(heightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlign returns the style's implicit horizontal alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Left is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlign() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Left
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlignHorizontal returns the style's implicit horizontal alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Left is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlignHorizontal() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Left
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetAlignVertical returns the style's implicit vertical alignment setting.
|
||||
// If no alignment is set Position.Top is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetAlignVertical() Position {
|
||||
v := s.getAsPosition(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
if v == Position(0) {
|
||||
return Top
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPadding returns the style's top, right, bottom, and left padding values,
|
||||
// in that order. 0 is returned for unset values.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPadding() (top, right, bottom, left int) {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingTop returns the style's top padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingTop() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingRight returns the style's right padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingRight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingBottom returns the style's bottom padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingBottom() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPaddingLeft returns the style's left padding. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetPaddingLeft() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalPadding returns the style's left and right padding. Unset
|
||||
// values are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalPadding() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey) + s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalPadding returns the style's top and bottom padding. Unset values
|
||||
// are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalPadding() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey) + s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetColorWhitespace returns the style's whitespace coloring setting. If no
|
||||
// value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetColorWhitespace() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(colorWhitespaceKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMargin returns the style's top, right, bottom, and left margins, in that
|
||||
// order. 0 is returned for unset values.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMargin() (top, right, bottom, left int) {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginRightKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey),
|
||||
s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginTop returns the style's top margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginTop() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginRight returns the style's right margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginRight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginBottom returns the style's bottom margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginBottom() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMarginLeft returns the style's left margin. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMarginLeft() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalMargins returns the style's left and right margins. Unset
|
||||
// values are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalMargins() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey) + s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalMargins returns the style's top and bottom margins. Unset values
|
||||
// are measured as 0.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalMargins() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(marginTopKey) + s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorder returns the style's border style (type Border) and value for the
|
||||
// top, right, bottom, and left in that order. If no value is set for the
|
||||
// border style, Border{} is returned. For all other unset values false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorder() (b Border, top, right, bottom, left bool) {
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle(),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false),
|
||||
s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderStyle returns the style's border style (type Border). If no value
|
||||
// is set Border{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderStyle() Border {
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTop returns the style's top border setting. If no value is set
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTop() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRight returns the style's right border setting. If no value is set
|
||||
// false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRight() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottom returns the style's bottom border setting. If no value is
|
||||
// set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottom() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeft returns the style's left border setting. If no value is
|
||||
// set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeft() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopForeground returns the style's border top foreground color. If
|
||||
// no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightForeground returns the style's border right foreground color.
|
||||
// If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomForeground returns the style's border bottom foreground
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftForeground returns the style's border left foreground
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftForeground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopBackground returns the style's border top background color. If
|
||||
// no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightBackground returns the style's border right background color.
|
||||
// If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomBackground returns the style's border bottom background
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftBackground returns the style's border left background
|
||||
// color. If no value is set NoColor{} is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftBackground() TerminalColor {
|
||||
return s.getAsColor(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopWidth returns the width of the top border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the top edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: This function simply calls Style.GetBorderTopSize.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderTopSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderTopSize returns the width of the top border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the top edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderTopSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderTopKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetTopSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderLeftSize returns the width of the left border. If borders contain
|
||||
// runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border exists on
|
||||
// the left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderLeftSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderLeftKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetLeftSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderBottomSize returns the width of the bottom border. If borders
|
||||
// contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border
|
||||
// exists on the left edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderBottomSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderBottomKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetBottomSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetBorderRightSize returns the width of the right border. If borders
|
||||
// contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no border
|
||||
// exists on the right edge, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetBorderRightSize() int {
|
||||
if !s.getAsBool(borderRightKey, false) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.getBorderStyle().GetRightSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalBorderSize returns the width of the horizontal borders. If
|
||||
// borders contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no
|
||||
// border exists on the horizontal edges, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalBorderSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderLeftSize() + s.GetBorderRightSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalBorderSize returns the width of the vertical borders. If
|
||||
// borders contain runes of varying widths, the widest rune is returned. If no
|
||||
// border exists on the vertical edges, 0 is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalBorderSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetBorderTopSize() + s.GetBorderBottomSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetInline returns the style's inline setting. If no value is set false is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetInline() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(inlineKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMaxWidth returns the style's max width setting. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMaxWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetMaxHeight returns the style's max height setting. If no value is set 0 is
|
||||
// returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetMaxHeight() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTabWidth returns the style's tab width setting. If no value is set 4 is
|
||||
// returned which is the implicit default.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetTabWidth() int {
|
||||
return s.getAsInt(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetUnderlineSpaces returns whether or not the style is set to underline
|
||||
// spaces. If not value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetUnderlineSpaces() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetStrikethroughSpaces returns whether or not the style is set to strikethrough
|
||||
// spaces. If not value is set false is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetStrikethroughSpaces() bool {
|
||||
return s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, false)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetHorizontalFrameSize returns the sum of the style's horizontal margins, padding
|
||||
// and border widths.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Provisional: this method may be renamed.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetHorizontalFrameSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetHorizontalMargins() + s.GetHorizontalPadding() + s.GetHorizontalBorderSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetVerticalFrameSize returns the sum of the style's vertical margins, padding
|
||||
// and border widths.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Provisional: this method may be renamed.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetVerticalFrameSize() int {
|
||||
return s.GetVerticalMargins() + s.GetVerticalPadding() + s.GetVerticalBorderSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetFrameSize returns the sum of the margins, padding and border width for
|
||||
// both the horizontal and vertical margins.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetFrameSize() (x, y int) {
|
||||
return s.GetHorizontalFrameSize(), s.GetVerticalFrameSize()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetTransform returns the transform set on the style. If no transform is set
|
||||
// nil is returned.
|
||||
func (s Style) GetTransform() func(string) string {
|
||||
return s.getAsTransform(transformKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns whether or not the given property is set.
|
||||
func (s Style) isSet(k propKey) bool {
|
||||
return s.props.has(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsBool(k propKey, defaultVal bool) bool {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return defaultVal
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.attrs&int(k) != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsColor(k propKey) TerminalColor {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return noColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var c TerminalColor
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.fgColor
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.bgColor
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.marginBgColor
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderTopFgColor
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderRightFgColor
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderBottomFgColor
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderLeftFgColor
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderTopBgColor
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderRightBgColor
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderBottomBgColor
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
c = s.borderLeftBgColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if c != nil {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return noColor
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsInt(k propKey) int {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
return s.width
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
return s.height
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingTop
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingRight
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingBottom
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
return s.paddingLeft
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
return s.marginTop
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
return s.marginRight
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
return s.marginBottom
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
return s.marginLeft
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
return s.maxWidth
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
return s.maxHeight
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
return s.tabWidth
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsPosition(k propKey) Position {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
return Position(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
return s.alignHorizontal
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
return s.alignVertical
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Position(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getBorderStyle() Border {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(borderStyleKey) {
|
||||
return noBorder
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.borderStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) getAsTransform(propKey) func(string) string {
|
||||
if !s.isSet(transformKey) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.transform
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Split a string into lines, additionally returning the size of the widest
|
||||
// line.
|
||||
func getLines(s string) (lines []string, widest int) {
|
||||
lines = strings.Split(s, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for _, l := range lines {
|
||||
w := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
if widest < w {
|
||||
widest = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lines, widest
|
||||
}
|
||||
175
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/join.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
175
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/join.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// JoinHorizontal is a utility function for horizontally joining two
|
||||
// potentially multi-lined strings along a vertical axis. The first argument is
|
||||
// the position, with 0 being all the way at the top and 1 being all the way
|
||||
// at the bottom.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you just want to align to the top, center or bottom you may as well just
|
||||
// use the helper constants Top, Center, and Bottom.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// blockB := "...\n...\n..."
|
||||
// blockA := "...\n...\n...\n...\n..."
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join 20% from the top
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(0.2, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join on the top edge
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Top, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
func JoinHorizontal(pos Position, strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(strs) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(strs) == 1 {
|
||||
return strs[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// Groups of strings broken into multiple lines
|
||||
blocks = make([][]string, len(strs))
|
||||
|
||||
// Max line widths for the above text blocks
|
||||
maxWidths = make([]int, len(strs))
|
||||
|
||||
// Height of the tallest block
|
||||
maxHeight int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Break text blocks into lines and get max widths for each text block
|
||||
for i, str := range strs {
|
||||
blocks[i], maxWidths[i] = getLines(str)
|
||||
if len(blocks[i]) > maxHeight {
|
||||
maxHeight = len(blocks[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add extra lines to make each side the same height
|
||||
for i := range blocks {
|
||||
if len(blocks[i]) >= maxHeight {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
extraLines := make([]string, maxHeight-len(blocks[i]))
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(blocks[i], extraLines...)
|
||||
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(extraLines, blocks[i]...)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
n := len(extraLines)
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(n) * pos.value()))
|
||||
top := n - split
|
||||
bottom := n - top
|
||||
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(extraLines[top:], blocks[i]...)
|
||||
blocks[i] = append(blocks[i], extraLines[bottom:]...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Merge lines
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i := range blocks[0] { // remember, all blocks have the same number of members now
|
||||
for j, block := range blocks {
|
||||
b.WriteString(block[i])
|
||||
|
||||
// Also make lines the same length
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", maxWidths[j]-ansi.StringWidth(block[i])))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(blocks[0])-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// JoinVertical is a utility function for vertically joining two potentially
|
||||
// multi-lined strings along a horizontal axis. The first argument is the
|
||||
// position, with 0 being all the way to the left and 1 being all the way to
|
||||
// the right.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// If you just want to align to the left, right or center you may as well just
|
||||
// use the helper constants Left, Center, and Right.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// blockB := "...\n...\n..."
|
||||
// blockA := "...\n...\n...\n...\n..."
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join 20% from the top
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinVertical(0.2, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Join on the right edge
|
||||
// str := lipgloss.JoinVertical(lipgloss.Right, blockA, blockB)
|
||||
func JoinVertical(pos Position, strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(strs) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(strs) == 1 {
|
||||
return strs[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
blocks = make([][]string, len(strs))
|
||||
maxWidth int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range strs {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
blocks[i], w = getLines(strs[i])
|
||||
if w > maxWidth {
|
||||
maxWidth = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i, block := range blocks {
|
||||
for j, line := range block {
|
||||
w := maxWidth - ansi.StringWidth(line)
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Left:
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", w))
|
||||
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", w))
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
if w < 1 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(w) * pos.value()))
|
||||
right := w - split
|
||||
left := w - right
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", left))
|
||||
b.WriteString(line)
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Write a newline as long as we're not on the last line of the
|
||||
// last block.
|
||||
if !(i == len(blocks)-1 && j == len(block)-1) {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
154
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/position.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
154
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/position.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Position represents a position along a horizontal or vertical axis. It's in
|
||||
// situations where an axis is involved, like alignment, joining, placement and
|
||||
// so on.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// A value of 0 represents the start (the left or top) and 1 represents the end
|
||||
// (the right or bottom). 0.5 represents the center.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// There are constants Top, Bottom, Center, Left and Right in this package that
|
||||
// can be used to aid readability.
|
||||
type Position float64
|
||||
|
||||
func (p Position) value() float64 {
|
||||
return math.Min(1, math.Max(0, float64(p)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Position aliases.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
Top Position = 0.0
|
||||
Bottom Position = 1.0
|
||||
Center Position = 0.5
|
||||
Left Position = 0.0
|
||||
Right Position = 1.0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Place places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled box of a given
|
||||
// width or height.
|
||||
func Place(width, height int, hPos, vPos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.Place(width, height, hPos, vPos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Place places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled box of a given
|
||||
// width or height.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) Place(width, height int, hPos, vPos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return r.PlaceVertical(height, vPos, r.PlaceHorizontal(width, hPos, str, opts...), opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceHorizontal places a string or text block horizontally in an unstyled
|
||||
// block of a given width. If the given width is shorter than the max width of
|
||||
// the string (measured by its longest line) this will be a noop.
|
||||
func PlaceHorizontal(width int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.PlaceHorizontal(width, pos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceHorizontal places a string or text block horizontally in an unstyled
|
||||
// block of a given width. If the given width is shorter than the max width of
|
||||
// the string (measured by its longest line) this will be a noöp.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) PlaceHorizontal(width int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
lines, contentWidth := getLines(str)
|
||||
gap := width - contentWidth
|
||||
|
||||
if gap <= 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ws := newWhitespace(r, opts...)
|
||||
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
for i, l := range lines {
|
||||
// Is this line shorter than the longest line?
|
||||
short := max(0, contentWidth-ansi.StringWidth(l))
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Left:
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(gap + short))
|
||||
|
||||
case Right:
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(gap + short))
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // somewhere in the middle
|
||||
totalGap := gap + short
|
||||
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(totalGap) * pos.value()))
|
||||
left := totalGap - split
|
||||
right := totalGap - left
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(left))
|
||||
b.WriteString(l)
|
||||
b.WriteString(ws.render(right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if i < len(lines)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceVertical places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled block
|
||||
// of a given height. If the given height is shorter than the height of the
|
||||
// string (measured by its newlines) then this will be a noop.
|
||||
func PlaceVertical(height int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
return renderer.PlaceVertical(height, pos, str, opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PlaceVertical places a string or text block vertically in an unstyled block
|
||||
// of a given height. If the given height is shorter than the height of the
|
||||
// string (measured by its newlines) then this will be a noöp.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) PlaceVertical(height int, pos Position, str string, opts ...WhitespaceOption) string {
|
||||
contentHeight := strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
gap := height - contentHeight
|
||||
|
||||
if gap <= 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
ws := newWhitespace(r, opts...)
|
||||
|
||||
_, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
emptyLine := ws.render(width)
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
|
||||
switch pos { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case Top:
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
for i := 0; i < gap; i++ {
|
||||
b.WriteString(emptyLine)
|
||||
if i < gap-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case Bottom:
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(emptyLine+"\n", gap))
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
|
||||
default: // Somewhere in the middle
|
||||
split := int(math.Round(float64(gap) * pos.value()))
|
||||
top := gap - split
|
||||
bottom := gap - top
|
||||
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(emptyLine+"\n", top))
|
||||
b.WriteString(str)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < bottom; i++ {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
b.WriteString(emptyLine)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
181
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
181
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/renderer.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// We're manually creating the struct here to avoid initializing the output and
|
||||
// query the terminal multiple times.
|
||||
var renderer = &Renderer{
|
||||
output: termenv.DefaultOutput(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Renderer is a lipgloss terminal renderer.
|
||||
type Renderer struct {
|
||||
output *termenv.Output
|
||||
colorProfile termenv.Profile
|
||||
hasDarkBackground bool
|
||||
|
||||
getColorProfile sync.Once
|
||||
explicitColorProfile bool
|
||||
|
||||
getBackgroundColor sync.Once
|
||||
explicitBackgroundColor bool
|
||||
|
||||
mtx sync.RWMutex
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultRenderer returns the default renderer.
|
||||
func DefaultRenderer() *Renderer {
|
||||
return renderer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDefaultRenderer sets the default global renderer.
|
||||
func SetDefaultRenderer(r *Renderer) {
|
||||
renderer = r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewRenderer creates a new Renderer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// w will be used to determine the terminal's color capabilities.
|
||||
func NewRenderer(w io.Writer, opts ...termenv.OutputOption) *Renderer {
|
||||
r := &Renderer{
|
||||
output: termenv.NewOutput(w, opts...),
|
||||
}
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Output returns the termenv output.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) Output() *termenv.Output {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
return r.output
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetOutput sets the termenv output.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetOutput(o *termenv.Output) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
r.output = o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorProfile returns the detected termenv color profile.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) ColorProfile() termenv.Profile {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !r.explicitColorProfile {
|
||||
r.getColorProfile.Do(func() {
|
||||
// NOTE: we don't need to lock here because sync.Once provides its
|
||||
// own locking mechanism.
|
||||
r.colorProfile = r.output.EnvColorProfile()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r.colorProfile
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorProfile returns the detected termenv color profile.
|
||||
func ColorProfile() termenv.Profile {
|
||||
return renderer.ColorProfile()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile sets the color profile on the renderer. This function exists
|
||||
// mostly for testing purposes so that you can assure you're testing against
|
||||
// a specific profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the color
|
||||
// profile will detect and cache the terminal's color capabilities and choose
|
||||
// the best available profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Available color profiles are:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// termenv.Ascii // no color, 1-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI //16 colors, 4-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI256 // 256 colors, 8-bit
|
||||
// termenv.TrueColor // 16,777,216 colors, 24-bit
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetColorProfile(p termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.colorProfile = p
|
||||
r.explicitColorProfile = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile sets the color profile on the default renderer. This
|
||||
// function exists mostly for testing purposes so that you can assure you're
|
||||
// testing against a specific profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the color
|
||||
// profile will detect and cache the terminal's color capabilities and choose
|
||||
// the best available profile.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Available color profiles are:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// termenv.Ascii // no color, 1-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI //16 colors, 4-bit
|
||||
// termenv.ANSI256 // 256 colors, 8-bit
|
||||
// termenv.TrueColor // 16,777,216 colors, 24-bit
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func SetColorProfile(p termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
renderer.SetColorProfile(p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasDarkBackground returns whether or not the terminal has a dark background.
|
||||
func HasDarkBackground() bool {
|
||||
return renderer.HasDarkBackground()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasDarkBackground returns whether or not the renderer will render to a dark
|
||||
// background. A dark background can either be auto-detected, or set explicitly
|
||||
// on the renderer.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) HasDarkBackground() bool {
|
||||
r.mtx.RLock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.RUnlock()
|
||||
|
||||
if !r.explicitBackgroundColor {
|
||||
r.getBackgroundColor.Do(func() {
|
||||
// NOTE: we don't need to lock here because sync.Once provides its
|
||||
// own locking mechanism.
|
||||
r.hasDarkBackground = r.output.HasDarkBackground()
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r.hasDarkBackground
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHasDarkBackground sets the background color detection value for the
|
||||
// default renderer. This function exists mostly for testing purposes so that
|
||||
// you can assure you're testing against a specific background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the
|
||||
// backgrounds value will be automatically detected and cached against the
|
||||
// terminal's current background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func SetHasDarkBackground(b bool) {
|
||||
renderer.SetHasDarkBackground(b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHasDarkBackground sets the background color detection value on the
|
||||
// renderer. This function exists mostly for testing purposes so that you can
|
||||
// assure you're testing against a specific background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Outside of testing you likely won't want to use this function as the
|
||||
// backgrounds value will be automatically detected and cached against the
|
||||
// terminal's current background color setting.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This function is thread-safe.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) SetHasDarkBackground(b bool) {
|
||||
r.mtx.Lock()
|
||||
defer r.mtx.Unlock()
|
||||
|
||||
r.hasDarkBackground = b
|
||||
r.explicitBackgroundColor = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
43
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/runes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
43
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/runes.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// StyleRunes apply a given style to runes at the given indices in the string.
|
||||
// Note that you must provide styling options for both matched and unmatched
|
||||
// runes. Indices out of bounds will be ignored.
|
||||
func StyleRunes(str string, indices []int, matched, unmatched Style) string {
|
||||
// Convert slice of indices to a map for easier lookups
|
||||
m := make(map[int]struct{})
|
||||
for _, i := range indices {
|
||||
m[i] = struct{}{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
out strings.Builder
|
||||
group strings.Builder
|
||||
style Style
|
||||
runes = []rune(str)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for i, r := range runes {
|
||||
group.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
|
||||
_, matches := m[i]
|
||||
_, nextMatches := m[i+1]
|
||||
|
||||
if matches != nextMatches || i == len(runes)-1 {
|
||||
// Flush
|
||||
if matches {
|
||||
style = matched
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
style = unmatched
|
||||
}
|
||||
out.WriteString(style.Render(group.String()))
|
||||
group.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return out.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
799
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/set.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
799
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/set.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,799 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// Set a value on the underlying rules map.
|
||||
func (s *Style) set(key propKey, value interface{}) {
|
||||
// We don't allow negative integers on any of our other values, so just keep
|
||||
// them at zero or above. We could use uints instead, but the
|
||||
// conversions are a little tedious, so we're sticking with ints for
|
||||
// sake of usability.
|
||||
switch key { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
s.fgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
s.bgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
s.width = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
s.height = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
s.alignHorizontal = value.(Position)
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
s.alignVertical = value.(Position)
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
s.paddingTop = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
s.paddingRight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
s.paddingBottom = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
s.paddingLeft = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
s.marginTop = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
s.marginRight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
s.marginBottom = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
s.marginLeft = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.marginBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderStyleKey:
|
||||
s.borderStyle = value.(Border)
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderTopFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderRightFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderBottomFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderLeftFgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderTopBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderRightBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderBottomBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.borderLeftBgColor = colorOrNil(value)
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
s.maxWidth = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
s.maxHeight = max(0, value.(int))
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
// TabWidth is the only property that may have a negative value (and
|
||||
// that negative value can be no less than -1).
|
||||
s.tabWidth = value.(int)
|
||||
case transformKey:
|
||||
s.transform = value.(func(string) string)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if v, ok := value.(bool); ok { //nolint:nestif
|
||||
if v {
|
||||
s.attrs |= int(key)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.attrs &^= int(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if attrs, ok := value.(int); ok {
|
||||
// bool attrs
|
||||
if attrs&int(key) != 0 {
|
||||
s.attrs |= int(key)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s.attrs &^= int(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set the prop on
|
||||
s.props = s.props.set(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// setFrom sets the property from another style.
|
||||
func (s *Style) setFrom(key propKey, i Style) {
|
||||
switch key { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case foregroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(foregroundKey, i.fgColor)
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(backgroundKey, i.bgColor)
|
||||
case widthKey:
|
||||
s.set(widthKey, i.width)
|
||||
case heightKey:
|
||||
s.set(heightKey, i.height)
|
||||
case alignHorizontalKey:
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, i.alignHorizontal)
|
||||
case alignVerticalKey:
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, i.alignVertical)
|
||||
case paddingTopKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, i.paddingTop)
|
||||
case paddingRightKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, i.paddingRight)
|
||||
case paddingBottomKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, i.paddingBottom)
|
||||
case paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, i.paddingLeft)
|
||||
case marginTopKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, i.marginTop)
|
||||
case marginRightKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, i.marginRight)
|
||||
case marginBottomKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, i.marginBottom)
|
||||
case marginLeftKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, i.marginLeft)
|
||||
case marginBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, i.marginBgColor)
|
||||
case borderStyleKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, i.borderStyle)
|
||||
case borderTopForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, i.borderTopFgColor)
|
||||
case borderRightForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, i.borderRightFgColor)
|
||||
case borderBottomForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, i.borderBottomFgColor)
|
||||
case borderLeftForegroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, i.borderLeftFgColor)
|
||||
case borderTopBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, i.borderTopBgColor)
|
||||
case borderRightBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, i.borderRightBgColor)
|
||||
case borderBottomBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, i.borderBottomBgColor)
|
||||
case borderLeftBackgroundKey:
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, i.borderLeftBgColor)
|
||||
case maxWidthKey:
|
||||
s.set(maxWidthKey, i.maxWidth)
|
||||
case maxHeightKey:
|
||||
s.set(maxHeightKey, i.maxHeight)
|
||||
case tabWidthKey:
|
||||
s.set(tabWidthKey, i.tabWidth)
|
||||
case transformKey:
|
||||
s.set(transformKey, i.transform)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
// Set attributes for set bool properties
|
||||
s.set(key, i.attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func colorOrNil(c interface{}) TerminalColor {
|
||||
if c, ok := c.(TerminalColor); ok {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bold sets a bold formatting rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) Bold(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(boldKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Italic sets an italic formatting rule. In some terminal emulators this will
|
||||
// render with "reverse" coloring if not italic font variant is available.
|
||||
func (s Style) Italic(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(italicKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Underline sets an underline rule. By default, underlines will not be drawn on
|
||||
// whitespace like margins and padding. To change this behavior set
|
||||
// UnderlineSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) Underline(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(underlineKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Strikethrough sets a strikethrough rule. By default, strikes will not be
|
||||
// drawn on whitespace like margins and padding. To change this behavior set
|
||||
// StrikethroughSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) Strikethrough(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(strikethroughKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse sets a rule for inverting foreground and background colors.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reverse(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(reverseKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Blink sets a rule for blinking foreground text.
|
||||
func (s Style) Blink(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(blinkKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Faint sets a rule for rendering the foreground color in a dimmer shade.
|
||||
func (s Style) Faint(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(faintKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Foreground sets a foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Sets the foreground to blue
|
||||
// s := lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("#0000ff"))
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Removes the foreground color
|
||||
// s.Foreground(lipgloss.NoColor)
|
||||
func (s Style) Foreground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(foregroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Background sets a background color.
|
||||
func (s Style) Background(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(backgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Width sets the width of the block before applying margins. The width, if
|
||||
// set, also determines where text will wrap.
|
||||
func (s Style) Width(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(widthKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height sets the height of the block before applying margins. If the height of
|
||||
// the text block is less than this value after applying padding (or not), the
|
||||
// block will be set to this height.
|
||||
func (s Style) Height(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(heightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Align is a shorthand method for setting horizontal and vertical alignment.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the position value is applied to the horizontal alignment.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the horizontal and vertical
|
||||
// alignments, in that order.
|
||||
func (s Style) Align(p ...Position) Style {
|
||||
if len(p) > 0 {
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, p[0])
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(p) > 1 {
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, p[1])
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AlignHorizontal sets a horizontal text alignment rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) AlignHorizontal(p Position) Style {
|
||||
s.set(alignHorizontalKey, p)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AlignVertical sets a vertical text alignment rule.
|
||||
func (s Style) AlignVertical(p Position) Style {
|
||||
s.set(alignVerticalKey, p)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding is a shorthand method for setting padding on all sides at once.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the value is applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the value is applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments no padding will be added.
|
||||
func (s Style) Padding(i ...int) Style {
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesInt(i...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, left)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingLeft adds padding on the left.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingLeft(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingLeftKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingRight adds padding on the right.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingRight(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingRightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingTop adds padding to the top of the block.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingTop(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingTopKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PaddingBottom adds padding to the bottom of the block.
|
||||
func (s Style) PaddingBottom(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(paddingBottomKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ColorWhitespace determines whether or not the background color should be
|
||||
// applied to the padding. This is true by default as it's more than likely the
|
||||
// desired and expected behavior, but it can be disabled for certain graphic
|
||||
// effects.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: Just use margins and padding.
|
||||
func (s Style) ColorWhitespace(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(colorWhitespaceKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Margin is a shorthand method for setting margins on all sides at once.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the value is applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the value is applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the value is applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments no margin will be added.
|
||||
func (s Style) Margin(i ...int) Style {
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesInt(i...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, left)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginLeft sets the value of the left margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginLeft(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginLeftKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginRight sets the value of the right margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginRight(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginRightKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginTop sets the value of the top margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginTop(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginTopKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginBottom sets the value of the bottom margin.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginBottom(i int) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginBottomKey, i)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MarginBackground sets the background color of the margin. Note that this is
|
||||
// also set when inheriting from a style with a background color. In that case
|
||||
// the background color on that style will set the margin color on this style.
|
||||
func (s Style) MarginBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Border is shorthand for setting the border style and which sides should
|
||||
// have a border at once. The variadic argument sides works as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one value, the value is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two values, the values are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three values, the values are applied to the top side, the horizontal
|
||||
// sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four values, the values are applied clockwise starting from the top
|
||||
// side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments the border will be applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Examples:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Applies borders to the top and bottom only
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().Border(lipgloss.NormalBorder(), true, false)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// // Applies rounded borders to the right and bottom only
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().Border(lipgloss.RoundedBorder(), false, true, true, false)
|
||||
func (s Style) Border(b Border, sides ...bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, b)
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesBool(sides...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
top = true
|
||||
right = true
|
||||
bottom = true
|
||||
left = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderStyle defines the Border on a style. A Border contains a series of
|
||||
// definitions for the sides and corners of a border.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that if border visibility has not been set for any sides when setting
|
||||
// the border style, the border will be enabled for all sides during rendering.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// You can define border characters as you'd like, though several default
|
||||
// styles are included: NormalBorder(), RoundedBorder(), BlockBorder(),
|
||||
// OuterHalfBlockBorder(), InnerHalfBlockBorder(), ThickBorder(),
|
||||
// and DoubleBorder().
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// lipgloss.NewStyle().BorderStyle(lipgloss.ThickBorder())
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderStyle(b Border) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderStyleKey, b)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTop determines whether or not to draw a top border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTop(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRight determines whether or not to draw a right border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRight(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottom determines whether or not to draw a bottom border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottom(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeft determines whether or not to draw a left border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeft(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderForeground is a shorthand function for setting all of the
|
||||
// foreground colors of the borders at once. The arguments work as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the argument is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the arguments are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the arguments are applied to the top side, the
|
||||
// horizontal sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the arguments are applied clockwise starting from the
|
||||
// top side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments nothing will be set.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderForeground(c ...TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
if len(c) == 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesColor(c...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTopForeground set the foreground color for the top of the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTopForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRightForeground sets the foreground color for the right side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRightForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottomForeground sets the foreground color for the bottom of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottomForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeftForeground sets the foreground color for the left side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeftForeground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftForegroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBackground is a shorthand function for setting all of the
|
||||
// background colors of the borders at once. The arguments work as follows:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With one argument, the argument is applied to all sides.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With two arguments, the arguments are applied to the vertical and horizontal
|
||||
// sides, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With three arguments, the arguments are applied to the top side, the
|
||||
// horizontal sides, and the bottom side, in that order.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With four arguments, the arguments are applied clockwise starting from the
|
||||
// top side, followed by the right side, then the bottom, and finally the left.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// With more than four arguments nothing will be set.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBackground(c ...TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
if len(c) == 0 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
top, right, bottom, left, ok := whichSidesColor(c...)
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, top)
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, right)
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, bottom)
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, left)
|
||||
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTopBackground sets the background color of the top of the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderTopBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderTopBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRightBackground sets the background color of right side the border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderRightBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderRightBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottomBackground sets the background color of the bottom of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderBottomBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderBottomBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeftBackground set the background color of the left side of the
|
||||
// border.
|
||||
func (s Style) BorderLeftBackground(c TerminalColor) Style {
|
||||
s.set(borderLeftBackgroundKey, c)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Inline makes rendering output one line and disables the rendering of
|
||||
// margins, padding and borders. This is useful when you need a style to apply
|
||||
// only to font rendering and don't want it to change any physical dimensions.
|
||||
// It works well with Style.MaxWidth.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead return a copy.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var userInput string = "..."
|
||||
// var userStyle = text.Style{ /* ... */ }
|
||||
// fmt.Println(userStyle.Inline(true).Render(userInput))
|
||||
func (s Style) Inline(v bool) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(inlineKey, v)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxWidth applies a max width to a given style. This is useful in enforcing
|
||||
// a certain width at render time, particularly with arbitrary strings and
|
||||
// styles.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead return a copy.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// var userInput string = "..."
|
||||
// var userStyle = text.Style{ /* ... */ }
|
||||
// fmt.Println(userStyle.MaxWidth(16).Render(userInput))
|
||||
func (s Style) MaxWidth(n int) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(maxWidthKey, n)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MaxHeight applies a max height to a given style. This is useful in enforcing
|
||||
// a certain height at render time, particularly with arbitrary strings and
|
||||
// styles.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Because this in intended to be used at the time of render, this method will
|
||||
// not mutate the style and instead returns a copy.
|
||||
func (s Style) MaxHeight(n int) Style {
|
||||
o := s // copy
|
||||
o.set(maxHeightKey, n)
|
||||
return o
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoTabConversion can be passed to [Style.TabWidth] to disable the replacement
|
||||
// of tabs with spaces at render time.
|
||||
const NoTabConversion = -1
|
||||
|
||||
// TabWidth sets the number of spaces that a tab (/t) should be rendered as.
|
||||
// When set to 0, tabs will be removed. To disable the replacement of tabs with
|
||||
// spaces entirely, set this to [NoTabConversion].
|
||||
//
|
||||
// By default, tabs will be replaced with 4 spaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) TabWidth(n int) Style {
|
||||
if n <= -1 {
|
||||
n = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.set(tabWidthKey, n)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineSpaces determines whether to underline spaces between words. By
|
||||
// default, this is true. Spaces can also be underlined without underlining the
|
||||
// text itself.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineSpaces(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(underlineSpacesKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StrikethroughSpaces determines whether to apply strikethroughs to spaces
|
||||
// between words. By default, this is true. Spaces can also be struck without
|
||||
// underlining the text itself.
|
||||
func (s Style) StrikethroughSpaces(v bool) Style {
|
||||
s.set(strikethroughSpacesKey, v)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transform applies a given function to a string at render time, allowing for
|
||||
// the string being rendered to be manipuated.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// s := NewStyle().Transform(strings.ToUpper)
|
||||
// fmt.Println(s.Render("raow!") // "RAOW!"
|
||||
func (s Style) Transform(fn func(string) string) Style {
|
||||
s.set(transformKey, fn)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Renderer sets the renderer for the style. This is useful for changing the
|
||||
// renderer for a style that is being used in a different context.
|
||||
func (s Style) Renderer(r *Renderer) Style {
|
||||
s.r = r
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesInt is a helper method for setting values on sides of a block based
|
||||
// on the number of arguments. It follows the CSS shorthand rules for blocks
|
||||
// like margin, padding. and borders. Here are how the rules work:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0 args: do nothing
|
||||
// 1 arg: all sides
|
||||
// 2 args: top -> bottom
|
||||
// 3 args: top -> horizontal -> bottom
|
||||
// 4 args: top -> right -> bottom -> left
|
||||
// 5+ args: do nothing.
|
||||
func whichSidesInt(i ...int) (top, right, bottom, left int, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesBool is like whichSidesInt, except it operates on a series of
|
||||
// boolean values. See the comment on whichSidesInt for details on how this
|
||||
// works.
|
||||
func whichSidesBool(i ...bool) (top, right, bottom, left bool, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// whichSidesColor is like whichSides, except it operates on a series of
|
||||
// boolean values. See the comment on whichSidesInt for details on how this
|
||||
// works.
|
||||
func whichSidesColor(i ...TerminalColor) (top, right, bottom, left TerminalColor, ok bool) {
|
||||
switch len(i) {
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[0]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 2: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
bottom = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 3: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
left = i[1]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
case 4: //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
top = i[0]
|
||||
right = i[1]
|
||||
bottom = i[2]
|
||||
left = i[3]
|
||||
ok = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
return top, right, bottom, left, ok
|
||||
}
|
||||
41
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/size.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
41
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/size.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Width returns the cell width of characters in the string. ANSI sequences are
|
||||
// ignored and characters wider than one cell (such as Chinese characters and
|
||||
// emojis) are appropriately measured.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// You should use this instead of len(string) len([]rune(string) as neither
|
||||
// will give you accurate results.
|
||||
func Width(str string) (width int) {
|
||||
for _, l := range strings.Split(str, "\n") {
|
||||
w := ansi.StringWidth(l)
|
||||
if w > width {
|
||||
width = w
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height returns height of a string in cells. This is done simply by
|
||||
// counting \n characters. If your strings use \r\n for newlines you should
|
||||
// convert them to \n first, or simply write a separate function for measuring
|
||||
// height.
|
||||
func Height(str string) int {
|
||||
return strings.Count(str, "\n") + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Size returns the width and height of the string in cells. ANSI sequences are
|
||||
// ignored and characters wider than one cell (such as Chinese characters and
|
||||
// emojis) are appropriately measured.
|
||||
func Size(str string) (width, height int) {
|
||||
width = Width(str)
|
||||
height = Height(str)
|
||||
return width, height
|
||||
}
|
||||
587
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
587
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,587 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const tabWidthDefault = 4
|
||||
|
||||
// Property for a key.
|
||||
type propKey int64
|
||||
|
||||
// Available properties.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Boolean props come first.
|
||||
boldKey propKey = 1 << iota
|
||||
italicKey
|
||||
underlineKey
|
||||
strikethroughKey
|
||||
reverseKey
|
||||
blinkKey
|
||||
faintKey
|
||||
underlineSpacesKey
|
||||
strikethroughSpacesKey
|
||||
colorWhitespaceKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Non-boolean props.
|
||||
foregroundKey
|
||||
backgroundKey
|
||||
widthKey
|
||||
heightKey
|
||||
alignHorizontalKey
|
||||
alignVerticalKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding.
|
||||
paddingTopKey
|
||||
paddingRightKey
|
||||
paddingBottomKey
|
||||
paddingLeftKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Margins.
|
||||
marginTopKey
|
||||
marginRightKey
|
||||
marginBottomKey
|
||||
marginLeftKey
|
||||
marginBackgroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border runes.
|
||||
borderStyleKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border edges.
|
||||
borderTopKey
|
||||
borderRightKey
|
||||
borderBottomKey
|
||||
borderLeftKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border foreground colors.
|
||||
borderTopForegroundKey
|
||||
borderRightForegroundKey
|
||||
borderBottomForegroundKey
|
||||
borderLeftForegroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
// Border background colors.
|
||||
borderTopBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderRightBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderBottomBackgroundKey
|
||||
borderLeftBackgroundKey
|
||||
|
||||
inlineKey
|
||||
maxWidthKey
|
||||
maxHeightKey
|
||||
tabWidthKey
|
||||
|
||||
transformKey
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// props is a set of properties.
|
||||
type props int64
|
||||
|
||||
// set sets a property.
|
||||
func (p props) set(k propKey) props {
|
||||
return p | props(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// unset unsets a property.
|
||||
func (p props) unset(k propKey) props {
|
||||
return p &^ props(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// has checks if a property is set.
|
||||
func (p props) has(k propKey) bool {
|
||||
return p&props(k) != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewStyle returns a new, empty Style. While it's syntactic sugar for the
|
||||
// Style{} primitive, it's recommended to use this function for creating styles
|
||||
// in case the underlying implementation changes. It takes an optional string
|
||||
// value to be set as the underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func NewStyle() Style {
|
||||
return renderer.NewStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewStyle returns a new, empty Style. While it's syntactic sugar for the
|
||||
// Style{} primitive, it's recommended to use this function for creating styles
|
||||
// in case the underlying implementation changes. It takes an optional string
|
||||
// value to be set as the underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func (r *Renderer) NewStyle() Style {
|
||||
s := Style{r: r}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Style contains a set of rules that comprise a style as a whole.
|
||||
type Style struct {
|
||||
r *Renderer
|
||||
props props
|
||||
value string
|
||||
|
||||
// we store bool props values here
|
||||
attrs int
|
||||
|
||||
// props that have values
|
||||
fgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
bgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
|
||||
alignHorizontal Position
|
||||
alignVertical Position
|
||||
|
||||
paddingTop int
|
||||
paddingRight int
|
||||
paddingBottom int
|
||||
paddingLeft int
|
||||
|
||||
marginTop int
|
||||
marginRight int
|
||||
marginBottom int
|
||||
marginLeft int
|
||||
marginBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
borderStyle Border
|
||||
borderTopFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderRightFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderBottomFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderLeftFgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderTopBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderRightBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderBottomBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
borderLeftBgColor TerminalColor
|
||||
|
||||
maxWidth int
|
||||
maxHeight int
|
||||
tabWidth int
|
||||
|
||||
transform func(string) string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// joinString joins a list of strings into a single string separated with a
|
||||
// space.
|
||||
func joinString(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
return strings.Join(strs, " ")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetString sets the underlying string value for this style. To render once
|
||||
// the underlying string is set, use the Style.String. This method is
|
||||
// a convenience for cases when having a stringer implementation is handy, such
|
||||
// as when using fmt.Sprintf. You can also simply define a style and render out
|
||||
// strings directly with Style.Render.
|
||||
func (s Style) SetString(strs ...string) Style {
|
||||
s.value = joinString(strs...)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Value returns the raw, unformatted, underlying string value for this style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Value() string {
|
||||
return s.value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements stringer for a Style, returning the rendered result based
|
||||
// on the rules in this style. An underlying string value must be set with
|
||||
// Style.SetString prior to using this method.
|
||||
func (s Style) String() string {
|
||||
return s.Render()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Copy returns a copy of this style, including any underlying string values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: to copy just use assignment (i.e. a := b). All methods also
|
||||
// return a new style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Copy() Style {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Inherit overlays the style in the argument onto this style by copying each explicitly
|
||||
// set value from the argument style onto this style if it is not already explicitly set.
|
||||
// Existing set values are kept intact and not overwritten.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Margins, padding, and underlying string values are not inherited.
|
||||
func (s Style) Inherit(i Style) Style {
|
||||
for k := boldKey; k <= transformKey; k <<= 1 {
|
||||
if !i.isSet(k) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch k { //nolint:exhaustive
|
||||
case marginTopKey, marginRightKey, marginBottomKey, marginLeftKey:
|
||||
// Margins are not inherited
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case paddingTopKey, paddingRightKey, paddingBottomKey, paddingLeftKey:
|
||||
// Padding is not inherited
|
||||
continue
|
||||
case backgroundKey:
|
||||
// The margins also inherit the background color
|
||||
if !s.isSet(marginBackgroundKey) && !i.isSet(marginBackgroundKey) {
|
||||
s.set(marginBackgroundKey, i.bgColor)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s.isSet(k) {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.setFrom(k, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render applies the defined style formatting to a given string.
|
||||
func (s Style) Render(strs ...string) string {
|
||||
if s.r == nil {
|
||||
s.r = renderer
|
||||
}
|
||||
if s.value != "" {
|
||||
strs = append([]string{s.value}, strs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
str = joinString(strs...)
|
||||
|
||||
p = s.r.ColorProfile()
|
||||
te = p.String()
|
||||
teSpace = p.String()
|
||||
teWhitespace = p.String()
|
||||
|
||||
bold = s.getAsBool(boldKey, false)
|
||||
italic = s.getAsBool(italicKey, false)
|
||||
underline = s.getAsBool(underlineKey, false)
|
||||
strikethrough = s.getAsBool(strikethroughKey, false)
|
||||
reverse = s.getAsBool(reverseKey, false)
|
||||
blink = s.getAsBool(blinkKey, false)
|
||||
faint = s.getAsBool(faintKey, false)
|
||||
|
||||
fg = s.getAsColor(foregroundKey)
|
||||
bg = s.getAsColor(backgroundKey)
|
||||
|
||||
width = s.getAsInt(widthKey)
|
||||
height = s.getAsInt(heightKey)
|
||||
horizontalAlign = s.getAsPosition(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
verticalAlign = s.getAsPosition(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
|
||||
topPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
rightPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
bottomPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
leftPadding = s.getAsInt(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
colorWhitespace = s.getAsBool(colorWhitespaceKey, true)
|
||||
inline = s.getAsBool(inlineKey, false)
|
||||
maxWidth = s.getAsInt(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
maxHeight = s.getAsInt(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
|
||||
underlineSpaces = s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, false) || (underline && s.getAsBool(underlineSpacesKey, true))
|
||||
strikethroughSpaces = s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, false) || (strikethrough && s.getAsBool(strikethroughSpacesKey, true))
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we need to style whitespace (padding and space outside
|
||||
// paragraphs) separately?
|
||||
styleWhitespace = reverse
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we need to style spaces separately?
|
||||
useSpaceStyler = (underline && !underlineSpaces) || (strikethrough && !strikethroughSpaces) || underlineSpaces || strikethroughSpaces
|
||||
|
||||
transform = s.getAsTransform(transformKey)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if transform != nil {
|
||||
str = transform(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if s.props == 0 {
|
||||
return s.maybeConvertTabs(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable support for ANSI on the legacy Windows cmd.exe console. This is a
|
||||
// no-op on non-Windows systems and on Windows runs only once.
|
||||
enableLegacyWindowsANSI()
|
||||
|
||||
if bold {
|
||||
te = te.Bold()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if italic {
|
||||
te = te.Italic()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if underline {
|
||||
te = te.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
if reverse {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
te = te.Reverse()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if blink {
|
||||
te = te.Blink()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if faint {
|
||||
te = te.Faint()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if fg != noColor {
|
||||
te = te.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
if styleWhitespace {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Foreground(fg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bg != noColor {
|
||||
te = te.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
if colorWhitespace {
|
||||
teWhitespace = teWhitespace.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Background(bg.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if underline {
|
||||
te = te.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strikethrough {
|
||||
te = te.CrossOut()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if underlineSpaces {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.Underline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if strikethroughSpaces {
|
||||
teSpace = teSpace.CrossOut()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Potentially convert tabs to spaces
|
||||
str = s.maybeConvertTabs(str)
|
||||
|
||||
// Strip newlines in single line mode
|
||||
if inline {
|
||||
str = strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\n", "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Word wrap
|
||||
if !inline && width > 0 {
|
||||
wrapAt := width - leftPadding - rightPadding
|
||||
str = ansi.Wrap(str, wrapAt, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render core text
|
||||
{
|
||||
var b strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
l := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
for i := range l {
|
||||
if useSpaceStyler {
|
||||
// Look for spaces and apply a different styler
|
||||
for _, r := range l[i] {
|
||||
if unicode.IsSpace(r) {
|
||||
b.WriteString(teSpace.Styled(string(r)))
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString(te.Styled(string(r)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteString(te.Styled(l[i]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i != len(l)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
str = b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Padding
|
||||
if !inline { //nolint:nestif
|
||||
if leftPadding > 0 {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = padLeft(str, leftPadding, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if rightPadding > 0 {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = padRight(str, rightPadding, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if topPadding > 0 {
|
||||
str = strings.Repeat("\n", topPadding) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if bottomPadding > 0 {
|
||||
str += strings.Repeat("\n", bottomPadding)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height
|
||||
if height > 0 {
|
||||
str = alignTextVertical(str, verticalAlign, height, nil)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Set alignment. This will also pad short lines with spaces so that all
|
||||
// lines are the same length, so we run it under a few different conditions
|
||||
// beyond alignment.
|
||||
{
|
||||
numLines := strings.Count(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
if !(numLines == 0 && width == 0) {
|
||||
var st *termenv.Style
|
||||
if colorWhitespace || styleWhitespace {
|
||||
st = &teWhitespace
|
||||
}
|
||||
str = alignTextHorizontal(str, horizontalAlign, width, st)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if !inline {
|
||||
str = s.applyBorder(str)
|
||||
str = s.applyMargins(str, inline)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate according to MaxWidth
|
||||
if maxWidth > 0 {
|
||||
lines := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range lines {
|
||||
lines[i] = ansi.Truncate(lines[i], maxWidth, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
str = strings.Join(lines, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate according to MaxHeight
|
||||
if maxHeight > 0 {
|
||||
lines := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
height := min(maxHeight, len(lines))
|
||||
if len(lines) > 0 {
|
||||
str = strings.Join(lines[:height], "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) maybeConvertTabs(str string) string {
|
||||
tw := tabWidthDefault
|
||||
if s.isSet(tabWidthKey) {
|
||||
tw = s.getAsInt(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch tw {
|
||||
case -1:
|
||||
return str
|
||||
case 0:
|
||||
return strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\t", "")
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return strings.ReplaceAll(str, "\t", strings.Repeat(" ", tw))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s Style) applyMargins(str string, inline bool) string {
|
||||
var (
|
||||
topMargin = s.getAsInt(marginTopKey)
|
||||
rightMargin = s.getAsInt(marginRightKey)
|
||||
bottomMargin = s.getAsInt(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
leftMargin = s.getAsInt(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
|
||||
styler termenv.Style
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
bgc := s.getAsColor(marginBackgroundKey)
|
||||
if bgc != noColor {
|
||||
styler = styler.Background(bgc.color(s.r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add left and right margin
|
||||
str = padLeft(str, leftMargin, &styler)
|
||||
str = padRight(str, rightMargin, &styler)
|
||||
|
||||
// Top/bottom margin
|
||||
if !inline {
|
||||
_, width := getLines(str)
|
||||
spaces := strings.Repeat(" ", width)
|
||||
|
||||
if topMargin > 0 {
|
||||
str = styler.Styled(strings.Repeat(spaces+"\n", topMargin)) + str
|
||||
}
|
||||
if bottomMargin > 0 {
|
||||
str += styler.Styled(strings.Repeat("\n"+spaces, bottomMargin))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply left padding.
|
||||
func padLeft(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
return pad(str, -n, style)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Apply right padding.
|
||||
func padRight(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
return pad(str, n, style)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// pad adds padding to either the left or right side of a string.
|
||||
// Positive values add to the right side while negative values
|
||||
// add to the left side.
|
||||
func pad(str string, n int, style *termenv.Style) string {
|
||||
if n == 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sp := strings.Repeat(" ", abs(n))
|
||||
if style != nil {
|
||||
sp = style.Styled(sp)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
l := strings.Split(str, "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
for i := range l {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
// pad right
|
||||
case n > 0:
|
||||
b.WriteString(l[i])
|
||||
b.WriteString(sp)
|
||||
// pad left
|
||||
default:
|
||||
b.WriteString(sp)
|
||||
b.WriteString(l[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if i != len(l)-1 {
|
||||
b.WriteRune('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int { //nolint:unparam
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func abs(a int) int {
|
||||
if a < 0 {
|
||||
return -a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
113
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/rows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
113
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/rows.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
package table
|
||||
|
||||
// Data is the interface that wraps the basic methods of a table model.
|
||||
type Data interface {
|
||||
// At returns the contents of the cell at the given index.
|
||||
At(row, cell int) string
|
||||
|
||||
// Rows returns the number of rows in the table.
|
||||
Rows() int
|
||||
|
||||
// Columns returns the number of columns in the table.
|
||||
Columns() int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringData is a string-based implementation of the Data interface.
|
||||
type StringData struct {
|
||||
rows [][]string
|
||||
columns int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewStringData creates a new StringData with the given number of columns.
|
||||
func NewStringData(rows ...[]string) *StringData {
|
||||
m := StringData{columns: 0}
|
||||
|
||||
for _, row := range rows {
|
||||
m.columns = max(m.columns, len(row))
|
||||
m.rows = append(m.rows, row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return &m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Append appends the given row to the table.
|
||||
func (m *StringData) Append(row []string) {
|
||||
m.columns = max(m.columns, len(row))
|
||||
m.rows = append(m.rows, row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// At returns the contents of the cell at the given index.
|
||||
func (m *StringData) At(row, cell int) string {
|
||||
if row >= len(m.rows) || cell >= len(m.rows[row]) {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return m.rows[row][cell]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Columns returns the number of columns in the table.
|
||||
func (m *StringData) Columns() int {
|
||||
return m.columns
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Item appends the given row to the table.
|
||||
func (m *StringData) Item(rows ...string) *StringData {
|
||||
m.columns = max(m.columns, len(rows))
|
||||
m.rows = append(m.rows, rows)
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rows returns the number of rows in the table.
|
||||
func (m *StringData) Rows() int {
|
||||
return len(m.rows)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter applies a filter on some data.
|
||||
type Filter struct {
|
||||
data Data
|
||||
filter func(row int) bool
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewFilter initializes a new Filter.
|
||||
func NewFilter(data Data) *Filter {
|
||||
return &Filter{data: data}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter applies the given filter function to the data.
|
||||
func (m *Filter) Filter(f func(row int) bool) *Filter {
|
||||
m.filter = f
|
||||
return m
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// At returns the row at the given index.
|
||||
func (m *Filter) At(row, cell int) string {
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < m.data.Rows(); i++ {
|
||||
if m.filter(i) {
|
||||
if j == row {
|
||||
return m.data.At(i, cell)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
j++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Columns returns the number of columns in the table.
|
||||
func (m *Filter) Columns() int {
|
||||
return m.data.Columns()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rows returns the number of rows in the table.
|
||||
func (m *Filter) Rows() int {
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
for i := 0; i < m.data.Rows(); i++ {
|
||||
if m.filter(i) {
|
||||
j++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return j
|
||||
}
|
||||
521
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
521
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,521 @@
|
||||
package table
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// StyleFunc is the style function that determines the style of a Cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It takes the row and column of the cell as an input and determines the
|
||||
// lipgloss Style to use for that cell position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// t := table.New().
|
||||
// Headers("Name", "Age").
|
||||
// Row("Kini", 4).
|
||||
// Row("Eli", 1).
|
||||
// Row("Iris", 102).
|
||||
// StyleFunc(func(row, col int) lipgloss.Style {
|
||||
// switch {
|
||||
// case row == 0:
|
||||
// return HeaderStyle
|
||||
// case row%2 == 0:
|
||||
// return EvenRowStyle
|
||||
// default:
|
||||
// return OddRowStyle
|
||||
// }
|
||||
// })
|
||||
type StyleFunc func(row, col int) lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultStyles is a TableStyleFunc that returns a new Style with no attributes.
|
||||
func DefaultStyles(_, _ int) lipgloss.Style {
|
||||
return lipgloss.NewStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Table is a type for rendering tables.
|
||||
type Table struct {
|
||||
styleFunc StyleFunc
|
||||
border lipgloss.Border
|
||||
|
||||
borderTop bool
|
||||
borderBottom bool
|
||||
borderLeft bool
|
||||
borderRight bool
|
||||
borderHeader bool
|
||||
borderColumn bool
|
||||
borderRow bool
|
||||
|
||||
borderStyle lipgloss.Style
|
||||
headers []string
|
||||
data Data
|
||||
|
||||
width int
|
||||
height int
|
||||
offset int
|
||||
|
||||
// widths tracks the width of each column.
|
||||
widths []int
|
||||
|
||||
// heights tracks the height of each row.
|
||||
heights []int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New returns a new Table that can be modified through different
|
||||
// attributes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// By default, a table has no border, no styling, and no rows.
|
||||
func New() *Table {
|
||||
return &Table{
|
||||
styleFunc: DefaultStyles,
|
||||
border: lipgloss.RoundedBorder(),
|
||||
borderBottom: true,
|
||||
borderColumn: true,
|
||||
borderHeader: true,
|
||||
borderLeft: true,
|
||||
borderRight: true,
|
||||
borderTop: true,
|
||||
data: NewStringData(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ClearRows clears the table rows.
|
||||
func (t *Table) ClearRows() *Table {
|
||||
t.data = nil
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StyleFunc sets the style for a cell based on it's position (row, column).
|
||||
func (t *Table) StyleFunc(style StyleFunc) *Table {
|
||||
t.styleFunc = style
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// style returns the style for a cell based on it's position (row, column).
|
||||
func (t *Table) style(row, col int) lipgloss.Style {
|
||||
if t.styleFunc == nil {
|
||||
return lipgloss.NewStyle()
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t.styleFunc(row, col)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Data sets the table data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Data(data Data) *Table {
|
||||
t.data = data
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rows appends rows to the table data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Rows(rows ...[]string) *Table {
|
||||
for _, row := range rows {
|
||||
switch t.data.(type) {
|
||||
case *StringData:
|
||||
t.data.(*StringData).Append(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Row appends a row to the table data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Row(row ...string) *Table {
|
||||
switch t.data.(type) {
|
||||
case *StringData:
|
||||
t.data.(*StringData).Append(row)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Headers sets the table headers.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Headers(headers ...string) *Table {
|
||||
t.headers = headers
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Border sets the table border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Border(border lipgloss.Border) *Table {
|
||||
t.border = border
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderTop sets the top border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderTop(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderTop = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderBottom sets the bottom border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderBottom(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderBottom = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderLeft sets the left border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderLeft(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderLeft = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRight sets the right border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderRight(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderRight = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderHeader sets the header separator border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderHeader(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderHeader = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderColumn sets the column border separator.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderColumn(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderColumn = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderRow sets the row border separator.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderRow(v bool) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderRow = v
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BorderStyle sets the style for the table border.
|
||||
func (t *Table) BorderStyle(style lipgloss.Style) *Table {
|
||||
t.borderStyle = style
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Width sets the table width, this auto-sizes the columns to fit the width by
|
||||
// either expanding or contracting the widths of each column as a best effort
|
||||
// approach.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Width(w int) *Table {
|
||||
t.width = w
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Height sets the table height.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Height(h int) *Table {
|
||||
t.height = h
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Offset sets the table rendering offset.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Offset(o int) *Table {
|
||||
t.offset = o
|
||||
return t
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the table as a string.
|
||||
func (t *Table) String() string {
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
hasRows := t.data != nil && t.data.Rows() > 0
|
||||
|
||||
if !hasHeaders && !hasRows {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
// Add empty cells to the headers, until it's the same length as the longest
|
||||
// row (only if there are at headers in the first place).
|
||||
if hasHeaders {
|
||||
for i := len(t.headers); i < t.data.Columns(); i++ {
|
||||
t.headers = append(t.headers, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initialize the widths.
|
||||
t.widths = make([]int, max(len(t.headers), t.data.Columns()))
|
||||
t.heights = make([]int, btoi(hasHeaders)+t.data.Rows())
|
||||
|
||||
// The style function may affect width of the table. It's possible to set
|
||||
// the StyleFunc after the headers and rows. Update the widths for a final
|
||||
// time.
|
||||
for i, cell := range t.headers {
|
||||
t.widths[i] = max(t.widths[i], lipgloss.Width(t.style(0, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
t.heights[0] = max(t.heights[0], lipgloss.Height(t.style(0, i).Render(cell)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for r := 0; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < t.data.Columns(); i++ {
|
||||
cell := t.data.At(r, i)
|
||||
|
||||
rendered := t.style(r+1, i).Render(cell)
|
||||
t.heights[r+btoi(hasHeaders)] = max(t.heights[r+btoi(hasHeaders)], lipgloss.Height(rendered))
|
||||
t.widths[i] = max(t.widths[i], lipgloss.Width(rendered))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Table Resizing Logic.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Given a user defined table width, we must ensure the table is exactly that
|
||||
// width. This must account for all borders, column, separators, and column
|
||||
// data.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the case where the table is narrower than the specified table width,
|
||||
// we simply expand the columns evenly to fit the width.
|
||||
// For example, a table with 3 columns takes up 50 characters total, and the
|
||||
// width specified is 80, we expand each column by 10 characters, adding 30
|
||||
// to the total width.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In the case where the table is wider than the specified table width, we
|
||||
// _could_ simply shrink the columns evenly but this would result in data
|
||||
// being truncated (perhaps unnecessarily). The naive approach could result
|
||||
// in very poor cropping of the table data. So, instead of shrinking columns
|
||||
// evenly, we calculate the median non-whitespace length of each column, and
|
||||
// shrink the columns based on the largest median.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example,
|
||||
// ┌──────┬───────────────┬──────────┐
|
||||
// │ Name │ Age of Person │ Location │
|
||||
// ├──────┼───────────────┼──────────┤
|
||||
// │ Kini │ 40 │ New York │
|
||||
// │ Eli │ 30 │ London │
|
||||
// │ Iris │ 20 │ Paris │
|
||||
// └──────┴───────────────┴──────────┘
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Median non-whitespace length vs column width of each column:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Name: 4 / 5
|
||||
// Age of Person: 2 / 15
|
||||
// Location: 6 / 10
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The biggest difference is 15 - 2, so we can shrink the 2nd column by 13.
|
||||
|
||||
width := t.computeWidth()
|
||||
|
||||
if width < t.width && t.width > 0 {
|
||||
// Table is too narrow, expand the columns evenly until it reaches the
|
||||
// desired width.
|
||||
var i int
|
||||
for width < t.width {
|
||||
t.widths[i]++
|
||||
width++
|
||||
i = (i + 1) % len(t.widths)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else if width > t.width && t.width > 0 {
|
||||
// Table is too wide, calculate the median non-whitespace length of each
|
||||
// column, and shrink the columns based on the largest difference.
|
||||
columnMedians := make([]int, len(t.widths))
|
||||
for c := range t.widths {
|
||||
trimmedWidth := make([]int, t.data.Rows())
|
||||
for r := 0; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
renderedCell := t.style(r+btoi(hasHeaders), c).Render(t.data.At(r, c))
|
||||
nonWhitespaceChars := lipgloss.Width(strings.TrimRight(renderedCell, " "))
|
||||
trimmedWidth[r] = nonWhitespaceChars + 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
columnMedians[c] = median(trimmedWidth)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the biggest differences between the median and the column width.
|
||||
// Shrink the columns based on the largest difference.
|
||||
differences := make([]int, len(t.widths))
|
||||
for i := range t.widths {
|
||||
differences[i] = t.widths[i] - columnMedians[i]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for width > t.width {
|
||||
index, _ := largest(differences)
|
||||
if differences[index] < 1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
shrink := min(differences[index], width-t.width)
|
||||
t.widths[index] -= shrink
|
||||
width -= shrink
|
||||
differences[index] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Table is still too wide, begin shrinking the columns based on the
|
||||
// largest column.
|
||||
for width > t.width {
|
||||
index, _ := largest(t.widths)
|
||||
if t.widths[index] < 1 {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
t.widths[index]--
|
||||
width--
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if t.borderTop {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructTopBorder())
|
||||
s.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if hasHeaders {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructHeaders())
|
||||
s.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for r := t.offset; r < t.data.Rows(); r++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructRow(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if t.borderBottom {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.constructBottomBorder())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
MaxHeight(t.computeHeight()).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.width).Render(s.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// computeWidth computes the width of the table in it's current configuration.
|
||||
func (t *Table) computeWidth() int {
|
||||
width := sum(t.widths) + btoi(t.borderLeft) + btoi(t.borderRight)
|
||||
if t.borderColumn {
|
||||
width += len(t.widths) - 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// computeHeight computes the height of the table in it's current configuration.
|
||||
func (t *Table) computeHeight() int {
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
return sum(t.heights) - 1 + btoi(hasHeaders) +
|
||||
btoi(t.borderTop) + btoi(t.borderBottom) +
|
||||
btoi(t.borderHeader) + t.data.Rows()*btoi(t.borderRow)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render returns the table as a string.
|
||||
func (t *Table) Render() string {
|
||||
return t.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// constructTopBorder constructs the top border for the table given it's current
|
||||
// border configuration and data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructTopBorder() string {
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
if t.borderLeft {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.TopLeft))
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t.widths); i++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(strings.Repeat(t.border.Top, t.widths[i])))
|
||||
if i < len(t.widths)-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleTop))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.borderRight {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.TopRight))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// constructBottomBorder constructs the bottom border for the table given it's current
|
||||
// border configuration and data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructBottomBorder() string {
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
if t.borderLeft {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.BottomLeft))
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t.widths); i++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(strings.Repeat(t.border.Bottom, t.widths[i])))
|
||||
if i < len(t.widths)-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleBottom))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.borderRight {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.BottomRight))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// constructHeaders constructs the headers for the table given it's current
|
||||
// header configuration and data.
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructHeaders() string {
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
if t.borderLeft {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Left))
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i, header := range t.headers {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.style(0, i).
|
||||
MaxHeight(1).
|
||||
Width(t.widths[i]).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.widths[i]).
|
||||
Render(ansi.Truncate(header, t.widths[i], "…")))
|
||||
if i < len(t.headers)-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Left))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.borderHeader {
|
||||
if t.borderRight {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.WriteString("\n")
|
||||
if t.borderLeft {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleLeft))
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t.headers); i++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(strings.Repeat(t.border.Top, t.widths[i])))
|
||||
if i < len(t.headers)-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Middle))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.borderRight {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleRight))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if t.borderRight && !t.borderHeader {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Right))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// constructRow constructs the row for the table given an index and row data
|
||||
// based on the current configuration.
|
||||
func (t *Table) constructRow(index int) string {
|
||||
var s strings.Builder
|
||||
|
||||
hasHeaders := t.headers != nil && len(t.headers) > 0
|
||||
height := t.heights[index+btoi(hasHeaders)]
|
||||
|
||||
var cells []string
|
||||
left := strings.Repeat(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Left)+"\n", height)
|
||||
if t.borderLeft {
|
||||
cells = append(cells, left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for c := 0; c < t.data.Columns(); c++ {
|
||||
cell := t.data.At(index, c)
|
||||
|
||||
cells = append(cells, t.style(index+1, c).
|
||||
Height(height).
|
||||
MaxHeight(height).
|
||||
Width(t.widths[c]).
|
||||
MaxWidth(t.widths[c]).
|
||||
Render(ansi.Truncate(cell, t.widths[c]*height, "…")))
|
||||
|
||||
if c < t.data.Columns()-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
cells = append(cells, left)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if t.borderRight {
|
||||
right := strings.Repeat(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Right)+"\n", height)
|
||||
cells = append(cells, right)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i, cell := range cells {
|
||||
cells[i] = strings.TrimRight(cell, "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s.WriteString(lipgloss.JoinHorizontal(lipgloss.Top, cells...) + "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
if t.borderRow && index < t.data.Rows()-1 {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleLeft))
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t.widths); i++ {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(strings.Repeat(t.border.Bottom, t.widths[i])))
|
||||
if i < len(t.widths)-1 && t.borderColumn {
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.Middle))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.WriteString(t.borderStyle.Render(t.border.MiddleRight) + "\n")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
64
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
64
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/table/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
package table
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"sort"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// btoi converts a boolean to an integer, 1 if true, 0 if false.
|
||||
func btoi(b bool) int {
|
||||
if b {
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// max returns the greater of two integers.
|
||||
func max(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a > b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// min returns the greater of two integers.
|
||||
func min(a, b int) int {
|
||||
if a < b {
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
return b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// sum returns the sum of all integers in a slice.
|
||||
func sum(n []int) int {
|
||||
var sum int
|
||||
for _, i := range n {
|
||||
sum += i
|
||||
}
|
||||
return sum
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// median returns the median of a slice of integers.
|
||||
func median(n []int) int {
|
||||
sort.Ints(n)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(n) <= 0 {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(n)%2 == 0 {
|
||||
h := len(n) / 2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
return (n[h-1] + n[h]) / 2 //nolint:gomnd
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n[len(n)/2]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// largest returns the largest element and it's index from a slice of integers.
|
||||
func largest(n []int) (int, int) { //nolint:unparam
|
||||
var largest, index int
|
||||
for i, e := range n {
|
||||
if n[i] > n[index] {
|
||||
largest = e
|
||||
index = i
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return index, largest
|
||||
}
|
||||
331
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/unset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
331
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/unset.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,331 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
// unset unsets a property from a style.
|
||||
func (s *Style) unset(key propKey) {
|
||||
s.props = s.props.unset(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBold removes the bold style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBold() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(boldKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetItalic removes the italic style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetItalic() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(italicKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetUnderline removes the underline style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetUnderline() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(underlineKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetStrikethrough removes the strikethrough style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetStrikethrough() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(strikethroughKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetReverse removes the reverse style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetReverse() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(reverseKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBlink removes the blink style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBlink() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(blinkKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetFaint removes the faint style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetFaint() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(faintKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetForeground removes the foreground style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(foregroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBackground removes the background style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(backgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetWidth removes the width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(widthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetHeight removes the height style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetHeight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(heightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlign removes the horizontal and vertical text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlign() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
s.unset(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlignHorizontal removes the horizontal text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlignHorizontal() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignHorizontalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetAlignVertical removes the vertical text alignment style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetAlignVertical() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(alignVerticalKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPadding removes all padding style rules.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPadding() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
s.unset(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingLeft removes the left padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingRight removes the right padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingTop removes the top padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetPaddingBottom removes the bottom padding style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetPaddingBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(paddingBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetColorWhitespace removes the rule for coloring padding, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetColorWhitespace() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(colorWhitespaceKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMargins removes all margin style rules.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMargins() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginRightKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginTopKey)
|
||||
s.unset(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginLeft removes the left margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginRight removes the right margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginTop removes the top margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginBottom removes the bottom margin style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMarginBackground removes the margin's background color. Note that the
|
||||
// margin's background color can be set from the background color of another
|
||||
// style during inheritance.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMarginBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(marginBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderStyle removes the border style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderStyle() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderStyleKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTop removes the border top style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTop() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRight removes the border right style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottom removes the border bottom style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottom() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeft removes the border left style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeft() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderForeground removes all border foreground color styles, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopForeground removes the top border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRightForeground removes the right border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRightForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottomForeground removes the bottom border foreground color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottomForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeftForeground removes the left border foreground color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeftForeground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftForegroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBackground removes all border background color styles, if
|
||||
// set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopBackgroundColor removes the top border background color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Deprecated: This function simply calls Style.UnsetBorderTopBackground.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopBackgroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return s.UnsetBorderTopBackground()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderTopBackground removes the top border background color rule,
|
||||
// if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderTopBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderTopBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderRightBackground removes the right border background color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderRightBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderRightBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderBottomBackground removes the bottom border background color
|
||||
// rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderBottomBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderBottomBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetBorderLeftBackground removes the left border color rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetBorderLeftBackground() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(borderLeftBackgroundKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetInline removes the inline style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetInline() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(inlineKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMaxWidth removes the max width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMaxWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(maxWidthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetMaxHeight removes the max height style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetMaxHeight() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(maxHeightKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetTabWidth removes the tab width style rule, if set.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetTabWidth() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(tabWidthKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetUnderlineSpaces removes the value set by UnderlineSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetUnderlineSpaces() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(underlineSpacesKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetStrikethroughSpaces removes the value set by StrikethroughSpaces.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetStrikethroughSpaces() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(strikethroughSpacesKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetTransform removes the value set by Transform.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetTransform() Style {
|
||||
s.unset(transformKey)
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnsetString sets the underlying string value to the empty string.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnsetString() Style {
|
||||
s.value = ""
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/whitespace.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
83
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss/whitespace.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
package lipgloss
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// whitespace is a whitespace renderer.
|
||||
type whitespace struct {
|
||||
re *Renderer
|
||||
style termenv.Style
|
||||
chars string
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// newWhitespace creates a new whitespace renderer. The order of the options
|
||||
// matters, if you're using WithWhitespaceRenderer, make sure it comes first as
|
||||
// other options might depend on it.
|
||||
func newWhitespace(r *Renderer, opts ...WhitespaceOption) *whitespace {
|
||||
w := &whitespace{
|
||||
re: r,
|
||||
style: r.ColorProfile().String(),
|
||||
}
|
||||
for _, opt := range opts {
|
||||
opt(w)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return w
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Render whitespaces.
|
||||
func (w whitespace) render(width int) string {
|
||||
if w.chars == "" {
|
||||
w.chars = " "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r := []rune(w.chars)
|
||||
j := 0
|
||||
b := strings.Builder{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cycle through runes and print them into the whitespace.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < width; {
|
||||
b.WriteRune(r[j])
|
||||
j++
|
||||
if j >= len(r) {
|
||||
j = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += ansi.StringWidth(string(r[j]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fill any extra gaps white spaces. This might be necessary if any runes
|
||||
// are more than one cell wide, which could leave a one-rune gap.
|
||||
short := width - ansi.StringWidth(b.String())
|
||||
if short > 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strings.Repeat(" ", short))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return w.style.Styled(b.String())
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WhitespaceOption sets a styling rule for rendering whitespace.
|
||||
type WhitespaceOption func(*whitespace)
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceForeground sets the color of the characters in the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceForeground(c TerminalColor) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.style = w.style.Foreground(c.color(w.re))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceBackground sets the background color of the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceBackground(c TerminalColor) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.style = w.style.Background(c.color(w.re))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithWhitespaceChars sets the characters to be rendered in the whitespace.
|
||||
func WithWhitespaceChars(s string) WhitespaceOption {
|
||||
return func(w *whitespace) {
|
||||
w.chars = s
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.gitignore
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
*.txt
|
||||
*.gif
|
||||
|
||||
examples/batch2/batch2
|
||||
examples/chocolate-chips/chocolate-chips
|
||||
examples/cookie/cookie
|
||||
examples/error/error
|
||||
examples/format/format
|
||||
examples/log/log
|
||||
examples/new/new
|
||||
examples/options/options
|
||||
examples/oven/oven
|
||||
examples/temperature/temperature
|
||||
|
||||
.vscode
|
||||
.history
|
||||
go.work
|
||||
34
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
34
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.golangci.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
run:
|
||||
tests: false
|
||||
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- EXC0001
|
||||
- EXC0005
|
||||
- EXC0011
|
||||
- EXC0012
|
||||
- EXC0013
|
||||
|
||||
max-issues-per-linter: 0
|
||||
max-same-issues: 0
|
||||
|
||||
linters:
|
||||
enable:
|
||||
- bodyclose
|
||||
- dupl
|
||||
- exportloopref
|
||||
- goconst
|
||||
- godot
|
||||
- godox
|
||||
- goimports
|
||||
- goprintffuncname
|
||||
- gosec
|
||||
- misspell
|
||||
- nolintlint
|
||||
- prealloc
|
||||
- revive
|
||||
- rowserrcheck
|
||||
- sqlclosecheck
|
||||
- unconvert
|
||||
- unparam
|
||||
- whitespace
|
||||
3
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
3
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/.goreleaser.yml
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
includes:
|
||||
- from_url:
|
||||
url: charmbracelet/meta/main/goreleaser-lib.yaml
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2022-2023 Charmbracelet, Inc
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
367
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
367
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/README.md
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,367 @@
|
||||
# Log
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25087/219742757-c8afe0d9-608a-4845-a555-ef59c0af9ebc.png" width="359">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25087/219743408-3d7bef51-1409-40c0-8159-acc6e52f078e.png" width="359">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/25087/219742757-c8afe0d9-608a-4845-a555-ef59c0af9ebc.png" width="359" />
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/log/releases"><img src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/charmbracelet/log.svg" alt="Latest Release"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/charmbracelet/log?tab=doc"><img src="https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/gddo?status.svg" alt="Go Docs"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/charmbracelet/log/actions"><img src="https://github.com/charmbracelet/log/workflows/build/badge.svg" alt="Build Status"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/charmbracelet/log"><img alt="Codecov branch" src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/charmbracelet/log/main.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/charmbracelet/log"><img alt="Go Report Card" src="https://goreportcard.com/badge/github.com/charmbracelet/log"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
A minimal and colorful Go logging library. 🪵
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1wBImk2iSIuiiD7Ib9rufi.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1wBImk2iSIuiiD7Ib9rufi.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-2NvOYS29AauVRgRRPmquXx.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1wBImk2iSIuiiD7Ib9rufi.gif" alt="Made with VHS" />
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
It provides a leveled structured human readable logger with a small API. Unlike
|
||||
[standard `log`][stdlog], the Charm logger provides customizable colorful human
|
||||
readable logging with batteries included.
|
||||
|
||||
- Uses [Lip Gloss][lipgloss] to style and colorize the output.
|
||||
- Colorful, human readable format.
|
||||
- Ability to customize the time stamp format.
|
||||
- Skips caller frames and marks function as helpers.
|
||||
- Leveled logging.
|
||||
- Text, JSON, and Logfmt formatters.
|
||||
- Store and retrieve logger in and from context.
|
||||
- Slog handler.
|
||||
- Standard log adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Use `go get` to download the dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
go get github.com/charmbracelet/log@latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, `import` it in your Go files:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
import "github.com/charmbracelet/log"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The Charm logger comes with a global package-wise logger with timestamps turned
|
||||
on, and the logging level set to `info`.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
log.Debug("Cookie 🍪") // won't print anything
|
||||
log.Info("Hello World!")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-cKiS8OuRrF1VVVpscM9e3.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-cKiS8OuRrF1VVVpscM9e3.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4AeLaEuO3tDbECR1qe9Jvp.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4AeLaEuO3tDbECR1qe9Jvp.gif" alt="Made with VHS" />
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
All logging levels accept optional key/value pairs to be printed along with a
|
||||
message.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
err := fmt.Errorf("too much sugar")
|
||||
log.Error("failed to bake cookies", "err", err)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="600" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-65KIpGw4FTESK0IzkDB9VQ.gif" >
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="600" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-65KIpGw4FTESK0IzkDB9VQ.gif" >
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="600" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-7rk8wALXRDoFw8SLFwn9rW.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="600" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-65KIpGw4FTESK0IzkDB9VQ.gif" alt="Made with VHS">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `log.Print()` to print messages without a level prefix.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
log.Print("Baking 101")
|
||||
// 2023/01/04 10:04:06 Baking 101
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### New loggers
|
||||
|
||||
Use `New()` to create new loggers.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
logger := log.New(os.Stderr)
|
||||
if butter {
|
||||
logger.Warn("chewy!", "butter", true)
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="300" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-3QQdzOW4Zc0bN2tOhAest9.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="300" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-3QQdzOW4Zc0bN2tOhAest9.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="300" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1nrhNSuFnQkxWD4RoMlE4O.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="300" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-3QQdzOW4Zc0bN2tOhAest9.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
### Levels
|
||||
|
||||
Log offers multiple levels to filter your logs on. Available levels are:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
log.DebugLevel
|
||||
log.InfoLevel
|
||||
log.WarnLevel
|
||||
log.ErrorLevel
|
||||
log.FatalLevel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use `log.SetLevel()` to set the log level. You can also create a new logger with
|
||||
a specific log level using `log.Options{Level: }`.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the corresponding function to log a message:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
err := errors.New("Baking error 101")
|
||||
log.Debug(err)
|
||||
log.Info(err)
|
||||
log.Warn(err)
|
||||
log.Error(err)
|
||||
log.Fatal(err) // this calls os.Exit(1)
|
||||
log.Print(err) // prints regardless of log level
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or use the formatter variant:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
format := "%s %d"
|
||||
log.Debugf(format, "chocolate", 10)
|
||||
log.Warnf(format, "adding more", 5)
|
||||
log.Errorf(format, "increasing temp", 420)
|
||||
log.Fatalf(format, "too hot!", 500) // this calls os.Exit(1)
|
||||
log.Printf(format, "baking cookies") // prints regardless of log level
|
||||
|
||||
// Use these in conjunction with `With(...)` to add more context
|
||||
log.With("err", err).Errorf("unable to start %s", "oven")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Structured
|
||||
|
||||
All the functions above take a message and key-value pairs of anything. The
|
||||
message can also be of type any.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
ingredients := []string{"flour", "butter", "sugar", "chocolate"}
|
||||
log.Debug("Available ingredients", "ingredients", ingredients)
|
||||
// DEBUG Available ingredients ingredients="[flour butter sugar chocolate]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Options
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the logger with options. Use `log.NewWithOptions()` and
|
||||
`log.Options{}` to customize your new logger.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
logger := log.NewWithOptions(os.Stderr, log.Options{
|
||||
ReportCaller: true,
|
||||
ReportTimestamp: true,
|
||||
TimeFormat: time.Kitchen,
|
||||
Prefix: "Baking 🍪 ",
|
||||
})
|
||||
logger.Info("Starting oven!", "degree", 375)
|
||||
time.Sleep(10 * time.Minute)
|
||||
logger.Info("Finished baking")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6oSCJcQ5EmFKKELcskJhLo.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6oSCJcQ5EmFKKELcskJhLo.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-2X8Esd8ZsHo4DVPVgR36yx.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="700" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6oSCJcQ5EmFKKELcskJhLo.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use logger setters to customize the logger.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
logger := log.New(os.Stderr)
|
||||
logger.SetReportTimestamp(false)
|
||||
logger.SetReportCaller(false)
|
||||
logger.SetLevel(log.DebugLevel)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use `log.SetFormatter()` or `log.Options{Formatter: }` to change the output
|
||||
format. Available options are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `log.TextFormatter` (_default_)
|
||||
- `log.JSONFormatter`
|
||||
- `log.LogfmtFormatter`
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note** styling only affects the `TextFormatter`. Styling is disabled if the
|
||||
> output is not a TTY.
|
||||
|
||||
For a list of available options, refer to [options.go](./options.go).
|
||||
|
||||
### Styles
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the logger styles using [Lipgloss][lipgloss]. The styles are
|
||||
defined at a global level in [styles.go](./styles.go).
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
// Override the default error level style.
|
||||
styles := log.DefaultStyles()
|
||||
styles.Levels[log.ErrorLevel] = lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString("ERROR!!").
|
||||
Padding(0, 1, 0, 1).
|
||||
Background(lipgloss.Color("204")).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("0"))
|
||||
// Add a custom style for key `err`
|
||||
styles.Keys["err"] = lipgloss.NewStyle().Foreground(lipgloss.Color("204"))
|
||||
styles.Values["err"] = lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true)
|
||||
logger := log.New(os.Stderr)
|
||||
logger.SetStyles(styles)
|
||||
logger.Error("Whoops!", "err", "kitchen on fire")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4LXsGvzyH4RdjJaTF4a9MG.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4LXsGvzyH4RdjJaTF4a9MG.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="400" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4f6qLnIfudMMLDD9sxXUrv.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4LXsGvzyH4RdjJaTF4a9MG.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
### Sub-logger
|
||||
|
||||
Create sub-loggers with their specific fields.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
logger := log.NewWithOptions(os.Stderr, log.Options{
|
||||
Prefix: "Baking 🍪 "
|
||||
})
|
||||
batch2 := logger.With("batch", 2, "chocolateChips", true)
|
||||
batch2.Debug("Preparing batch 2...")
|
||||
batch2.Debug("Adding chocolate chips")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1JgP5ZRL0oXVspeg50CczR.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1JgP5ZRL0oXVspeg50CczR.gif">
|
||||
<img width="700" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-1JgP5ZRL0oXVspeg50CczR.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
### Format Messages
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `fmt.Sprintf()` to format messages.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
for item := 1; i <= 100; i++ {
|
||||
log.Info(fmt.Sprintf("Baking %d/100...", item))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="500" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4nX5I7qHT09aJ2gU7OaGV5.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="500" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4nX5I7qHT09aJ2gU7OaGV5.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="500" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4RHXd4JSucomcPqJGZTpKh.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="500" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4nX5I7qHT09aJ2gU7OaGV5.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
Or arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
for temp := 375; temp <= 400; temp++ {
|
||||
log.Info("Increasing temperature", "degree", fmt.Sprintf("%d°F", temp))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-79YvXcDOsqgHte3bv42UTr.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-79YvXcDOsqgHte3bv42UTr.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-4AvAnoA2S53QTOteX8krp4.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="700" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-79YvXcDOsqgHte3bv42UTr.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
### Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
Skip caller frames in helper functions. Similar to what you can do with
|
||||
`testing.TB().Helper()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
func startOven(degree int) {
|
||||
log.Helper()
|
||||
log.Info("Starting oven", "degree", degree)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
log.SetReportCaller(true)
|
||||
startOven(400) // INFO <cookies/oven.go:123> Starting oven degree=400
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6CeQGIV8Ovgr8GD0N6NgTq.gif">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6CeQGIV8Ovgr8GD0N6NgTq.gif">
|
||||
<!-- <source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" width="700" srcset="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6DPg0bVL4K4TkfoHkAn2ap.gif"> -->
|
||||
<img width="700" src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6CeQGIV8Ovgr8GD0N6NgTq.gif">
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
|
||||
This will use the _caller_ function (`startOven`) line number instead of the
|
||||
logging function (`log.Info`) to report the source location.
|
||||
|
||||
### Slog Handler
|
||||
|
||||
You can use Log as an [`log/slog`](https://pkg.go.dev/log/slog) handler. Just
|
||||
pass a logger instance to Slog and you're good to go.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
handler := log.New(os.Stderr)
|
||||
logger := slog.New(handler)
|
||||
logger.Error("meow?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Standard Log Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
Some Go libraries, especially the ones in the standard library, will only accept
|
||||
the [standard logger][stdlog] interface. For instance, the HTTP Server from
|
||||
`net/http` will only take a `*log.Logger` for its `ErrorLog` field.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, you can use the standard log adapter, which simply wraps the logger in
|
||||
a `*log.Logger` interface.
|
||||
|
||||
```go
|
||||
logger := log.NewWithOptions(os.Stderr, log.Options{Prefix: "http"})
|
||||
stdlog := logger.StandardLog(log.StandardLogOptions{
|
||||
ForceLevel: log.ErrorLevel,
|
||||
})
|
||||
s := &http.Server{
|
||||
Addr: ":8080",
|
||||
Handler: handler,
|
||||
ErrorLog: stdlog,
|
||||
}
|
||||
stdlog.Printf("Failed to make bake request, %s", fmt.Errorf("temperature is too low"))
|
||||
// ERROR http: Failed to make bake request, temperature is too low
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gum
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://vhs.charm.sh/vhs-6jupuFM0s2fXiUrBE0I1vU.gif" width="600" alt="Running gum log with debug and error levels" />
|
||||
|
||||
Log integrates with [Gum][gum] to log messages to output. Use `gum log [flags]
|
||||
[message]` to handle logging in your shell scripts. See
|
||||
[charmbracelet/gum](https://github.com/charmbracelet/gum#log) for more
|
||||
information.
|
||||
|
||||
[gum]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/gum
|
||||
[lipgloss]: https://github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss
|
||||
[stdlog]: https://pkg.go.dev/log
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
[MIT](https://github.com/charmbracelet/log/raw/master/LICENSE)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Part of [Charm](https://charm.sh).
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://charm.sh/"><img alt="the Charm logo" src="https://stuff.charm.sh/charm-badge.jpg" width="400"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Charm热爱开源 • Charm loves open source • نحنُ نحب المصادر المفتوحة
|
||||
23
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
23
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/context.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import "context"
|
||||
|
||||
// WithContext wraps the given logger in context.
|
||||
func WithContext(ctx context.Context, logger *Logger) context.Context {
|
||||
return context.WithValue(ctx, ContextKey, logger)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FromContext returns the logger from the given context.
|
||||
// This will return the default package logger if no logger
|
||||
// found in context.
|
||||
func FromContext(ctx context.Context) *Logger {
|
||||
if logger, ok := ctx.Value(ContextKey).(*Logger); ok {
|
||||
return logger
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Default()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
type contextKey struct{ string }
|
||||
|
||||
// ContextKey is the key used to store the logger in context.
|
||||
var ContextKey = contextKey{"log"}
|
||||
27
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/formatter.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
27
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/formatter.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
// Formatter is a formatter for log messages.
|
||||
type Formatter uint8
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// TextFormatter is a formatter that formats log messages as text. Suitable for
|
||||
// console output and log files.
|
||||
TextFormatter Formatter = iota
|
||||
// JSONFormatter is a formatter that formats log messages as JSON.
|
||||
JSONFormatter
|
||||
// LogfmtFormatter is a formatter that formats log messages as logfmt.
|
||||
LogfmtFormatter
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// TimestampKey is the key for the timestamp.
|
||||
TimestampKey = "time"
|
||||
// MessageKey is the key for the message.
|
||||
MessageKey = "msg"
|
||||
// LevelKey is the key for the level.
|
||||
LevelKey = "level"
|
||||
// CallerKey is the key for the caller.
|
||||
CallerKey = "caller"
|
||||
// PrefixKey is the key for the prefix.
|
||||
PrefixKey = "prefix"
|
||||
)
|
||||
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/json.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/json.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/json"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) jsonFormatter(keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
m := make(map[string]interface{}, len(keyvals)/2)
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(keyvals); i += 2 {
|
||||
switch keyvals[i] {
|
||||
case TimestampKey:
|
||||
if t, ok := keyvals[i+1].(time.Time); ok {
|
||||
m[TimestampKey] = t.Format(l.timeFormat)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case LevelKey:
|
||||
if level, ok := keyvals[i+1].(Level); ok {
|
||||
m[LevelKey] = level.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
case CallerKey:
|
||||
if caller, ok := keyvals[i+1].(string); ok {
|
||||
m[CallerKey] = caller
|
||||
}
|
||||
case PrefixKey:
|
||||
if prefix, ok := keyvals[i+1].(string); ok {
|
||||
m[PrefixKey] = prefix
|
||||
}
|
||||
case MessageKey:
|
||||
if msg := keyvals[i+1]; msg != nil {
|
||||
m[MessageKey] = fmt.Sprint(msg)
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
var (
|
||||
key string
|
||||
val interface{}
|
||||
)
|
||||
switch k := keyvals[i].(type) {
|
||||
case fmt.Stringer:
|
||||
key = k.String()
|
||||
case error:
|
||||
key = k.Error()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
key = fmt.Sprint(k)
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch v := keyvals[i+1].(type) {
|
||||
case error:
|
||||
val = v.Error()
|
||||
case fmt.Stringer:
|
||||
val = v.String()
|
||||
default:
|
||||
val = v
|
||||
}
|
||||
m[key] = val
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
e := json.NewEncoder(&l.b)
|
||||
e.SetEscapeHTML(false)
|
||||
_ = e.Encode(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
65
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
65
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"math"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Level is a logging level.
|
||||
type Level int32
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// DebugLevel is the debug level.
|
||||
DebugLevel Level = -4
|
||||
// InfoLevel is the info level.
|
||||
InfoLevel Level = 0
|
||||
// WarnLevel is the warn level.
|
||||
WarnLevel Level = 4
|
||||
// ErrorLevel is the error level.
|
||||
ErrorLevel Level = 8
|
||||
// FatalLevel is the fatal level.
|
||||
FatalLevel Level = 12
|
||||
// noLevel is used with log.Print.
|
||||
noLevel Level = math.MaxInt32
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the level.
|
||||
func (l Level) String() string {
|
||||
switch l {
|
||||
case DebugLevel:
|
||||
return "debug"
|
||||
case InfoLevel:
|
||||
return "info"
|
||||
case WarnLevel:
|
||||
return "warn"
|
||||
case ErrorLevel:
|
||||
return "error"
|
||||
case FatalLevel:
|
||||
return "fatal"
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrInvalidLevel is an error returned when parsing an invalid level string.
|
||||
var ErrInvalidLevel = errors.New("invalid level")
|
||||
|
||||
// ParseLevel converts level in string to Level type. Default level is InfoLevel.
|
||||
func ParseLevel(level string) (Level, error) {
|
||||
switch strings.ToLower(level) {
|
||||
case DebugLevel.String():
|
||||
return DebugLevel, nil
|
||||
case InfoLevel.String():
|
||||
return InfoLevel, nil
|
||||
case WarnLevel.String():
|
||||
return WarnLevel, nil
|
||||
case ErrorLevel.String():
|
||||
return ErrorLevel, nil
|
||||
case FatalLevel.String():
|
||||
return FatalLevel, nil
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return 0, fmt.Errorf("%w: %q", ErrInvalidLevel, level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level_121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level_121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
//go:build go1.21
|
||||
// +build go1.21
|
||||
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import "log/slog"
|
||||
|
||||
// fromSlogLevel converts slog.Level to log.Level.
|
||||
var fromSlogLevel = map[slog.Level]Level{
|
||||
slog.LevelDebug: DebugLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelInfo: InfoLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelWarn: WarnLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelError: ErrorLevel,
|
||||
slog.Level(12): FatalLevel,
|
||||
}
|
||||
15
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level_no121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
15
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/level_no121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
//go:build !go1.21
|
||||
// +build !go1.21
|
||||
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import "golang.org/x/exp/slog"
|
||||
|
||||
// fromSlogLevel converts slog.Level to log.Level.
|
||||
var fromSlogLevel = map[slog.Level]Level{
|
||||
slog.LevelDebug: DebugLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelInfo: InfoLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelWarn: WarnLevel,
|
||||
slog.LevelError: ErrorLevel,
|
||||
slog.Level(12): FatalLevel,
|
||||
}
|
||||
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logfmt.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logfmt.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"errors"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/go-logfmt/logfmt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) logfmtFormatter(keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
e := logfmt.NewEncoder(&l.b)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(keyvals); i += 2 {
|
||||
switch keyvals[i] {
|
||||
case TimestampKey:
|
||||
if t, ok := keyvals[i+1].(time.Time); ok {
|
||||
keyvals[i+1] = t.Format(l.timeFormat)
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if key := fmt.Sprint(keyvals[i]); key != "" {
|
||||
keyvals[i] = key
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
err := e.EncodeKeyval(keyvals[i], keyvals[i+1])
|
||||
if err != nil && errors.Is(err, logfmt.ErrUnsupportedValueType) {
|
||||
// If the value is not supported by logfmt, we try to convert it to a string.
|
||||
_ = e.EncodeKeyval(keyvals[i], fmt.Sprintf("%+v", keyvals[i+1]))
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
_ = e.EndRecord()
|
||||
}
|
||||
409
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
409
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,409 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ErrMissingValue is returned when a key is missing a value.
|
||||
var ErrMissingValue = fmt.Errorf("missing value")
|
||||
|
||||
// LoggerOption is an option for a logger.
|
||||
type LoggerOption = func(*Logger)
|
||||
|
||||
// Logger is a Logger that implements Logger.
|
||||
type Logger struct {
|
||||
w io.Writer
|
||||
b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
mu *sync.RWMutex
|
||||
re *lipgloss.Renderer
|
||||
|
||||
isDiscard uint32
|
||||
|
||||
level int32
|
||||
prefix string
|
||||
timeFunc TimeFunction
|
||||
timeFormat string
|
||||
callerOffset int
|
||||
callerFormatter CallerFormatter
|
||||
formatter Formatter
|
||||
|
||||
reportCaller bool
|
||||
reportTimestamp bool
|
||||
|
||||
fields []interface{}
|
||||
|
||||
helpers *sync.Map
|
||||
styles *Styles
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Logf logs a message with formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Logf(level Level, format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(level, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Log logs the given message with the given keyvals for the given level.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Log(level Level, msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
if atomic.LoadUint32(&l.isDiscard) != 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// check if the level is allowed
|
||||
if atomic.LoadInt32(&l.level) > int32(level) {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var frame runtime.Frame
|
||||
if l.reportCaller {
|
||||
// Skip log.log, the caller, and any offset added.
|
||||
frames := l.frames(l.callerOffset + 2)
|
||||
for {
|
||||
f, more := frames.Next()
|
||||
_, helper := l.helpers.Load(f.Function)
|
||||
if !helper || !more {
|
||||
// Found a frame that wasn't a helper function.
|
||||
// Or we ran out of frames to check.
|
||||
frame = f
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.handle(level, l.timeFunc(time.Now()), []runtime.Frame{frame}, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) handle(level Level, ts time.Time, frames []runtime.Frame, msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
var kvs []interface{}
|
||||
if l.reportTimestamp && !ts.IsZero() {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, TimestampKey, ts)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, ok := l.styles.Levels[level]
|
||||
if ok {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, LevelKey, level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if l.reportCaller && len(frames) > 0 && frames[0].PC != 0 {
|
||||
file, line, fn := l.location(frames)
|
||||
if file != "" {
|
||||
caller := l.callerFormatter(file, line, fn)
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, CallerKey, caller)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if l.prefix != "" {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, PrefixKey, l.prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if msg != nil {
|
||||
if m := fmt.Sprint(msg); m != "" {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, MessageKey, m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// append logger fields
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, l.fields...)
|
||||
if len(l.fields)%2 != 0 {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, ErrMissingValue)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// append the rest
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, keyvals...)
|
||||
if len(keyvals)%2 != 0 {
|
||||
kvs = append(kvs, ErrMissingValue)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
switch l.formatter {
|
||||
case LogfmtFormatter:
|
||||
l.logfmtFormatter(kvs...)
|
||||
case JSONFormatter:
|
||||
l.jsonFormatter(kvs...)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
l.textFormatter(kvs...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WriteTo will reset the buffer
|
||||
l.b.WriteTo(l.w) //nolint: errcheck
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Helper marks the calling function as a helper
|
||||
// and skips it for source location information.
|
||||
// It's the equivalent of testing.TB.Helper().
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Helper() {
|
||||
l.helper(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) helper(skip int) {
|
||||
var pcs [1]uintptr
|
||||
// Skip runtime.Callers, and l.helper
|
||||
n := runtime.Callers(skip+2, pcs[:])
|
||||
frames := runtime.CallersFrames(pcs[:n])
|
||||
frame, _ := frames.Next()
|
||||
l.helpers.LoadOrStore(frame.Function, struct{}{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// frames returns the runtime.Frames for the caller.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) frames(skip int) *runtime.Frames {
|
||||
// Copied from testing.T
|
||||
const maxStackLen = 50
|
||||
var pc [maxStackLen]uintptr
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip runtime.Callers, and l.frame
|
||||
n := runtime.Callers(skip+2, pc[:])
|
||||
frames := runtime.CallersFrames(pc[:n])
|
||||
return frames
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) location(frames []runtime.Frame) (file string, line int, fn string) {
|
||||
if len(frames) == 0 {
|
||||
return "", 0, ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
f := frames[0]
|
||||
return f.File, f.Line, f.Function
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Cleanup a path by returning the last n segments of the path only.
|
||||
func trimCallerPath(path string, n int) string {
|
||||
// lovely borrowed from zap
|
||||
// nb. To make sure we trim the path correctly on Windows too, we
|
||||
// counter-intuitively need to use '/' and *not* os.PathSeparator here,
|
||||
// because the path given originates from Go stdlib, specifically
|
||||
// runtime.Caller() which (as of Mar/17) returns forward slashes even on
|
||||
// Windows.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://github.com/golang/go/issues/3335
|
||||
// and https://github.com/golang/go/issues/18151
|
||||
//
|
||||
// for discussion on the issue on Go side.
|
||||
|
||||
// Return the full path if n is 0.
|
||||
if n <= 0 {
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Find the last separator.
|
||||
idx := strings.LastIndexByte(path, '/')
|
||||
if idx == -1 {
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {
|
||||
// Find the penultimate separator.
|
||||
idx = strings.LastIndexByte(path[:idx], '/')
|
||||
if idx == -1 {
|
||||
return path
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return path[idx+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetReportTimestamp sets whether the timestamp should be reported.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetReportTimestamp(report bool) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.reportTimestamp = report
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetReportCaller sets whether the caller location should be reported.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetReportCaller(report bool) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.reportCaller = report
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetLevel returns the current level.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) GetLevel() Level {
|
||||
l.mu.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.RUnlock()
|
||||
return Level(l.level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetLevel sets the current level.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetLevel(level Level) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
atomic.StoreInt32(&l.level, int32(level))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPrefix returns the current prefix.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) GetPrefix() string {
|
||||
l.mu.RLock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.RUnlock()
|
||||
return l.prefix
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPrefix sets the current prefix.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetPrefix(prefix string) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.prefix = prefix
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTimeFormat sets the time format.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetTimeFormat(format string) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.timeFormat = format
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTimeFunction sets the time function.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetTimeFunction(f TimeFunction) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.timeFunc = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetOutput sets the output destination.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetOutput(w io.Writer) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
if w == nil {
|
||||
w = os.Stderr
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.w = w
|
||||
var isDiscard uint32
|
||||
if w == io.Discard {
|
||||
isDiscard = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
atomic.StoreUint32(&l.isDiscard, isDiscard)
|
||||
// Reuse cached renderers
|
||||
if v, ok := registry.Load(w); ok {
|
||||
l.re = v.(*lipgloss.Renderer)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
l.re = lipgloss.NewRenderer(w, termenv.WithColorCache(true))
|
||||
registry.Store(w, l.re)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetFormatter sets the formatter.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetFormatter(f Formatter) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.formatter = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCallerFormatter sets the caller formatter.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetCallerFormatter(f CallerFormatter) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.callerFormatter = f
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCallerOffset sets the caller offset.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetCallerOffset(offset int) {
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.callerOffset = offset
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile force sets the underlying Lip Gloss renderer color profile
|
||||
// for the TextFormatter.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetColorProfile(profile termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
l.re.SetColorProfile(profile)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStyles sets the logger styles for the TextFormatter.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) SetStyles(s *Styles) {
|
||||
if s == nil {
|
||||
s = DefaultStyles()
|
||||
}
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
defer l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
l.styles = s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// With returns a new logger with the given keyvals added.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) With(keyvals ...interface{}) *Logger {
|
||||
var st Styles
|
||||
l.mu.Lock()
|
||||
sl := *l
|
||||
st = *l.styles
|
||||
l.mu.Unlock()
|
||||
sl.b = bytes.Buffer{}
|
||||
sl.mu = &sync.RWMutex{}
|
||||
sl.helpers = &sync.Map{}
|
||||
sl.fields = append(l.fields, keyvals...)
|
||||
sl.styles = &st
|
||||
return &sl
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithPrefix returns a new logger with the given prefix.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) WithPrefix(prefix string) *Logger {
|
||||
sl := l.With()
|
||||
sl.SetPrefix(prefix)
|
||||
return sl
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Debug prints a debug message.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Debug(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(DebugLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Info prints an info message.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Info(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(InfoLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Warn prints a warning message.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Warn(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(WarnLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Error prints an error message.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Error(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(ErrorLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatal prints a fatal message and exits.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Fatal(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(FatalLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Print prints a message with no level.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Print(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(noLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Debugf prints a debug message with formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Debugf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(DebugLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Infof prints an info message with formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Infof(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(InfoLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Warnf prints a warning message with formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Warnf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(WarnLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Errorf prints an error message with formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(ErrorLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatalf prints a fatal message with formatting and exits.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(FatalLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Printf prints a message with no level and formatting.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Printf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
l.Log(noLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
62
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger_121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
62
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger_121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
//go:build go1.21
|
||||
// +build go1.21
|
||||
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"log/slog"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether the logger is enabled for the given level.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Enabled(_ context.Context, level slog.Level) bool {
|
||||
return atomic.LoadInt32(&l.level) <= int32(fromSlogLevel[level])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle handles the Record. It will only be called if Enabled returns true.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Handle(ctx context.Context, record slog.Record) error {
|
||||
if !l.Enabled(ctx, record.Level) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fields := make([]interface{}, 0, record.NumAttrs()*2)
|
||||
record.Attrs(func(a slog.Attr) bool {
|
||||
fields = append(fields, a.Key, a.Value.String())
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
// Get the caller frame using the record's PC.
|
||||
frames := runtime.CallersFrames([]uintptr{record.PC})
|
||||
frame, _ := frames.Next()
|
||||
l.handle(fromSlogLevel[record.Level], l.timeFunc(record.Time), []runtime.Frame{frame}, record.Message, fields...)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithAttrs returns a new Handler with the given attributes added.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) WithAttrs(attrs []slog.Attr) slog.Handler {
|
||||
fields := make([]interface{}, 0, len(attrs)*2)
|
||||
for _, attr := range attrs {
|
||||
fields = append(fields, attr.Key, attr.Value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l.With(fields...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithGroup returns a new Handler with the given group name prepended to the
|
||||
// current group name or prefix.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) WithGroup(name string) slog.Handler {
|
||||
if l.prefix != "" {
|
||||
name = l.prefix + "." + name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l.WithPrefix(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ slog.Handler = (*Logger)(nil)
|
||||
59
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger_no121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
59
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/logger_no121.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
//go:build !go1.21
|
||||
// +build !go1.21
|
||||
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"context"
|
||||
"runtime"
|
||||
"sync/atomic"
|
||||
|
||||
"golang.org/x/exp/slog"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Enabled reports whether the logger is enabled for the given level.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Enabled(_ context.Context, level slog.Level) bool {
|
||||
return atomic.LoadInt32(&l.level) <= int32(fromSlogLevel[level])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle handles the Record. It will only be called if Enabled returns true.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) Handle(_ context.Context, record slog.Record) error {
|
||||
fields := make([]interface{}, 0, record.NumAttrs()*2)
|
||||
record.Attrs(func(a slog.Attr) bool {
|
||||
fields = append(fields, a.Key, a.Value.String())
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
// Get the caller frame using the record's PC.
|
||||
frames := runtime.CallersFrames([]uintptr{record.PC})
|
||||
frame, _ := frames.Next()
|
||||
l.handle(fromSlogLevel[record.Level], l.timeFunc(record.Time), []runtime.Frame{frame}, record.Message, fields...)
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithAttrs returns a new Handler with the given attributes added.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) WithAttrs(attrs []slog.Attr) slog.Handler {
|
||||
fields := make([]interface{}, 0, len(attrs)*2)
|
||||
for _, attr := range attrs {
|
||||
fields = append(fields, attr.Key, attr.Value)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l.With(fields...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithGroup returns a new Handler with the given group name prepended to the
|
||||
// current group name or prefix.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Implements slog.Handler.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) WithGroup(name string) slog.Handler {
|
||||
if l.prefix != "" {
|
||||
name = l.prefix + "." + name
|
||||
}
|
||||
return l.WithPrefix(name)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ slog.Handler = (*Logger)(nil)
|
||||
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/options.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/options.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultTimeFormat is the default time format.
|
||||
const DefaultTimeFormat = "2006/01/02 15:04:05"
|
||||
|
||||
// TimeFunction is a function that returns a time.Time.
|
||||
type TimeFunction = func(time.Time) time.Time
|
||||
|
||||
// NowUTC is a convenient function that returns the
|
||||
// current time in UTC timezone.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is to be used as a time function.
|
||||
// For example:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// log.SetTimeFunction(log.NowUTC)
|
||||
func NowUTC(t time.Time) time.Time {
|
||||
return t.UTC()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CallerFormatter is the caller formatter.
|
||||
type CallerFormatter func(string, int, string) string
|
||||
|
||||
// ShortCallerFormatter is a caller formatter that returns the last 2 levels of the path
|
||||
// and line number.
|
||||
func ShortCallerFormatter(file string, line int, _ string) string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", trimCallerPath(file, 2), line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LongCallerFormatter is a caller formatter that returns the full path and line number.
|
||||
func LongCallerFormatter(file string, line int, _ string) string {
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", file, line)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Options is the options for the logger.
|
||||
type Options struct {
|
||||
// TimeFunction is the time function for the logger. The default is time.Now.
|
||||
TimeFunction TimeFunction
|
||||
// TimeFormat is the time format for the logger. The default is "2006/01/02 15:04:05".
|
||||
TimeFormat string
|
||||
// Level is the level for the logger. The default is InfoLevel.
|
||||
Level Level
|
||||
// Prefix is the prefix for the logger. The default is no prefix.
|
||||
Prefix string
|
||||
// ReportTimestamp is whether the logger should report the timestamp. The default is false.
|
||||
ReportTimestamp bool
|
||||
// ReportCaller is whether the logger should report the caller location. The default is false.
|
||||
ReportCaller bool
|
||||
// CallerFormatter is the caller format for the logger. The default is ShortCallerFormatter.
|
||||
CallerFormatter CallerFormatter
|
||||
// CallerOffset is the caller format for the logger. The default is 0.
|
||||
CallerOffset int
|
||||
// Fields is the fields for the logger. The default is no fields.
|
||||
Fields []interface{}
|
||||
// Formatter is the formatter for the logger. The default is TextFormatter.
|
||||
Formatter Formatter
|
||||
}
|
||||
246
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/pkg.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
246
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/pkg.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"os"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/muesli/termenv"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
// registry is a map of all registered lipgloss renderers.
|
||||
registry = sync.Map{}
|
||||
|
||||
// defaultLogger is the default global logger instance.
|
||||
defaultLoggerOnce sync.Once
|
||||
defaultLogger *Logger
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Default returns the default logger. The default logger comes with timestamp enabled.
|
||||
func Default() *Logger {
|
||||
defaultLoggerOnce.Do(func() {
|
||||
if defaultLogger != nil {
|
||||
// already set via SetDefault.
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
defaultLogger = NewWithOptions(os.Stderr, Options{ReportTimestamp: true})
|
||||
})
|
||||
return defaultLogger
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDefault sets the default global logger.
|
||||
func SetDefault(logger *Logger) {
|
||||
defaultLogger = logger
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// New returns a new logger with the default options.
|
||||
func New(w io.Writer) *Logger {
|
||||
return NewWithOptions(w, Options{})
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewWithOptions returns a new logger using the provided options.
|
||||
func NewWithOptions(w io.Writer, o Options) *Logger {
|
||||
l := &Logger{
|
||||
b: bytes.Buffer{},
|
||||
mu: &sync.RWMutex{},
|
||||
helpers: &sync.Map{},
|
||||
level: int32(o.Level),
|
||||
reportTimestamp: o.ReportTimestamp,
|
||||
reportCaller: o.ReportCaller,
|
||||
prefix: o.Prefix,
|
||||
timeFunc: o.TimeFunction,
|
||||
timeFormat: o.TimeFormat,
|
||||
formatter: o.Formatter,
|
||||
fields: o.Fields,
|
||||
callerFormatter: o.CallerFormatter,
|
||||
callerOffset: o.CallerOffset,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
l.SetOutput(w)
|
||||
l.SetLevel(Level(l.level))
|
||||
l.SetStyles(DefaultStyles())
|
||||
|
||||
if l.callerFormatter == nil {
|
||||
l.callerFormatter = ShortCallerFormatter
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if l.timeFunc == nil {
|
||||
l.timeFunc = func(t time.Time) time.Time { return t }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if l.timeFormat == "" {
|
||||
l.timeFormat = DefaultTimeFormat
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return l
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetReportTimestamp sets whether to report timestamp for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetReportTimestamp(report bool) {
|
||||
Default().SetReportTimestamp(report)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetReportCaller sets whether to report caller location for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetReportCaller(report bool) {
|
||||
Default().SetReportCaller(report)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetLevel sets the level for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetLevel(level Level) {
|
||||
Default().SetLevel(level)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetLevel returns the level for the default logger.
|
||||
func GetLevel() Level {
|
||||
return Default().GetLevel()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTimeFormat sets the time format for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetTimeFormat(format string) {
|
||||
Default().SetTimeFormat(format)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetTimeFunction sets the time function for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetTimeFunction(f TimeFunction) {
|
||||
Default().SetTimeFunction(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetOutput sets the output for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetOutput(w io.Writer) {
|
||||
Default().SetOutput(w)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetFormatter sets the formatter for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetFormatter(f Formatter) {
|
||||
Default().SetFormatter(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCallerFormatter sets the caller formatter for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetCallerFormatter(f CallerFormatter) {
|
||||
Default().SetCallerFormatter(f)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCallerOffset sets the caller offset for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetCallerOffset(offset int) {
|
||||
Default().SetCallerOffset(offset)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPrefix sets the prefix for the default logger.
|
||||
func SetPrefix(prefix string) {
|
||||
Default().SetPrefix(prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetColorProfile force sets the underlying Lip Gloss renderer color profile
|
||||
// for the TextFormatter.
|
||||
func SetColorProfile(profile termenv.Profile) {
|
||||
Default().SetColorProfile(profile)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetStyles sets the logger styles for the TextFormatter.
|
||||
func SetStyles(s *Styles) {
|
||||
Default().SetStyles(s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GetPrefix returns the prefix for the default logger.
|
||||
func GetPrefix() string {
|
||||
return Default().GetPrefix()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// With returns a new logger with the given keyvals.
|
||||
func With(keyvals ...interface{}) *Logger {
|
||||
return Default().With(keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// WithPrefix returns a new logger with the given prefix.
|
||||
func WithPrefix(prefix string) *Logger {
|
||||
return Default().WithPrefix(prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Helper marks the calling function as a helper
|
||||
// and skips it for source location information.
|
||||
// It's the equivalent of testing.TB.Helper().
|
||||
func Helper() {
|
||||
Default().helper(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Log logs a message with the given level.
|
||||
func Log(level Level, msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(level, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Debug logs a debug message.
|
||||
func Debug(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(DebugLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Info logs an info message.
|
||||
func Info(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(InfoLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Warn logs a warning message.
|
||||
func Warn(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(WarnLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Error logs an error message.
|
||||
func Error(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(ErrorLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatal logs a fatal message and exit.
|
||||
func Fatal(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(FatalLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Print logs a message with no level.
|
||||
func Print(msg interface{}, keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(noLevel, msg, keyvals...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Logf logs a message with formatting and level.
|
||||
func Logf(level Level, format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Logf(level, format, args...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Debugf logs a debug message with formatting.
|
||||
func Debugf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(DebugLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Infof logs an info message with formatting.
|
||||
func Infof(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(InfoLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Warnf logs a warning message with formatting.
|
||||
func Warnf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(WarnLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Errorf logs an error message with formatting.
|
||||
func Errorf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(ErrorLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Fatalf logs a fatal message with formatting and exit.
|
||||
func Fatalf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(FatalLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
os.Exit(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Printf logs a message with formatting and no level.
|
||||
func Printf(format string, args ...interface{}) {
|
||||
Default().Log(noLevel, fmt.Sprintf(format, args...))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StandardLog returns a standard logger from the default logger.
|
||||
func StandardLog(opts ...StandardLogOptions) *log.Logger {
|
||||
return Default().StandardLog(opts...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
67
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/stdlog.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
67
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/stdlog.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"log"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
type stdLogWriter struct {
|
||||
l *Logger
|
||||
opt *StandardLogOptions
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *stdLogWriter) Write(p []byte) (n int, err error) {
|
||||
str := strings.TrimSuffix(string(p), "\n")
|
||||
|
||||
if l.opt != nil {
|
||||
switch l.opt.ForceLevel {
|
||||
case DebugLevel:
|
||||
l.l.Debug(str)
|
||||
case InfoLevel:
|
||||
l.l.Info(str)
|
||||
case WarnLevel:
|
||||
l.l.Warn(str)
|
||||
case ErrorLevel:
|
||||
l.l.Error(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(str, "DEBUG"):
|
||||
l.l.Debug(strings.TrimSpace(str[5:]))
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(str, "INFO"):
|
||||
l.l.Info(strings.TrimSpace(str[4:]))
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(str, "WARN"):
|
||||
l.l.Warn(strings.TrimSpace(str[4:]))
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(str, "ERROR"):
|
||||
l.l.Error(strings.TrimSpace(str[5:]))
|
||||
case strings.HasPrefix(str, "ERR"):
|
||||
l.l.Error(strings.TrimSpace(str[3:]))
|
||||
default:
|
||||
l.l.Info(str)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return len(p), nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StandardLogOptions can be used to configure the standard log adapter.
|
||||
type StandardLogOptions struct {
|
||||
ForceLevel Level
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StandardLog returns a standard logger from Logger. The returned logger
|
||||
// can infer log levels from message prefix. Expected prefixes are DEBUG, INFO,
|
||||
// WARN, ERROR, and ERR.
|
||||
func (l *Logger) StandardLog(opts ...StandardLogOptions) *log.Logger {
|
||||
nl := l.With()
|
||||
// The caller stack is
|
||||
// log.Printf() -> l.Output() -> l.out.Write(stdLogger.Write)
|
||||
nl.callerOffset += 3
|
||||
sl := &stdLogWriter{
|
||||
l: nl,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if len(opts) > 0 {
|
||||
sl.opt = &opts[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
return log.New(sl, "", 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
82
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/styles.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
82
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/styles.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/lipgloss"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Styles defines the styles for the text logger.
|
||||
type Styles struct {
|
||||
// Timestamp is the style for timestamps.
|
||||
Timestamp lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Caller is the style for source caller.
|
||||
Caller lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Prefix is the style for prefix.
|
||||
Prefix lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Message is the style for messages.
|
||||
Message lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Key is the style for keys.
|
||||
Key lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Value is the style for values.
|
||||
Value lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Separator is the style for separators.
|
||||
Separator lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Levels are the styles for each level.
|
||||
Levels map[Level]lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Keys overrides styles for specific keys.
|
||||
Keys map[string]lipgloss.Style
|
||||
|
||||
// Values overrides value styles for specific keys.
|
||||
Values map[string]lipgloss.Style
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultStyles returns the default styles.
|
||||
func DefaultStyles() *Styles {
|
||||
return &Styles{
|
||||
Timestamp: lipgloss.NewStyle(),
|
||||
Caller: lipgloss.NewStyle().Faint(true),
|
||||
Prefix: lipgloss.NewStyle().Bold(true).Faint(true),
|
||||
Message: lipgloss.NewStyle(),
|
||||
Key: lipgloss.NewStyle().Faint(true),
|
||||
Value: lipgloss.NewStyle(),
|
||||
Separator: lipgloss.NewStyle().Faint(true),
|
||||
Levels: map[Level]lipgloss.Style{
|
||||
DebugLevel: lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString(strings.ToUpper(DebugLevel.String())).
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
MaxWidth(4).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("63")),
|
||||
InfoLevel: lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString(strings.ToUpper(InfoLevel.String())).
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
MaxWidth(4).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("86")),
|
||||
WarnLevel: lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString(strings.ToUpper(WarnLevel.String())).
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
MaxWidth(4).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("192")),
|
||||
ErrorLevel: lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString(strings.ToUpper(ErrorLevel.String())).
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
MaxWidth(4).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("204")),
|
||||
FatalLevel: lipgloss.NewStyle().
|
||||
SetString(strings.ToUpper(FatalLevel.String())).
|
||||
Bold(true).
|
||||
MaxWidth(4).
|
||||
Foreground(lipgloss.Color("134")),
|
||||
},
|
||||
Keys: map[string]lipgloss.Style{},
|
||||
Values: map[string]lipgloss.Style{},
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
272
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/text.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
272
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/log/text.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,272 @@
|
||||
package log
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"io"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
"sync"
|
||||
"time"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
separator = "="
|
||||
indentSeparator = " │ "
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) writeIndent(w io.Writer, str string, indent string, newline bool, key string) {
|
||||
st := l.styles
|
||||
|
||||
// kindly borrowed from hclog
|
||||
for {
|
||||
nl := strings.IndexByte(str, '\n')
|
||||
if nl == -1 {
|
||||
if str != "" {
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte(indent))
|
||||
val := escapeStringForOutput(str, false)
|
||||
if valueStyle, ok := st.Values[key]; ok {
|
||||
val = valueStyle.Renderer(l.re).Render(val)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
val = st.Value.Renderer(l.re).Render(val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte(val))
|
||||
if newline {
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte{'\n'})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte(indent))
|
||||
val := escapeStringForOutput(str[:nl], false)
|
||||
val = st.Value.Renderer(l.re).Render(val)
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte(val))
|
||||
_, _ = w.Write([]byte{'\n'})
|
||||
str = str[nl+1:]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func needsEscaping(str string) bool {
|
||||
for _, b := range str {
|
||||
if !unicode.IsPrint(b) || b == '"' {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
lowerhex = "0123456789abcdef"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
var bufPool = sync.Pool{
|
||||
New: func() interface{} {
|
||||
return new(strings.Builder)
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func escapeStringForOutput(str string, escapeQuotes bool) string {
|
||||
// kindly borrowed from hclog
|
||||
if !needsEscaping(str) {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bb := bufPool.Get().(*strings.Builder)
|
||||
bb.Reset()
|
||||
|
||||
defer bufPool.Put(bb)
|
||||
for _, r := range str {
|
||||
if escapeQuotes && r == '"' {
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\"`)
|
||||
} else if unicode.IsPrint(r) {
|
||||
bb.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
switch r {
|
||||
case '\a':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\a`)
|
||||
case '\b':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\b`)
|
||||
case '\f':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\f`)
|
||||
case '\n':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\n`)
|
||||
case '\r':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\r`)
|
||||
case '\t':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\t`)
|
||||
case '\v':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\v`)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r < ' ':
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\x`)
|
||||
bb.WriteByte(lowerhex[byte(r)>>4])
|
||||
bb.WriteByte(lowerhex[byte(r)&0xF])
|
||||
case !utf8.ValidRune(r):
|
||||
r = 0xFFFD
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case r < 0x10000:
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\u`)
|
||||
for s := 12; s >= 0; s -= 4 {
|
||||
bb.WriteByte(lowerhex[r>>uint(s)&0xF])
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
bb.WriteString(`\U`)
|
||||
for s := 28; s >= 0; s -= 4 {
|
||||
bb.WriteByte(lowerhex[r>>uint(s)&0xF])
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return bb.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func needsQuoting(s string) bool {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); {
|
||||
b := s[i]
|
||||
if b < utf8.RuneSelf {
|
||||
if needsQuotingSet[b] {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, size := utf8.DecodeRuneInString(s[i:])
|
||||
if r == utf8.RuneError || unicode.IsSpace(r) || !unicode.IsPrint(r) {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
i += size
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var needsQuotingSet = [utf8.RuneSelf]bool{
|
||||
'"': true,
|
||||
'=': true,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func init() {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < utf8.RuneSelf; i++ {
|
||||
r := rune(i)
|
||||
if unicode.IsSpace(r) || !unicode.IsPrint(r) {
|
||||
needsQuotingSet[i] = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func writeSpace(w io.Writer, first bool) {
|
||||
if !first {
|
||||
w.Write([]byte{' '}) //nolint: errcheck
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (l *Logger) textFormatter(keyvals ...interface{}) {
|
||||
st := l.styles
|
||||
lenKeyvals := len(keyvals)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < lenKeyvals; i += 2 {
|
||||
firstKey := i == 0
|
||||
moreKeys := i < lenKeyvals-2
|
||||
|
||||
switch keyvals[i] {
|
||||
case TimestampKey:
|
||||
if t, ok := keyvals[i+1].(time.Time); ok {
|
||||
ts := t.Format(l.timeFormat)
|
||||
ts = st.Timestamp.Renderer(l.re).Render(ts)
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(ts)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case LevelKey:
|
||||
if level, ok := keyvals[i+1].(Level); ok {
|
||||
var lvl string
|
||||
lvlStyle, ok := st.Levels[level]
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lvl = lvlStyle.Renderer(l.re).String()
|
||||
if lvl != "" {
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(lvl)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
case CallerKey:
|
||||
if caller, ok := keyvals[i+1].(string); ok {
|
||||
caller = fmt.Sprintf("<%s>", caller)
|
||||
caller = st.Caller.Renderer(l.re).Render(caller)
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(caller)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case PrefixKey:
|
||||
if prefix, ok := keyvals[i+1].(string); ok {
|
||||
prefix = st.Prefix.Renderer(l.re).Render(prefix + ":")
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(prefix)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case MessageKey:
|
||||
if msg := keyvals[i+1]; msg != nil {
|
||||
m := fmt.Sprint(msg)
|
||||
m = st.Message.Renderer(l.re).Render(m)
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(m)
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
sep := separator
|
||||
indentSep := indentSeparator
|
||||
sep = st.Separator.Renderer(l.re).Render(sep)
|
||||
indentSep = st.Separator.Renderer(l.re).Render(indentSep)
|
||||
key := fmt.Sprint(keyvals[i])
|
||||
val := fmt.Sprintf("%+v", keyvals[i+1])
|
||||
raw := val == ""
|
||||
if raw {
|
||||
val = `""`
|
||||
}
|
||||
if key == "" {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
actualKey := key
|
||||
valueStyle := st.Value
|
||||
if vs, ok := st.Values[actualKey]; ok {
|
||||
valueStyle = vs
|
||||
}
|
||||
if keyStyle, ok := st.Keys[key]; ok {
|
||||
key = keyStyle.Renderer(l.re).Render(key)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
key = st.Key.Renderer(l.re).Render(key)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Values may contain multiple lines, and that format
|
||||
// is preserved, with each line prefixed with a " | "
|
||||
// to show it's part of a collection of lines.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Values may also need quoting, if not all the runes
|
||||
// in the value string are "normal", like if they
|
||||
// contain ANSI escape sequences.
|
||||
if strings.Contains(val, "\n") {
|
||||
l.b.WriteString("\n ")
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(key)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(sep + "\n")
|
||||
l.writeIndent(&l.b, val, indentSep, moreKeys, actualKey)
|
||||
} else if !raw && needsQuoting(val) {
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(key)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(sep)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(valueStyle.Renderer(l.re).Render(fmt.Sprintf(`"%s"`,
|
||||
escapeStringForOutput(val, true))))
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
val = valueStyle.Renderer(l.re).Render(val)
|
||||
writeSpace(&l.b, firstKey)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(key)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(sep)
|
||||
l.b.WriteString(val)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add a newline to the end of the log message.
|
||||
l.b.WriteByte('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
21
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/LICENSE
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
MIT License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2023 Charmbracelet, Inc.
|
||||
|
||||
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
|
||||
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
|
||||
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
|
||||
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
|
||||
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
|
||||
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
|
||||
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
|
||||
|
||||
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
|
||||
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
|
||||
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
||||
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
|
||||
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
|
||||
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
|
||||
SOFTWARE.
|
||||
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ansi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
11
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ansi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "io"
|
||||
|
||||
// Execute is a function that "execute" the given escape sequence by writing it
|
||||
// to the provided output writter.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is a syntactic sugar over [io.WriteString].
|
||||
func Execute(w io.Writer, s string) (int, error) {
|
||||
return io.WriteString(w, s)
|
||||
}
|
||||
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ascii.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
8
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ascii.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// SP is the space character (Char: \x20).
|
||||
SP = 0x20
|
||||
// DEL is the delete character (Caret: ^?, Char: \x7f).
|
||||
DEL = 0x7F
|
||||
)
|
||||
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
61
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/background.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SetForegroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 10 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 10 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetForegroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]10;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestForegroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
// terminal foreground color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestForegroundColor = "\x1b]10;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetBackgroundColor returns a sequence that sets the default terminal
|
||||
// background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 11 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 11 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetBackgroundColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]11;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestBackgroundColor is a sequence that requests the current default
|
||||
// terminal background color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestBackgroundColor = "\x1b]11;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetCursorColor returns a sequence that sets the terminal cursor color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 12 ; color ST
|
||||
// OSC 12 ; color BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where color is the encoded color number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetCursorColor(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]12;" + colorToHexString(c) + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorColor is a sequence that requests the current terminal cursor
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
const RequestCursorColor = "\x1b]12;?\x07"
|
||||
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c0.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// C0 control characters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These range from (0x00-0x1F) as defined in ISO 646 (ASCII).
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C0_and_C1_control_codes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// NUL is the null character (Caret: ^@, Char: \0).
|
||||
NUL = 0x00
|
||||
// SOH is the start of heading character (Caret: ^A).
|
||||
SOH = 0x01
|
||||
// STX is the start of text character (Caret: ^B).
|
||||
STX = 0x02
|
||||
// ETX is the end of text character (Caret: ^C).
|
||||
ETX = 0x03
|
||||
// EOT is the end of transmission character (Caret: ^D).
|
||||
EOT = 0x04
|
||||
// ENQ is the enquiry character (Caret: ^E).
|
||||
ENQ = 0x05
|
||||
// ACK is the acknowledge character (Caret: ^F).
|
||||
ACK = 0x06
|
||||
// BEL is the bell character (Caret: ^G, Char: \a).
|
||||
BEL = 0x07
|
||||
// BS is the backspace character (Caret: ^H, Char: \b).
|
||||
BS = 0x08
|
||||
// HT is the horizontal tab character (Caret: ^I, Char: \t).
|
||||
HT = 0x09
|
||||
// LF is the line feed character (Caret: ^J, Char: \n).
|
||||
LF = 0x0A
|
||||
// VT is the vertical tab character (Caret: ^K, Char: \v).
|
||||
VT = 0x0B
|
||||
// FF is the form feed character (Caret: ^L, Char: \f).
|
||||
FF = 0x0C
|
||||
// CR is the carriage return character (Caret: ^M, Char: \r).
|
||||
CR = 0x0D
|
||||
// SO is the shift out character (Caret: ^N).
|
||||
SO = 0x0E
|
||||
// SI is the shift in character (Caret: ^O).
|
||||
SI = 0x0F
|
||||
// DLE is the data link escape character (Caret: ^P).
|
||||
DLE = 0x10
|
||||
// DC1 is the device control 1 character (Caret: ^Q).
|
||||
DC1 = 0x11
|
||||
// DC2 is the device control 2 character (Caret: ^R).
|
||||
DC2 = 0x12
|
||||
// DC3 is the device control 3 character (Caret: ^S).
|
||||
DC3 = 0x13
|
||||
// DC4 is the device control 4 character (Caret: ^T).
|
||||
DC4 = 0x14
|
||||
// NAK is the negative acknowledge character (Caret: ^U).
|
||||
NAK = 0x15
|
||||
// SYN is the synchronous idle character (Caret: ^V).
|
||||
SYN = 0x16
|
||||
// ETB is the end of transmission block character (Caret: ^W).
|
||||
ETB = 0x17
|
||||
// CAN is the cancel character (Caret: ^X).
|
||||
CAN = 0x18
|
||||
// EM is the end of medium character (Caret: ^Y).
|
||||
EM = 0x19
|
||||
// SUB is the substitute character (Caret: ^Z).
|
||||
SUB = 0x1A
|
||||
// ESC is the escape character (Caret: ^[, Char: \e).
|
||||
ESC = 0x1B
|
||||
// FS is the file separator character (Caret: ^\).
|
||||
FS = 0x1C
|
||||
// GS is the group separator character (Caret: ^]).
|
||||
GS = 0x1D
|
||||
// RS is the record separator character (Caret: ^^).
|
||||
RS = 0x1E
|
||||
// US is the unit separator character (Caret: ^_).
|
||||
US = 0x1F
|
||||
)
|
||||
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
72
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/c1.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// C1 control characters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// These range from (0x80-0x9F) as defined in ISO 6429 (ECMA-48).
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/C0_and_C1_control_codes
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// PAD is the padding character.
|
||||
PAD = 0x80
|
||||
// HOP is the high octet preset character.
|
||||
HOP = 0x81
|
||||
// BPH is the break permitted here character.
|
||||
BPH = 0x82
|
||||
// NBH is the no break here character.
|
||||
NBH = 0x83
|
||||
// IND is the index character.
|
||||
IND = 0x84
|
||||
// NEL is the next line character.
|
||||
NEL = 0x85
|
||||
// SSA is the start of selected area character.
|
||||
SSA = 0x86
|
||||
// ESA is the end of selected area character.
|
||||
ESA = 0x87
|
||||
// HTS is the horizontal tab set character.
|
||||
HTS = 0x88
|
||||
// HTJ is the horizontal tab with justification character.
|
||||
HTJ = 0x89
|
||||
// VTS is the vertical tab set character.
|
||||
VTS = 0x8A
|
||||
// PLD is the partial line forward character.
|
||||
PLD = 0x8B
|
||||
// PLU is the partial line backward character.
|
||||
PLU = 0x8C
|
||||
// RI is the reverse index character.
|
||||
RI = 0x8D
|
||||
// SS2 is the single shift 2 character.
|
||||
SS2 = 0x8E
|
||||
// SS3 is the single shift 3 character.
|
||||
SS3 = 0x8F
|
||||
// DCS is the device control string character.
|
||||
DCS = 0x90
|
||||
// PU1 is the private use 1 character.
|
||||
PU1 = 0x91
|
||||
// PU2 is the private use 2 character.
|
||||
PU2 = 0x92
|
||||
// STS is the set transmit state character.
|
||||
STS = 0x93
|
||||
// CCH is the cancel character.
|
||||
CCH = 0x94
|
||||
// MW is the message waiting character.
|
||||
MW = 0x95
|
||||
// SPA is the start of guarded area character.
|
||||
SPA = 0x96
|
||||
// EPA is the end of guarded area character.
|
||||
EPA = 0x97
|
||||
// SOS is the start of string character.
|
||||
SOS = 0x98
|
||||
// SGCI is the single graphic character introducer character.
|
||||
SGCI = 0x99
|
||||
// SCI is the single character introducer character.
|
||||
SCI = 0x9A
|
||||
// CSI is the control sequence introducer character.
|
||||
CSI = 0x9B
|
||||
// ST is the string terminator character.
|
||||
ST = 0x9C
|
||||
// OSC is the operating system command character.
|
||||
OSC = 0x9D
|
||||
// PM is the privacy message character.
|
||||
PM = 0x9E
|
||||
// APC is the application program command character.
|
||||
APC = 0x9F
|
||||
)
|
||||
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
75
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/clipboard.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "encoding/base64"
|
||||
|
||||
// Clipboard names.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
SystemClipboard = 'c'
|
||||
PrimaryClipboard = 'p'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SetClipboard returns a sequence for manipulating the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 52 ; Pc ; Pd ST
|
||||
// OSC 52 ; Pc ; Pd BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pc is the clipboard name and Pd is the base64 encoded data.
|
||||
// Empty data or invalid base64 data will reset the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetClipboard(c byte, d string) string {
|
||||
if d != "" {
|
||||
d = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(d))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]52;" + string(c) + ";" + d + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetSystemClipboard returns a sequence for setting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(SystemClipboard, d).
|
||||
func SetSystemClipboard(d string) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(SystemClipboard, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetPrimaryClipboard returns a sequence for setting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard, d).
|
||||
func SetPrimaryClipboard(d string) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard, d)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetClipboard returns a sequence for resetting the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetClipboard(c, "").
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func ResetClipboard(c byte) string {
|
||||
return SetClipboard(c, "")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetSystemClipboard is a sequence for resetting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to ResetClipboard(SystemClipboard).
|
||||
const ResetSystemClipboard = "\x1b]52;c;\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetPrimaryClipboard is a sequence for resetting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to ResetClipboard(PrimaryClipboard).
|
||||
const ResetPrimaryClipboard = "\x1b]52;p;\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestClipboard returns a sequence for requesting the clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func RequestClipboard(c byte) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]52;" + string(c) + ";?\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestSystemClipboard is a sequence for requesting the system clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to RequestClipboard(SystemClipboard).
|
||||
const RequestSystemClipboard = "\x1b]52;c;?\x07"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPrimaryClipboard is a sequence for requesting the primary clipboard.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to RequestClipboard(PrimaryClipboard).
|
||||
const RequestPrimaryClipboard = "\x1b]52;p;?\x07"
|
||||
196
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
196
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/color.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Technically speaking, the 16 basic ANSI colors are arbitrary and can be
|
||||
// customized at the terminal level. Given that, we're returning what we feel
|
||||
// are good defaults.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This could also be a slice, but we use a map to make the mappings very
|
||||
// explicit.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://www.ditig.com/publications/256-colors-cheat-sheet
|
||||
var lowANSI = map[uint32]uint32{
|
||||
0: 0x000000, // black
|
||||
1: 0x800000, // red
|
||||
2: 0x008000, // green
|
||||
3: 0x808000, // yellow
|
||||
4: 0x000080, // blue
|
||||
5: 0x800080, // magenta
|
||||
6: 0x008080, // cyan
|
||||
7: 0xc0c0c0, // white
|
||||
8: 0x808080, // bright black
|
||||
9: 0xff0000, // bright red
|
||||
10: 0x00ff00, // bright green
|
||||
11: 0xffff00, // bright yellow
|
||||
12: 0x0000ff, // bright blue
|
||||
13: 0xff00ff, // bright magenta
|
||||
14: 0x00ffff, // bright cyan
|
||||
15: 0xffffff, // bright white
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Color is a color that can be used in a terminal. ANSI (including
|
||||
// ANSI256) and 24-bit "true colors" fall under this category.
|
||||
type Color interface {
|
||||
color.Color
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BasicColor is an ANSI 3-bit or 4-bit color with a value from 0 to 15.
|
||||
type BasicColor uint8
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = BasicColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// Black is the ANSI black color.
|
||||
Black BasicColor = iota
|
||||
|
||||
// Red is the ANSI red color.
|
||||
Red
|
||||
|
||||
// Green is the ANSI green color.
|
||||
Green
|
||||
|
||||
// Yellow is the ANSI yellow color.
|
||||
Yellow
|
||||
|
||||
// Blue is the ANSI blue color.
|
||||
Blue
|
||||
|
||||
// Magenta is the ANSI magenta color.
|
||||
Magenta
|
||||
|
||||
// Cyan is the ANSI cyan color.
|
||||
Cyan
|
||||
|
||||
// White is the ANSI white color.
|
||||
White
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightBlack is the ANSI bright black color.
|
||||
BrightBlack
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightRed is the ANSI bright red color.
|
||||
BrightRed
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightGreen is the ANSI bright green color.
|
||||
BrightGreen
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightYellow is the ANSI bright yellow color.
|
||||
BrightYellow
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightBlue is the ANSI bright blue color.
|
||||
BrightBlue
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightMagenta is the ANSI bright magenta color.
|
||||
BrightMagenta
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightCyan is the ANSI bright cyan color.
|
||||
BrightCyan
|
||||
|
||||
// BrightWhite is the ANSI bright white color.
|
||||
BrightWhite
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c BasicColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
ansi := uint32(c)
|
||||
if ansi > 15 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0, 0xffff
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
r, g, b := ansiToRGB(ansi)
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExtendedColor is an ANSI 256 (8-bit) color with a value from 0 to 255.
|
||||
type ExtendedColor uint8
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = ExtendedColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c ExtendedColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r, g, b := ansiToRGB(uint32(c))
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TrueColor is a 24-bit color that can be used in the terminal.
|
||||
// This can be used to represent RGB colors.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, the color red can be represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TrueColor(0xff0000)
|
||||
type TrueColor uint32
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Color = TrueColor(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// RGBA returns the red, green, blue and alpha components of the color. It
|
||||
// satisfies the color.Color interface.
|
||||
func (c TrueColor) RGBA() (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r, g, b := hexToRGB(uint32(c))
|
||||
return toRGBA(r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ansiToRGB converts an ANSI color to a 24-bit RGB color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// r, g, b := ansiToRGB(57)
|
||||
func ansiToRGB(ansi uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
// For out-of-range values return black.
|
||||
if ansi > 255 {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Low ANSI.
|
||||
if ansi < 16 {
|
||||
h, ok := lowANSI[ansi]
|
||||
if !ok {
|
||||
return 0, 0, 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b := hexToRGB(h)
|
||||
return r, g, b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Grays.
|
||||
if ansi > 231 {
|
||||
s := (ansi-232)*10 + 8
|
||||
return s, s, s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ANSI256.
|
||||
n := ansi - 16
|
||||
b := n % 6
|
||||
g := (n - b) / 6 % 6
|
||||
r := (n - b - g*6) / 36 % 6
|
||||
for _, v := range []*uint32{&r, &g, &b} {
|
||||
if *v > 0 {
|
||||
c := *v*40 + 55
|
||||
*v = c
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return r, g, b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// hexToRGB converts a number in hexadecimal format to red, green, and blue
|
||||
// values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// r, g, b := hexToRGB(0x0000FF)
|
||||
func hexToRGB(hex uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
return hex >> 16, hex >> 8 & 0xff, hex & 0xff
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// toRGBA converts an RGB 8-bit color values to 32-bit color values suitable
|
||||
// for color.Color.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// color.Color requires 16-bit color values, so we duplicate the 8-bit values
|
||||
// to fill the 16-bit values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This always returns 0xffff (opaque) for the alpha channel.
|
||||
func toRGBA(r, g, b uint32) (uint32, uint32, uint32, uint32) {
|
||||
r |= r << 8
|
||||
g |= g << 8
|
||||
b |= b << 8
|
||||
return r, g, b, 0xffff
|
||||
}
|
||||
141
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
141
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/csi.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// CsiSequence represents a control sequence introducer (CSI) sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The sequence starts with a CSI sequence, CSI (0x9B) in a 8-bit environment
|
||||
// or ESC [ (0x1B 0x5B) in a 7-bit environment, followed by any number of
|
||||
// parameters in the range of 0x30-0x3F, then by any number of intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the range of 0x20-0x2F, then finally with a single final byte in the
|
||||
// range of 0x20-0x7E.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI P..P I..I F
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.
|
||||
type CsiSequence struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
// The command is a 32-bit integer containing the CSI command byte in the
|
||||
// lower 8 bits, the private marker in the next 8 bits, and the intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the next 8 bits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'u' | '?' << 8
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = CsiSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return CsiSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The string will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC [ P..P I..I F).
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns a buffer containing the sequence.
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b[")
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
if param >= 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The bytes will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC [ P..P I..I F).
|
||||
func (s CsiSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
17
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/ctrl.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestXTVersion is a control sequence that requests the terminal's XTVERSION. It responds with a DSR sequence identifying the version.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > Ps q
|
||||
// DCS > | text ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-PC-Style-Function-Keys
|
||||
const RequestXTVersion = "\x1b[>0q"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes is a control sequence that requests the
|
||||
// terminal's primary device attributes (DA1).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI c
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DA1.html
|
||||
const RequestPrimaryDeviceAttributes = "\x1b[c"
|
||||
190
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
190
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/cursor.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCursor (DECSC) is an escape sequence that saves the current cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC 7
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSC.html
|
||||
const SaveCursor = "\x1b7"
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursor (DECRC) is an escape sequence that restores the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ESC 8
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRC.html
|
||||
const RestoreCursor = "\x1b8"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestCursorPosition (CPR) is an escape sequence that requests the current
|
||||
// cursor position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI 6 n
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal will report the cursor position as a CSI sequence in the
|
||||
// following format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pl ; Pc R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number and Pc is the column number.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CPR.html
|
||||
const RequestCursorPosition = "\x1b[6n"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestExtendedCursorPosition (DECXCPR) is a sequence for requesting the
|
||||
// cursor position report including the current page number.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? 6 n
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal will report the cursor position as a CSI sequence in the
|
||||
// following format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pl ; Pc ; Pp R
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pl is the line number, Pc is the column number, and Pp is the page
|
||||
// number.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECXCPR.html
|
||||
const RequestExtendedCursorPosition = "\x1b[?6n"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorUp (CUU) returns a sequence for moving the cursor up n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n A
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUU.html
|
||||
func CursorUp(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "A"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorUp1 is a sequence for moving the cursor up one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorUp(1).
|
||||
const CursorUp1 = "\x1b[A"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown (CUD) returns a sequence for moving the cursor down n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n B
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUD.html
|
||||
func CursorDown(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "B"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorDown1 is a sequence for moving the cursor down one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorDown(1).
|
||||
const CursorDown1 = "\x1b[B"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight (CUF) returns a sequence for moving the cursor right n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n C
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUF.html
|
||||
func CursorRight(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "C"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorRight1 is a sequence for moving the cursor right one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorRight(1).
|
||||
const CursorRight1 = "\x1b[C"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft (CUB) returns a sequence for moving the cursor left n cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n D
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUB.html
|
||||
func CursorLeft(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "D"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorLeft1 is a sequence for moving the cursor left one cell.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to CursorLeft(1).
|
||||
const CursorLeft1 = "\x1b[D"
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorNextLine (CNL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the next line n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n E
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CNL.html
|
||||
func CursorNextLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "E"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CursorPreviousLine (CPL) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the
|
||||
// beginning of the previous line n times.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n F
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CPL.html
|
||||
func CursorPreviousLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "F"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursor (CUP) returns a sequence for moving the cursor to the given row
|
||||
// and column.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI n ; m H
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/CUP.html
|
||||
func MoveCursor(row, col int) string {
|
||||
if row < 0 {
|
||||
row = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if col < 0 {
|
||||
col = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(row) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(col) + "H"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MoveCursorOrigin is a sequence for moving the cursor to the upper left
|
||||
// corner of the screen. This is equivalent to MoveCursor(1, 1).
|
||||
const MoveCursorOrigin = "\x1b[1;1H"
|
||||
|
||||
// SaveCursorPosition (SCP or SCOSC) is a sequence for saving the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI s
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like Save, except the page number where the cursor is located is
|
||||
// not saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCOSC.html
|
||||
const SaveCursorPosition = "\x1b[s"
|
||||
|
||||
// RestoreCursorPosition (RCP or SCORC) is a sequence for restoring the cursor
|
||||
// position.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This acts like Restore, except the cursor stays on the same page where the
|
||||
// cursor was saved.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SCORC.html
|
||||
const RestoreCursorPosition = "\x1b[u"
|
||||
148
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
148
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/dcs.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// DcsSequence represents a Device Control String (DCS) escape sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The DCS sequence is used to send device control strings to the terminal. The
|
||||
// sequence starts with the C1 control code character DCS (0x9B) or ESC P in
|
||||
// 7-bit environments, followed by parameter bytes, intermediate bytes, a
|
||||
// command byte, followed by data bytes, and ends with the C1 control code
|
||||
// character ST (0x9C) or ESC \ in 7-bit environments.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This follows the parameter string format.
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.1
|
||||
type DcsSequence struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is a slice of integers, where each integer is a 32-bit integer
|
||||
// containing the parameter value in the lower 31 bits and a flag in the
|
||||
// most significant bit indicating whether there are more sub-parameters.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the string raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is the data between the final byte and the escape sequence terminator.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
// The command is a 32-bit integer containing the DCS command byte in the
|
||||
// lower 8 bits, the private marker in the next 8 bits, and the intermediate
|
||||
// byte in the next 8 bits.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS > 0 ; 1 $ r <data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Is represented as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 'r' | '>' << 8 | '$' << 16
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = DcsSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Marker() int {
|
||||
return parser.Marker(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(s.Cmd)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Param(i int) int {
|
||||
return parser.Param(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) HasMore(i int) bool {
|
||||
return parser.HasMore(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Subparams(i int) []int {
|
||||
return parser.Subparams(s.Params, i)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Len() int {
|
||||
return parser.Len(s.Params)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Range(fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
parser.Range(s.Params, fn)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the DCS sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return DcsSequence{
|
||||
Params: append([]int(nil), s.Params...),
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns a string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The string will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC P p..p i..i f <data> ESC \).
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns a buffer containing the sequence.
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bP")
|
||||
if m := s.Marker(); m != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(m))
|
||||
}
|
||||
s.Range(func(i, param int, hasMore bool) bool {
|
||||
if param >= -1 {
|
||||
b.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(param))
|
||||
}
|
||||
if i < len(s.Params)-1 {
|
||||
if hasMore {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(':')
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(';')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return true
|
||||
})
|
||||
if i := s.Intermediate(); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(s.Command()))
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteByte(ESC)
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\\')
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
// The bytes will always be in the 7-bit format i.e (ESC P p..p i..i F <data> ESC \).
|
||||
func (s DcsSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
7
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/doc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
// Package ansi defines common ANSI escape sequences based on the ECMA-48
|
||||
// specs.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// All sequences use 7-bit C1 control codes, which are supported by most
|
||||
// terminal emulators. OSC sequences are terminated by a BEL for wider
|
||||
// compatibility with terminals.
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/hyperlink.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
28
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/hyperlink.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strings"
|
||||
|
||||
// SetHyperlink returns a sequence for starting a hyperlink.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 8 ; Params ; Uri ST
|
||||
// OSC 8 ; Params ; Uri BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To reset the hyperlink, omit the URI.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/egmontkob/eb114294efbcd5adb1944c9f3cb5feda
|
||||
func SetHyperlink(uri string, params ...string) string {
|
||||
var p string
|
||||
if len(params) > 0 {
|
||||
p = strings.Join(params, ":")
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b]8;" + p + ";" + uri + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetHyperlink returns a sequence for resetting the hyperlink.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to SetHyperlink("", params...).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/egmontkob/eb114294efbcd5adb1944c9f3cb5feda
|
||||
func ResetHyperlink(params ...string) string {
|
||||
return SetHyperlink("", params...)
|
||||
}
|
||||
58
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
58
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/kitty.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// Kitty keyboard protocol progressive enhancement flags.
|
||||
// See: https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
const (
|
||||
KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes = 1 << iota
|
||||
KittyReportEventTypes
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAllKeys
|
||||
KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
|
||||
KittyAllFlags = KittyDisambiguateEscapeCodes | KittyReportEventTypes |
|
||||
KittyReportAlternateKeys | KittyReportAllKeys | KittyReportAssociatedKeys
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestKittyKeyboard is a sequence to request the terminal Kitty keyboard
|
||||
// protocol enabled flags.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/
|
||||
const RequestKittyKeyboard = "\x1b[?u"
|
||||
|
||||
// PushKittyKeyboard returns a sequence to push the given flags to the terminal
|
||||
// Kitty Keyboard stack.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > flags u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
func PushKittyKeyboard(flags int) string {
|
||||
var f string
|
||||
if flags > 0 {
|
||||
f = strconv.Itoa(flags)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1b[>" + f + "u"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableKittyKeyboard is a sequence to push zero into the terminal Kitty
|
||||
// Keyboard stack to disable the protocol.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This is equivalent to PushKittyKeyboard(0).
|
||||
const DisableKittyKeyboard = "\x1b[>0u"
|
||||
|
||||
// PopKittyKeyboard returns a sequence to pop n number of flags from the
|
||||
// terminal Kitty Keyboard stack.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI < flags u
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See https://sw.kovidgoyal.net/kitty/keyboard-protocol/#progressive-enhancement
|
||||
func PopKittyKeyboard(n int) string {
|
||||
var num string
|
||||
if n > 0 {
|
||||
num = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return "\x1b[<" + num + "u"
|
||||
}
|
||||
132
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
132
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/mode.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// This file define uses multiple sequences to set (SM), reset (RM), and request
|
||||
// (DECRQM) different ANSI and DEC modes.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/RM.html
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRQM.html
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The terminal then responds to the request with a Report Mode function
|
||||
// (DECRPM) in the format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ANSI format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI Pa ; Ps ; $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DEC format:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? Pa ; Ps $ y
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where Pa is the mode number, and Ps is the mode value.
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECRPM.html
|
||||
|
||||
// Application Cursor Keys (DECCKM) is a mode that determines whether the
|
||||
// cursor keys send ANSI cursor sequences or application sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECCKM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1h"
|
||||
DisableCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1l"
|
||||
RequestCursorKeys = "\x1b[?1$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Text Cursor Enable Mode (DECTCEM) is a mode that shows/hides the cursor.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECTCEM.html
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ShowCursor = "\x1b[?25h"
|
||||
HideCursor = "\x1b[?25l"
|
||||
RequestCursorVisibility = "\x1b[?25$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press and release.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouse = "\x1b[?1000h"
|
||||
DisableMouse = "\x1b[?1000l"
|
||||
RequestMouse = "\x1b[?1000$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// VT Hilite Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button presses, releases, and highlighted cells.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001h"
|
||||
DisableMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001l"
|
||||
RequestMouseHilite = "\x1b[?1001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Cell Motion Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse
|
||||
// reports on button press, release, and motion events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002h"
|
||||
DisableMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002l"
|
||||
RequestMouseCellMotion = "\x1b[?1002$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// All Mouse Tracking is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports on
|
||||
// button press, release, motion, and highlight events.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003h"
|
||||
DisableMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003l"
|
||||
RequestMouseAllMotion = "\x1b[?1003$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR Mouse Extension is a mode that determines whether the mouse reports events
|
||||
// formatted with SGR parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Mouse-Tracking
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006h"
|
||||
DisableMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006l"
|
||||
RequestMouseSgrExt = "\x1b[?1006$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Alternate Screen Buffer is a mode that determines whether the alternate screen
|
||||
// buffer is active.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-The-Alternate-Screen-Buffer
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049h"
|
||||
DisableAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049l"
|
||||
RequestAltScreenBuffer = "\x1b[?1049$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bracketed Paste Mode is a mode that determines whether pasted text is
|
||||
// bracketed with escape sequences.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://cirw.in/blog/bracketed-paste
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Bracketed-Paste-Mode
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004h"
|
||||
DisableBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004l"
|
||||
RequestBracketedPaste = "\x1b[?2004$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Synchronized Output Mode is a mode that determines whether output is
|
||||
// synchronized with the terminal.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://gist.github.com/christianparpart/d8a62cc1ab659194337d73e399004036
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026h"
|
||||
DisableSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026l"
|
||||
RequestSyncdOutput = "\x1b[?2026$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Win32Input is a mode that determines whether input is processed by the
|
||||
// Win32 console and Conpty.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/microsoft/terminal/blob/main/doc/specs/%234999%20-%20Improved%20keyboard%20handling%20in%20Conpty.md
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EnableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001h"
|
||||
DisableWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001l"
|
||||
RequestWin32Input = "\x1b[?9001$p"
|
||||
)
|
||||
69
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
69
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/osc.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// OscSequence represents an OSC sequence.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The sequence starts with a OSC sequence, OSC (0x9D) in a 8-bit environment
|
||||
// or ESC ] (0x1B 0x5D) in a 7-bit environment, followed by positive integer identifier,
|
||||
// then by arbitrary data terminated by a ST (0x9C) in a 8-bit environment,
|
||||
// ESC \ (0x1B 0x5C) in a 7-bit environment, or BEL (0x07) for backwards compatibility.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC Ps ; Pt ST
|
||||
// OSC Ps ; Pt BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.7.
|
||||
type OscSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence including the identifier
|
||||
// command.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command of the sequence.
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = OscSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return s.Cmd
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Params returns the parameters of the OSC sequence split by ';'.
|
||||
// The first element is the identifier command.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Params() []string {
|
||||
return strings.Split(string(s.Data), ";")
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return OscSequence{
|
||||
Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...),
|
||||
Cmd: s.Cmd,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
// To be more compatible with different terminal, this will always return a
|
||||
// 7-bit formatted sequence, terminated by BEL.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the OSC sequence.
|
||||
// To be more compatible with different terminal, this will always return a
|
||||
// 7-bit formatted sequence, terminated by BEL.
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s OscSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b]")
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteByte(BEL)
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
45
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/params.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
45
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/params.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Params parses and returns a list of control sequence parameters.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Parameters are positive integers separated by semicolons. Empty parameters
|
||||
// default to zero. Parameters can have sub-parameters separated by colons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Any non-parameter bytes are ignored. This includes bytes that are not in the
|
||||
// range of 0x30-0x3B.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See ECMA-48 § 5.4.1.
|
||||
func Params(p []byte) [][]uint {
|
||||
if len(p) == 0 {
|
||||
return [][]uint{}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Filter out non-parameter bytes i.e. non 0x30-0x3B.
|
||||
p = bytes.TrimFunc(p, func(r rune) bool {
|
||||
return r < 0x30 || r > 0x3B
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
parts := bytes.Split(p, []byte{';'})
|
||||
params := make([][]uint, len(parts))
|
||||
for i, part := range parts {
|
||||
sparts := bytes.Split(part, []byte{':'})
|
||||
params[i] = make([]uint, len(sparts))
|
||||
for j, spart := range sparts {
|
||||
params[i][j] = bytesToUint16(spart)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return params
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func bytesToUint16(b []byte) uint {
|
||||
var n uint
|
||||
for _, c := range b {
|
||||
n = n*10 + uint(c-'0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
357
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
357
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,357 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ParserDispatcher is a function that dispatches a sequence.
|
||||
type ParserDispatcher func(Sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
// Parser represents a DEC ANSI compatible sequence parser.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It uses a state machine to parse ANSI escape sequences and control
|
||||
// characters. The parser is designed to be used with a terminal emulator or
|
||||
// similar application that needs to parse ANSI escape sequences and control
|
||||
// characters.
|
||||
// See package [parser] for more information.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//go:generate go run ./gen.go
|
||||
type Parser struct {
|
||||
// Params contains the raw parameters of the sequence.
|
||||
// These parameters used when constructing CSI and DCS sequences.
|
||||
Params []int
|
||||
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
// These data used when constructing OSC, DCS, SOS, PM, and APC sequences.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// DataLen keeps track of the length of the data buffer.
|
||||
// If DataLen is -1, the data buffer is unlimited and will grow as needed.
|
||||
// Otherwise, DataLen is limited by the size of the Data buffer.
|
||||
DataLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// ParamsLen keeps track of the number of parameters.
|
||||
// This is limited by the size of the Params buffer.
|
||||
ParamsLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// Cmd contains the raw command along with the private marker and
|
||||
// intermediate bytes of the sequence.
|
||||
// The first lower byte contains the command byte, the next byte contains
|
||||
// the private marker, and the next byte contains the intermediate byte.
|
||||
Cmd int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneLen keeps track of the number of bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneLen int
|
||||
|
||||
// RuneBuf contains the bytes collected for a UTF-8 rune.
|
||||
RuneBuf [utf8.MaxRune]byte
|
||||
|
||||
// State is the current state of the parser.
|
||||
State byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NewParser returns a new parser with the given sizes allocated.
|
||||
// If dataSize is zero, the underlying data buffer will be unlimited and will
|
||||
// grow as needed.
|
||||
func NewParser(paramsSize, dataSize int) *Parser {
|
||||
s := &Parser{
|
||||
Params: make([]int, paramsSize),
|
||||
Data: make([]byte, dataSize),
|
||||
}
|
||||
if dataSize <= 0 {
|
||||
s.DataLen = -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset resets the parser to its initial state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Reset() {
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// clear clears the parser parameters and command.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) clear() {
|
||||
if len(p.Params) > 0 {
|
||||
p.Params[0] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.ParamsLen = 0
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StateName returns the name of the current state.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) StateName() string {
|
||||
return parser.StateNames[p.State]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Parse parses the given dispatcher and byte buffer.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Parse(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b []byte) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(b); i++ {
|
||||
p.Advance(dispatcher, b[i], i < len(b)-1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Advance advances the parser with the given dispatcher and byte.
|
||||
func (p *Parser) Advance(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.Utf8State:
|
||||
// We handle UTF-8 here.
|
||||
return p.advanceUtf8(dispatcher, b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return p.advance(dispatcher, b, more)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) collectRune(b byte) {
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < utf8.UTFMax {
|
||||
p.RuneBuf[p.RuneLen] = b
|
||||
p.RuneLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advanceUtf8(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, b byte) parser.Action {
|
||||
// Collect UTF-8 rune bytes.
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
rw := utf8ByteLen(p.RuneBuf[0])
|
||||
if rw == -1 {
|
||||
// We panic here because the first byte comes from the state machine,
|
||||
// if this panics, it means there is a bug in the state machine!
|
||||
panic("invalid rune") // unreachable
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.RuneLen < rw {
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We have enough bytes to decode the rune
|
||||
bts := p.RuneBuf[:rw]
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(bts)
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = parser.GroundState
|
||||
p.RuneLen = 0
|
||||
|
||||
return parser.NoneAction
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) advance(d ParserDispatcher, b byte, more bool) parser.Action {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(p.State, b)
|
||||
|
||||
// We need to clear the parser state if the state changes from EscapeState.
|
||||
// This is because when we enter the EscapeState, we don't get a chance to
|
||||
// clear the parser state. For example, when a sequence terminates with a
|
||||
// ST (\x1b\\ or \x9c), we dispatch the current sequence and transition to
|
||||
// EscapeState. However, the parser state is not cleared in this case and
|
||||
// we need to clear it here before dispatching the esc sequence.
|
||||
if p.State != state {
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ClearAction, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
if action == parser.PutAction &&
|
||||
p.State == parser.DcsEntryState && state == parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// XXX: This is a special case where we need to start collecting
|
||||
// non-string parameterized data i.e. doesn't follow the ECMA-48 §
|
||||
// 5.4.1 string parameters format.
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.StartAction, 0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Handle special cases
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case b == ESC && p.State == parser.EscapeState:
|
||||
// Two ESCs in a row
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
if !more {
|
||||
// Two ESCs at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case b == ESC && !more:
|
||||
// Last byte is an ESC
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.ExecuteAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'P' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC P (DCS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == 'X' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC X (SOS) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '[' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC [ (CSI) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == ']' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ] (OSC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '^' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC ^ (PM) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
case p.State == parser.EscapeState && b == '_' && !more:
|
||||
// ESC _ (APC) at the end of the buffer
|
||||
p.performAction(d, parser.DispatchAction, b)
|
||||
default:
|
||||
p.performAction(d, action, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.State = state
|
||||
|
||||
return action
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (p *Parser) performAction(dispatcher ParserDispatcher, action parser.Action, b byte) {
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.IgnoreAction:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ClearAction:
|
||||
p.clear()
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b) > 1 {
|
||||
p.collectRune(b)
|
||||
} else if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(Rune(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
if dispatcher != nil {
|
||||
dispatcher(ControlCode(b))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.MarkerAction:
|
||||
// Collect private marker
|
||||
// we only store the last marker
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.MarkerShift
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.CollectAction:
|
||||
// Collect intermediate bytes
|
||||
// we only store the last intermediate byte
|
||||
p.Cmd &^= 0xff << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b) << parser.IntermedShift
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.ParamAction:
|
||||
// Collect parameters
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen >= len(p.Params) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b >= '0' && b <= '9' {
|
||||
if p.Params[p.ParamsLen] == parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] *= 10
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] += int(b - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ':' {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] |= parser.HasMoreFlag
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if b == ';' || b == ':' {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params) {
|
||||
p.Params[p.ParamsLen] = parser.MissingParam
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.StartAction:
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = make([]byte, 0)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.DataLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.State >= parser.DcsEntryState && p.State <= parser.DcsStringState {
|
||||
// Collect the command byte for DCS
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
p.Cmd = parser.MissingCommand
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.PutAction:
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
if b == ';' && p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
// Try to parse the command
|
||||
datalen := len(p.Data)
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
datalen = p.DataLen
|
||||
}
|
||||
for i := 0; i < datalen; i++ {
|
||||
d := p.Data[i]
|
||||
if d < '0' || d > '9' {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if p.Cmd == parser.MissingCommand {
|
||||
p.Cmd = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
p.Cmd *= 10
|
||||
p.Cmd += int(d - '0')
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if p.DataLen < 0 {
|
||||
p.Data = append(p.Data, b)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if p.DataLen < len(p.Data) {
|
||||
p.Data[p.DataLen] = b
|
||||
p.DataLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case parser.DispatchAction:
|
||||
// Increment the last parameter
|
||||
if p.ParamsLen > 0 && p.ParamsLen < len(p.Params)-1 ||
|
||||
p.ParamsLen == 0 && len(p.Params) > 0 && p.Params[0] != parser.MissingParam {
|
||||
p.ParamsLen++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if dispatcher == nil {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var seq Sequence
|
||||
data := p.Data
|
||||
if p.DataLen >= 0 {
|
||||
data = data[:p.DataLen]
|
||||
}
|
||||
switch p.State {
|
||||
case parser.CsiEntryState, parser.CsiParamState, parser.CsiIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = CsiSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen]}
|
||||
case parser.EscapeState, parser.EscapeIntermediateState:
|
||||
p.Cmd |= int(b)
|
||||
seq = EscSequence(p.Cmd)
|
||||
case parser.DcsEntryState, parser.DcsParamState, parser.DcsIntermediateState, parser.DcsStringState:
|
||||
seq = DcsSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Params: p.Params[:p.ParamsLen], Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.OscStringState:
|
||||
seq = OscSequence{Cmd: p.Cmd, Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.SosStringState:
|
||||
seq = SosSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.PmStringState:
|
||||
seq = PmSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
case parser.ApcStringState:
|
||||
seq = ApcSequence{Data: data}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dispatcher(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func utf8ByteLen(b byte) int {
|
||||
if b <= 0b0111_1111 { // 0x00-0x7F
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1100_0000 && b <= 0b1101_1111 { // 0xC0-0xDF
|
||||
return 2
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1110_0000 && b <= 0b1110_1111 { // 0xE0-0xEF
|
||||
return 3
|
||||
} else if b >= 0b1111_0000 && b <= 0b1111_0111 { // 0xF0-0xF7
|
||||
return 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
78
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/const.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
78
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/const.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
// Action is a DEC ANSI parser action.
|
||||
type Action = byte
|
||||
|
||||
// These are the actions that the parser can take.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
NoneAction Action = iota
|
||||
ClearAction
|
||||
CollectAction
|
||||
MarkerAction
|
||||
DispatchAction
|
||||
ExecuteAction
|
||||
StartAction // Start of a data string
|
||||
PutAction // Put into the data string
|
||||
ParamAction
|
||||
PrintAction
|
||||
|
||||
IgnoreAction = NoneAction
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// nolint: unused
|
||||
var ActionNames = []string{
|
||||
"NoneAction",
|
||||
"ClearAction",
|
||||
"CollectAction",
|
||||
"MarkerAction",
|
||||
"DispatchAction",
|
||||
"ExecuteAction",
|
||||
"StartAction",
|
||||
"PutAction",
|
||||
"ParamAction",
|
||||
"PrintAction",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// State is a DEC ANSI parser state.
|
||||
type State = byte
|
||||
|
||||
// These are the states that the parser can be in.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
GroundState State = iota
|
||||
CsiEntryState
|
||||
CsiIntermediateState
|
||||
CsiParamState
|
||||
DcsEntryState
|
||||
DcsIntermediateState
|
||||
DcsParamState
|
||||
DcsStringState
|
||||
EscapeState
|
||||
EscapeIntermediateState
|
||||
OscStringState
|
||||
SosStringState
|
||||
PmStringState
|
||||
ApcStringState
|
||||
|
||||
// Utf8State is not part of the DEC ANSI standard. It is used to handle
|
||||
// UTF-8 sequences.
|
||||
Utf8State
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// nolint: unused
|
||||
var StateNames = []string{
|
||||
"GroundState",
|
||||
"CsiEntryState",
|
||||
"CsiIntermediateState",
|
||||
"CsiParamState",
|
||||
"DcsEntryState",
|
||||
"DcsIntermediateState",
|
||||
"DcsParamState",
|
||||
"DcsStringState",
|
||||
"EscapeState",
|
||||
"EscapeIntermediateState",
|
||||
"OscStringState",
|
||||
"SosStringState",
|
||||
"PmStringState",
|
||||
"ApcStringState",
|
||||
"Utf8State",
|
||||
}
|
||||
136
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/seq.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
136
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/seq.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
import "math"
|
||||
|
||||
// Shift and masks for sequence parameters and intermediates.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
MarkerShift = 8
|
||||
IntermedShift = 16
|
||||
CommandMask = 0xff
|
||||
HasMoreFlag = math.MinInt32
|
||||
ParamMask = ^HasMoreFlag
|
||||
MissingParam = ParamMask
|
||||
MissingCommand = MissingParam
|
||||
MaxParam = math.MaxUint16 // the maximum value a parameter can have
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
const (
|
||||
// MaxParamsSize is the maximum number of parameters a sequence can have.
|
||||
MaxParamsSize = 32
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultParamValue is the default value used for missing parameters.
|
||||
DefaultParamValue = 0
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Marker returns the marker byte of the sequence.
|
||||
// This is always gonna be one of the following '<' '=' '>' '?' and in the
|
||||
// range of 0x3C-0x3F.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have a marker.
|
||||
func Marker(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return (cmd >> MarkerShift) & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the sequence.
|
||||
// An intermediate byte is in the range of 0x20-0x2F. This includes these
|
||||
// characters from ' ', '!', '"', '#', '$', '%', '&', ”', '(', ')', '*', '+',
|
||||
// ',', '-', '.', '/'.
|
||||
// Zero is returned if the sequence does not have an intermediate byte.
|
||||
func Intermediate(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return (cmd >> IntermedShift) & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the CSI sequence.
|
||||
func Command(cmd int) int {
|
||||
return cmd & CommandMask
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Param returns the parameter at the given index.
|
||||
// It returns -1 if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func Param(params []int, i int) int {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i < 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p := params[i] & ParamMask
|
||||
if p == MissingParam {
|
||||
return -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return p
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HasMore returns true if the parameter has more sub-parameters.
|
||||
func HasMore(params []int, i int) bool {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return params[i]&HasMoreFlag != 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Subparams returns the sub-parameters of the given parameter.
|
||||
// It returns nil if the parameter does not exist.
|
||||
func Subparams(params []int, i int) []int {
|
||||
if len(params) == 0 || i < 0 || i >= len(params) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Count the number of parameters before the given parameter index.
|
||||
var count int
|
||||
var j int
|
||||
for j = 0; j < len(params); j++ {
|
||||
if count == i {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, j) {
|
||||
count++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if count > i || j >= len(params) {
|
||||
return nil
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var subs []int
|
||||
for ; j < len(params); j++ {
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, j) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
p := Param(params, j)
|
||||
if p == -1 {
|
||||
p = DefaultParamValue
|
||||
}
|
||||
subs = append(subs, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
p := Param(params, j)
|
||||
if p == -1 {
|
||||
p = DefaultParamValue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return append(subs, p)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Len returns the number of parameters in the sequence.
|
||||
// This will return the number of parameters in the sequence, excluding any
|
||||
// sub-parameters.
|
||||
func Len(params []int) int {
|
||||
var n int
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(params); i++ {
|
||||
if !HasMore(params, i) {
|
||||
n++
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return n
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Range iterates over the parameters of the sequence and calls the given
|
||||
// function for each parameter.
|
||||
// The function should return false to stop the iteration.
|
||||
func Range(params []int, fn func(i int, param int, hasMore bool) bool) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(params); i++ {
|
||||
if !fn(i, Param(params, i), HasMore(params, i)) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
269
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
269
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser/transition_table.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
|
||||
package parser
|
||||
|
||||
// Table values are generated like this:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// index: currentState << IndexStateShift | charCode
|
||||
// value: action << TransitionActionShift | nextState
|
||||
const (
|
||||
TransitionActionShift = 4
|
||||
TransitionStateMask = 15
|
||||
IndexStateShift = 8
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultTableSize is the default size of the transition table.
|
||||
DefaultTableSize = 4096
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Table is a DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
var Table = GenerateTransitionTable()
|
||||
|
||||
// TransitionTable is a DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
// https://vt100.net/emu/dec_ansi_parser
|
||||
type TransitionTable []byte
|
||||
|
||||
// NewTransitionTable returns a new DEC ANSI transition table.
|
||||
func NewTransitionTable(size int) TransitionTable {
|
||||
if size <= 0 {
|
||||
size = DefaultTableSize
|
||||
}
|
||||
return TransitionTable(make([]byte, size))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetDefault sets default transition.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) SetDefault(action Action, state State) {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(t); i++ {
|
||||
t[i] = action<<TransitionActionShift | state
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddOne adds a transition.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddOne(code byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
idx := int(state)<<IndexStateShift | int(code)
|
||||
value := action<<TransitionActionShift | next
|
||||
t[idx] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddMany adds many transitions.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddMany(codes []byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
for _, code := range codes {
|
||||
t.AddOne(code, state, action, next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// AddRange adds a range of transitions.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) AddRange(start, end byte, state State, action Action, next State) {
|
||||
for i := int(start); i <= int(end); i++ {
|
||||
t.AddOne(byte(i), state, action, next)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transition returns the next state and action for the given state and byte.
|
||||
func (t TransitionTable) Transition(state State, code byte) (State, Action) {
|
||||
index := int(state)<<IndexStateShift | int(code)
|
||||
value := t[index]
|
||||
return value & TransitionStateMask, value >> TransitionActionShift
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// byte range macro
|
||||
func r(start, end byte) []byte {
|
||||
var a []byte
|
||||
for i := int(start); i <= int(end); i++ {
|
||||
a = append(a, byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
return a
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// GenerateTransitionTable generates a DEC ANSI transition table compatible
|
||||
// with the VT500-series of terminals. This implementation includes a few
|
||||
// modifications that include:
|
||||
// - A new Utf8State is introduced to handle UTF8 sequences.
|
||||
// - Osc and Dcs data accept UTF8 sequences by extending the printable range
|
||||
// to 0xFF and 0xFE respectively.
|
||||
// - We don't ignore 0x3A (':') when building Csi and Dcs parameters and
|
||||
// instead use it to denote sub-parameters.
|
||||
// - Support dispatching SosPmApc sequences.
|
||||
func GenerateTransitionTable() TransitionTable {
|
||||
table := NewTransitionTable(DefaultTableSize)
|
||||
table.SetDefault(NoneAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Anywhere
|
||||
for _, state := range r(GroundState, Utf8State) {
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1a, 0x99, 0x9a}, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0x8F, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x90, 0x97, state, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Escape
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, state, ClearAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> SosStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x98, state, StartAction, SosStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> PmStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9E, state, StartAction, PmStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> ApcStringState
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9F, state, StartAction, ApcStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> CsiEntry
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9B, state, ClearAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> DcsEntry
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x90, state, ClearAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> OscString
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9D, state, StartAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
// Anywhere -> Utf8
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xC2, 0xDF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 2 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xE0, 0xEF, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 3 byte sequence
|
||||
table.AddRange(0xF0, 0xF4, state, PrintAction, Utf8State) // UTF8 4 byte sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, GroundState, ExecuteAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7F, GroundState, PrintAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// EscapeIntermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, EscapeIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, EscapeIntermediateState, CollectAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, EscapeIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
// EscapeIntermediate -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x7E, EscapeIntermediateState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Escape
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, EscapeState, ExecuteAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, EscapeState, IgnoreAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x4F, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x51, 0x57, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x59, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x5A, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x5C, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x60, 0x7E, EscapeState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Escape_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, EscapeState, CollectAction, EscapeIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Sos_pm_apc_string
|
||||
table.AddOne('X', EscapeState, StartAction, SosStringState) // SOS
|
||||
table.AddOne('^', EscapeState, StartAction, PmStringState) // PM
|
||||
table.AddOne('_', EscapeState, StartAction, ApcStringState) // APC
|
||||
// Escape -> Dcs_entry
|
||||
table.AddOne('P', EscapeState, ClearAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Csi_entry
|
||||
table.AddOne('[', EscapeState, ClearAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Escape -> Osc_string
|
||||
table.AddOne(']', EscapeState, StartAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sos_pm_apc_string
|
||||
for _, state := range r(SosStringState, ApcStringState) {
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7F, state, PutAction, state)
|
||||
// ESC, ST, CAN, and SUB terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, state, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, state, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, state, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_entry
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x07, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x0E, 0x17, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsEntryState, IgnoreAction, DcsEntryState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsEntryState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, DcsEntryState, ParamAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, DcsEntryState, MarkerAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
// Dcs_entry -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x08, 0x0D, DcsEntryState, PutAction, DcsStringState) // Follows ECMA-48 § 8.3.27
|
||||
// XXX: allows passing ESC (not a ECMA-48 standard) this to allow for
|
||||
// passthrough of ANSI sequences like in Screen or Tmux passthrough mode.
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, DcsEntryState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsEntryState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsIntermediateState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_intermediate -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3F, DcsIntermediateState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsIntermediateState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, DcsParamState, ParamAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, DcsParamState, IgnoreAction, DcsParamState)
|
||||
// Dcs_param -> Dcs_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, DcsParamState, CollectAction, DcsIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Dcs_param -> Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, DcsParamState, StartAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Dcs_passthrough
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x7E, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, DcsStringState, IgnoreAction, DcsStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x80, 0xFF, DcsStringState, PutAction, DcsStringState) // Allow Utf8 characters by extending the printable range from 0x7F to 0xFF
|
||||
// ST, CAN, SUB, and ESC terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, DcsStringState, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, DcsStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, DcsStringState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiParamState, ExecuteAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, CsiParamState, ParamAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiParamState, IgnoreAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, CsiParamState, IgnoreAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
// Csi_param -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiParamState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_param -> Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiParamState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiIntermediateState, ExecuteAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiIntermediateState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiIntermediateState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_intermediate -> Csi_ignore
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3F, CsiIntermediateState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Csi_entry
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x17, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, CsiEntryState, ExecuteAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x7F, CsiEntryState, IgnoreAction, CsiEntryState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Ground
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x40, 0x7E, CsiEntryState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Csi_intermediate
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0x2F, CsiEntryState, CollectAction, CsiIntermediateState)
|
||||
// Csi_entry -> Csi_param
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x30, 0x3B, CsiEntryState, ParamAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x3C, 0x3F, CsiEntryState, MarkerAction, CsiParamState)
|
||||
|
||||
// Osc_string
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x00, 0x06, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x08, 0x17, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x19, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x1C, 0x1F, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, OscStringState)
|
||||
table.AddRange(0x20, 0xFF, OscStringState, PutAction, OscStringState) // Allow Utf8 characters by extending the printable range from 0x7F to 0xFF
|
||||
|
||||
// ST, CAN, SUB, ESC, and BEL terminate the sequence
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x1B, OscStringState, DispatchAction, EscapeState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x07, OscStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddOne(0x9C, OscStringState, DispatchAction, GroundState)
|
||||
table.AddMany([]byte{0x18, 0x1A}, OscStringState, IgnoreAction, GroundState)
|
||||
|
||||
return table
|
||||
}
|
||||
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/passthrough.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
63
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/passthrough.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ScreenPassthrough wraps the given ANSI sequence in a DCS passthrough
|
||||
// sequence to be sent to the outer terminal. This is used to send raw escape
|
||||
// sequences to the outer terminal when running inside GNU Screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS <data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: Screen limits the length of string sequences to 768 bytes (since 2014).
|
||||
// Use zero to indicate no limit, otherwise, this will chunk the returned
|
||||
// string into limit sized chunks.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://www.gnu.org/software/screen/manual/screen.html#String-Escapes
|
||||
// See: https://git.savannah.gnu.org/cgit/screen.git/tree/src/screen.h?id=c184c6ec27683ff1a860c45be5cf520d896fd2ef#n44
|
||||
func ScreenPassthrough(seq string, limit int) string {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bP")
|
||||
if limit > 0 {
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(seq); i += limit {
|
||||
end := i + limit
|
||||
if end > len(seq) {
|
||||
end = len(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString(seq[i:end])
|
||||
if end < len(seq) {
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\\x1bP")
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
b.WriteString(seq)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// TmuxPassthrough wraps the given ANSI sequence in a special DCS passthrough
|
||||
// sequence to be sent to the outer terminal. This is used to send raw escape
|
||||
// sequences to the outer terminal when running inside Tmux.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS tmux ; <escaped-data> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where <escaped-data> is the given sequence in which all occurrences of ESC
|
||||
// (0x1b) are doubled i.e. replaced with ESC ESC (0x1b 0x1b).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: this needs the `allow-passthrough` option to be set to `on`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://github.com/tmux/tmux/wiki/FAQ#what-is-the-passthrough-escape-sequence-and-how-do-i-use-it
|
||||
func TmuxPassthrough(seq string) string {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1bPtmux;")
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(seq); i++ {
|
||||
if seq[i] == ESC {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(ESC)
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(seq[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return b.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
126
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
126
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/screen.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import "strconv"
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay (ED) clears the screen or parts of the screen. Possible values:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Clear from cursor to end of screen.
|
||||
// 1: Clear from cursor to beginning of the screen.
|
||||
// 2: Clear entire screen (and moves cursor to upper left on DOS).
|
||||
// 3: Clear entire screen and delete all lines saved in the scrollback buffer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> J
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/ED.html
|
||||
func EraseDisplay(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "J"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseDisplay constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseDisplay function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseDisplayRight = "\x1b[0J"
|
||||
EraseDisplayLeft = "\x1b[1J"
|
||||
EraseEntireDisplay = "\x1b[2J"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine (EL) clears the current line or parts of the line. Possible values:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 0: Clear from cursor to end of line.
|
||||
// 1: Clear from cursor to beginning of the line.
|
||||
// 2: Clear entire line.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The cursor position is not affected.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> K
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/EL.html
|
||||
func EraseLine(n int) string {
|
||||
if n < 0 {
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(n) + "K"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EraseLine constants.
|
||||
// These are the possible values for the EraseLine function.
|
||||
const (
|
||||
EraseLineRight = "\x1b[0K"
|
||||
EraseLineLeft = "\x1b[1K"
|
||||
EraseEntireLine = "\x1b[2K"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollUp (SU) scrolls the screen up n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// bottom of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> S
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SU.html
|
||||
func ScrollUp(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "S"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ScrollDown (SD) scrolls the screen down n lines. New lines are added at the
|
||||
// top of the screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> T
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/SD.html
|
||||
func ScrollDown(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "T"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InsertLine (IL) inserts n blank lines at the current cursor position.
|
||||
// Existing lines are moved down.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> L
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/IL.html
|
||||
func InsertLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "L"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DeleteLine (DL) deletes n lines at the current cursor position. Existing
|
||||
// lines are moved up.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <n> M
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DL.html
|
||||
func DeleteLine(n int) string {
|
||||
var s string
|
||||
if n > 1 {
|
||||
s = strconv.Itoa(n)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + s + "M"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetScrollingRegion (DECSTBM) sets the top and bottom margins for the scrolling
|
||||
// region. The default is the entire screen.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI <top> ; <bottom> r
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://vt100.net/docs/vt510-rm/DECSTBM.html
|
||||
func SetScrollingRegion(t, b int) string {
|
||||
if t < 0 {
|
||||
t = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
if b < 0 {
|
||||
b = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strconv.Itoa(t) + ";" + strconv.Itoa(b) + "r"
|
||||
}
|
||||
199
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
199
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/sequence.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Sequence represents an ANSI sequence. This can be a control sequence, escape
|
||||
// sequence, a printable character, etc.
|
||||
type Sequence interface {
|
||||
// String returns the string representation of the sequence.
|
||||
String() string
|
||||
// Bytes returns the byte representation of the sequence.
|
||||
Bytes() []byte
|
||||
// Clone returns a copy of the sequence.
|
||||
Clone() Sequence
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Rune represents a printable character.
|
||||
type Rune rune
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = Rune(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return []byte(string(r))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) String() string {
|
||||
return string(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (r Rune) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return r
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ControlCode represents a control code character. This is a character that
|
||||
// is not printable and is used to control the terminal. This would be a
|
||||
// character in the C0 or C1 set in the range of 0x00-0x1F and 0x80-0x9F.
|
||||
type ControlCode byte
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = ControlCode(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return []byte{byte(c)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) String() string {
|
||||
return string(c)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (c ControlCode) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return c
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// EscSequence represents an escape sequence.
|
||||
type EscSequence int
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = EscSequence(0)
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
if i := parser.Intermediate(int(e)); i != 0 {
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(i))
|
||||
}
|
||||
b.WriteByte(byte(e.Command()))
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return e.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return e.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return e
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Command returns the command byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Command() int {
|
||||
return parser.Command(int(e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Intermediate returns the intermediate byte of the escape sequence.
|
||||
func (e EscSequence) Intermediate() int {
|
||||
return parser.Intermediate(int(e))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SosSequence represents a SOS sequence.
|
||||
type SosSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &SosSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return SosSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func (s SosSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('X')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// PmSequence represents a PM sequence.
|
||||
type PmSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &PmSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return PmSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the PM sequence.
|
||||
func (s PmSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('^')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ApcSequence represents an APC sequence.
|
||||
type ApcSequence struct {
|
||||
// Data contains the raw data of the sequence.
|
||||
Data []byte
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var _ Sequence = &ApcSequence{}
|
||||
|
||||
// Clone implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) Clone() Sequence {
|
||||
return ApcSequence{Data: append([]byte(nil), s.Data...)}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bytes implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) Bytes() []byte {
|
||||
return s.buffer().Bytes()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// String implements Sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) String() string {
|
||||
return s.buffer().String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// buffer returns the buffer of the APC sequence.
|
||||
func (s ApcSequence) buffer() *bytes.Buffer {
|
||||
var b bytes.Buffer
|
||||
b.WriteByte('\x1b')
|
||||
b.WriteByte('_')
|
||||
b.Write(s.Data)
|
||||
b.WriteString("\x1b\\")
|
||||
return &b
|
||||
}
|
||||
296
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
296
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/style.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,296 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
"strconv"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ResetStyle is a SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style sequence that resets
|
||||
// all attributes.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
const ResetStyle = "\x1b[m"
|
||||
|
||||
// Attr is a SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attribute.
|
||||
type Attr = string
|
||||
|
||||
// Style represents an ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style.
|
||||
type Style []Attr
|
||||
|
||||
// String returns the ANSI SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style sequence for
|
||||
// the given style.
|
||||
func (s Style) String() string {
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return ResetStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
return "\x1b[" + strings.Join(s, ";") + "m"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Styled returns a styled string with the given style applied.
|
||||
func (s Style) Styled(str string) string {
|
||||
if len(s) == 0 {
|
||||
return str
|
||||
}
|
||||
return s.String() + str + ResetStyle
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset appends the reset style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reset() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ResetAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bold appends the bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Bold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BoldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Faint appends the faint style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Faint() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, FaintAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Italic appends the italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Italic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ItalicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Underline appends the underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Underline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DoubleUnderline appends the double underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DoubleUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DoubleUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// CurlyUnderline appends the curly underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) CurlyUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, CurlyUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DottedUnderline appends the dotted underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DottedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DottedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DashedUnderline appends the dashed underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DashedUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DashedUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SlowBlink appends the slow blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) SlowBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, SlowBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// RapidBlink appends the rapid blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) RapidBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, RapidBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse appends the reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Reverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ReverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Conceal appends the conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Conceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ConcealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Strikethrough appends the strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) Strikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, StrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBold appends the no bold style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBold() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBoldAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NormalIntensity appends the normal intensity style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NormalIntensity() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NormalIntensityAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoItalic appends the no italic style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoItalic() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoItalicAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoUnderline appends the no underline style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoUnderline() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoUnderlineAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoBlink appends the no blink style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoBlink() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoBlinkAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoReverse appends the no reverse style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoReverse() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoReverseAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoConceal appends the no conceal style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoConceal() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoConcealAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// NoStrikethrough appends the no strikethrough style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) NoStrikethrough() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, NoStrikethroughAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultForegroundColor appends the default foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultForegroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultForegroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultBackgroundColor appends the default background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultBackgroundColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultBackgroundColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// DefaultUnderlineColor appends the default underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) DefaultUnderlineColor() Style {
|
||||
return append(s, DefaultUnderlineColorAttr)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColor appends the foreground color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) ForegroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, ForegroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColor appends the background color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) BackgroundColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, BackgroundColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColor appends the underline color style attribute to the style.
|
||||
func (s Style) UnderlineColor(c Color) Style {
|
||||
return append(s, UnderlineColorAttr(c))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SGR (Select Graphic Rendition) style attributes.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
const (
|
||||
ResetAttr Attr = "0"
|
||||
BoldAttr Attr = "1"
|
||||
FaintAttr Attr = "2"
|
||||
ItalicAttr Attr = "3"
|
||||
UnderlineAttr Attr = "4"
|
||||
DoubleUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:2"
|
||||
CurlyUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:3"
|
||||
DottedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:4"
|
||||
DashedUnderlineAttr Attr = "4:5"
|
||||
SlowBlinkAttr Attr = "5"
|
||||
RapidBlinkAttr Attr = "6"
|
||||
ReverseAttr Attr = "7"
|
||||
ConcealAttr Attr = "8"
|
||||
StrikethroughAttr Attr = "9"
|
||||
NoBoldAttr Attr = "21" // Some terminals treat this as double underline.
|
||||
NormalIntensityAttr Attr = "22"
|
||||
NoItalicAttr Attr = "23"
|
||||
NoUnderlineAttr Attr = "24"
|
||||
NoBlinkAttr Attr = "25"
|
||||
NoReverseAttr Attr = "27"
|
||||
NoConcealAttr Attr = "28"
|
||||
NoStrikethroughAttr Attr = "29"
|
||||
DefaultForegroundColorAttr Attr = "39"
|
||||
DefaultBackgroundColorAttr Attr = "49"
|
||||
DefaultUnderlineColorAttr Attr = "59"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// ForegroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given foreground
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func ForegroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "3<n>" or "9<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "3" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else if c < 16 {
|
||||
return "9" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "38;5;<n>"
|
||||
return "38;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "38;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultForegroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// BackgroundColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given background
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func BackgroundColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
// 3-bit or 4-bit ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "4<n>" or "10<n>" where n is the color number from 0 to 7
|
||||
if c < 8 {
|
||||
return "4" + string('0'+c)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return "10" + string('0'+c-8)
|
||||
}
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI foreground
|
||||
// "48;5;<n>"
|
||||
return "48;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "48;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultBackgroundColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// UnderlineColorAttr returns the style SGR attribute for the given underline
|
||||
// color.
|
||||
// See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#SGR_(Select_Graphic_Rendition)_parameters
|
||||
func UnderlineColorAttr(c Color) Attr {
|
||||
switch c := c.(type) {
|
||||
// NOTE: we can't use 3-bit and 4-bit ANSI color codes with underline
|
||||
// color, use 256-color instead.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 256-color ANSI underline color
|
||||
// "58;5;<n>"
|
||||
case BasicColor:
|
||||
return "58;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case ExtendedColor:
|
||||
return "58;5;" + strconv.FormatUint(uint64(c), 10)
|
||||
case TrueColor, color.Color:
|
||||
// 24-bit "true color" foreground
|
||||
// "38;2;<r>;<g>;<b>"
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
return "58;2;" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(r)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(g)), 10) + ";" +
|
||||
strconv.FormatUint(uint64(shift(b)), 10)
|
||||
}
|
||||
return DefaultUnderlineColorAttr
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func shift(v uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
if v > 0xff {
|
||||
return v >> 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
31
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/termcap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"encoding/hex"
|
||||
"strings"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestTermcap (XTGETTCAP) requests Termcap/Terminfo strings.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// DCS + q <Pt> ST
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Where <Pt> is a list of Termcap/Terminfo capabilities, encoded in 2-digit
|
||||
// hexadecimals, separated by semicolons.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/terminfo.5.html
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func RequestTermcap(caps ...string) string {
|
||||
if len(caps) == 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
s := "\x1bP+q"
|
||||
for i, c := range caps {
|
||||
if i > 0 {
|
||||
s += ";"
|
||||
}
|
||||
s += strings.ToUpper(hex.EncodeToString([]byte(c)))
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return s + "\x1b\\"
|
||||
}
|
||||
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/title.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
32
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/title.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// SetIconNameWindowTitle returns a sequence for setting the icon name and
|
||||
// window title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 0 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 0 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetIconNameWindowTitle(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]0;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetIconName returns a sequence for setting the icon name.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 1 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 1 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetIconName(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]1;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// SetWindowTitle returns a sequence for setting the window title.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// OSC 2 ; title ST
|
||||
// OSC 2 ; title BEL
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h2-Operating-System-Commands
|
||||
func SetWindowTitle(s string) string {
|
||||
return "\x1b]2;" + s + "\x07"
|
||||
}
|
||||
112
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
112
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/truncate.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Truncate truncates a string to a given length, adding a tail to the
|
||||
// end if the string is longer than the given length.
|
||||
// This function is aware of ANSI escape codes and will not break them, and
|
||||
// accounts for wide-characters (such as East Asians and emojis).
|
||||
func Truncate(s string, length int, tail string) string {
|
||||
if sw := StringWidth(s); sw <= length {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tw := StringWidth(tail)
|
||||
length -= tw
|
||||
if length < 0 {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var cluster []byte
|
||||
var buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth := 0
|
||||
ignoring := false
|
||||
gstate := -1
|
||||
pstate := parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b := []byte(s)
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
|
||||
// Here we iterate over the bytes of the string and collect printable
|
||||
// characters and runes. We also keep track of the width of the string
|
||||
// in cells.
|
||||
// Once we reach the given length, we start ignoring characters and only
|
||||
// collect ANSI escape codes until we reach the end of string.
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
|
||||
// increment the index by the length of the cluster
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
// Are we ignoring? Skip to the next byte
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > length {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
for _, r := range cluster {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(r)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gstate = -1 // reset grapheme state otherwise, width calculation might be off
|
||||
// Done collecting, now we're back in the ground state.
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Is this gonna be too wide?
|
||||
// If so write the tail and stop collecting.
|
||||
if curWidth >= length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip to the next byte if we're ignoring
|
||||
if ignoring {
|
||||
i++
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// collects printable ASCII
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
default:
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transition to the next state.
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
|
||||
// Once we reach the given length, we start ignoring runes and write
|
||||
// the tail to the buffer.
|
||||
if curWidth > length && !ignoring {
|
||||
ignoring = true
|
||||
buf.WriteString(tail)
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
29
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/util.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"fmt"
|
||||
"image/color"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// colorToHexString returns a hex string representation of a color.
|
||||
func colorToHexString(c color.Color) string {
|
||||
if c == nil {
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
shift := func(v uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
if v > 0xff {
|
||||
return v >> 8
|
||||
}
|
||||
return v
|
||||
}
|
||||
r, g, b, _ := c.RGBA()
|
||||
r, g, b = shift(r), shift(g), shift(b)
|
||||
return fmt.Sprintf("#%02x%02x%02x", r, g, b)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// rgbToHex converts red, green, and blue values to a hexadecimal value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// hex := rgbToHex(0, 0, 255) // 0x0000FF
|
||||
func rgbToHex(r, g, b uint32) uint32 {
|
||||
return r<<16 + g<<8 + b
|
||||
}
|
||||
99
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/width.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
99
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/width.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// Strip removes ANSI escape codes from a string.
|
||||
func Strip(s string) string {
|
||||
var (
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer // buffer for collecting printable characters
|
||||
ri int // rune index
|
||||
rw int // rune width
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// This implements a subset of the Parser to only collect runes and
|
||||
// printable characters.
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
var state, action byte
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
state, action = parser.Table.Transition(pstate, s[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case pstate == parser.Utf8State:
|
||||
// During this state, collect rw bytes to form a valid rune in the
|
||||
// buffer. After getting all the rune bytes into the buffer,
|
||||
// transition to GroundState and reset the counters.
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(s[i])
|
||||
ri++
|
||||
if ri < rw {
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
ri = 0
|
||||
rw = 0
|
||||
case action == parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
// This action happens when we transition to the Utf8State.
|
||||
if w := utf8ByteLen(s[i]); w > 1 {
|
||||
rw = w
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(s[i])
|
||||
ri++
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case action == parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
// collects printable ASCII and non-printable characters
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(s[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Transition to the next state.
|
||||
// The Utf8State is managed separately above.
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// StringWidth returns the width of a string in cells. This is the number of
|
||||
// cells that the string will occupy when printed in a terminal. ANSI escape
|
||||
// codes are ignored and wide characters (such as East Asians and emojis) are
|
||||
// accounted for.
|
||||
func StringWidth(s string) int {
|
||||
if s == "" {
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
cluster string
|
||||
width int
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
for i := 0; i < len(s); i++ {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, s[i])
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(s[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var w int
|
||||
cluster, _, w, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeClusterInString(s[i:], gstate)
|
||||
width += w
|
||||
i += len(cluster) - 1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
width++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return width
|
||||
}
|
||||
406
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/wrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
406
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/wrap.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,406 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
import (
|
||||
"bytes"
|
||||
"unicode"
|
||||
"unicode/utf8"
|
||||
|
||||
"github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/parser"
|
||||
"github.com/rivo/uniseg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
// nbsp is a non-breaking space
|
||||
const nbsp = 0xA0
|
||||
|
||||
// Hardwrap wraps a string or a block of text to a given line length, breaking
|
||||
// word boundaries. This will preserve ANSI escape codes and will account for
|
||||
// wide-characters in the string.
|
||||
// When preserveSpace is true, spaces at the beginning of a line will be
|
||||
// preserved.
|
||||
func Hardwrap(s string, limit int, preserveSpace bool) string {
|
||||
if limit < 1 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
cluster []byte
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int
|
||||
forceNewline bool
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
addNewline := func() {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('\n')
|
||||
curWidth = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+width > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
if !preserveSpace && curWidth == 0 && len(cluster) <= 4 {
|
||||
// Skip spaces at the beginning of a line
|
||||
if r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster); r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) {
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
gstate = -1 // reset grapheme state otherwise, width calculation might be off
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
if b[i] == '\n' {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
forceNewline = false
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+1 > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
forceNewline = true
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Skip spaces at the beginning of a line
|
||||
if curWidth == 0 {
|
||||
if !preserveSpace && forceNewline && unicode.IsSpace(rune(b[i])) {
|
||||
break
|
||||
}
|
||||
forceNewline = false
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
default:
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We manage the UTF8 state separately manually above.
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wordwrap wraps a string or a block of text to a given line length, not
|
||||
// breaking word boundaries. This will preserve ANSI escape codes and will
|
||||
// account for wide-characters in the string.
|
||||
// The breakpoints string is a list of characters that are considered
|
||||
// breakpoints for word wrapping. A hyphen (-) is always considered a
|
||||
// breakpoint.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: breakpoints must be a string of 1-cell wide rune characters.
|
||||
func Wordwrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
if limit < 1 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
cluster []byte
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
word bytes.Buffer
|
||||
space bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int
|
||||
wordLen int
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
addSpace := func() {
|
||||
curWidth += space.Len()
|
||||
buf.Write(space.Bytes())
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addWord := func() {
|
||||
if word.Len() == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
curWidth += wordLen
|
||||
buf.Write(word.Bytes())
|
||||
word.Reset()
|
||||
wordLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addNewline := func() {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('\n')
|
||||
curWidth = 0
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
if r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
} else if bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints) {
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len()+wordLen > limit &&
|
||||
wordLen < limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
r := rune(b[i])
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r == '\n':
|
||||
if wordLen == 0 {
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
curWidth = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
buf.Write(space.Bytes())
|
||||
}
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
case unicode.IsSpace(r):
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
case r == '-':
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case runeContainsAny(r, breakpoints):
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
default:
|
||||
word.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
wordLen++
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len()+wordLen > limit &&
|
||||
wordLen < limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
word.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We manage the UTF8 state separately manually above.
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Wrap wraps a string or a block of text to a given line length, breaking word
|
||||
// boundaries if necessary. This will preserve ANSI escape codes and will
|
||||
// account for wide-characters in the string. The breakpoints string is a list
|
||||
// of characters that are considered breakpoints for word wrapping. A hyphen
|
||||
// (-) is always considered a breakpoint.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note: breakpoints must be a string of 1-cell wide rune characters.
|
||||
func Wrap(s string, limit int, breakpoints string) string {
|
||||
if limit < 1 {
|
||||
return s
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
var (
|
||||
cluster []byte
|
||||
buf bytes.Buffer
|
||||
word bytes.Buffer
|
||||
space bytes.Buffer
|
||||
curWidth int // written width of the line
|
||||
wordLen int // word buffer len without ANSI escape codes
|
||||
gstate = -1
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState // initial state
|
||||
b = []byte(s)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
addSpace := func() {
|
||||
curWidth += space.Len()
|
||||
buf.Write(space.Bytes())
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addWord := func() {
|
||||
if word.Len() == 0 {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
curWidth += wordLen
|
||||
buf.Write(word.Bytes())
|
||||
word.Reset()
|
||||
wordLen = 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addNewline := func() {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('\n')
|
||||
curWidth = 0
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
i := 0
|
||||
for i < len(b) {
|
||||
state, action := parser.Table.Transition(pstate, b[i])
|
||||
|
||||
switch action {
|
||||
case parser.PrintAction:
|
||||
if utf8ByteLen(b[i]) > 1 {
|
||||
var width int
|
||||
cluster, _, width, gstate = uniseg.FirstGraphemeCluster(b[i:], gstate)
|
||||
i += len(cluster)
|
||||
|
||||
r, _ := utf8.DecodeRune(cluster)
|
||||
switch {
|
||||
case r != utf8.RuneError && unicode.IsSpace(r) && r != nbsp: // nbsp is a non-breaking space
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
case bytes.ContainsAny(cluster, breakpoints):
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.Write(cluster)
|
||||
curWidth += width
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
if wordLen+width > limit {
|
||||
// Hardwrap the word if it's too long
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
word.Write(cluster)
|
||||
wordLen += width
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
pstate = parser.GroundState
|
||||
continue
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case parser.ExecuteAction:
|
||||
switch r := rune(b[i]); {
|
||||
case r == '\n':
|
||||
if wordLen == 0 {
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
curWidth = 0
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
// preserve whitespaces
|
||||
buf.Write(space.Bytes())
|
||||
}
|
||||
space.Reset()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
case unicode.IsSpace(r):
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
space.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
case r == '-':
|
||||
fallthrough
|
||||
case runeContainsAny(r, breakpoints):
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen >= limit {
|
||||
// We can't fit the breakpoint in the current line, treat
|
||||
// it as part of the word.
|
||||
word.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
wordLen++
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
buf.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
curWidth++
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
word.WriteRune(r)
|
||||
wordLen++
|
||||
|
||||
if wordLen == limit {
|
||||
// Hardwrap the word if it's too long
|
||||
addWord()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if curWidth+wordLen+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
addNewline()
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
word.WriteByte(b[i])
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We manage the UTF8 state separately manually above.
|
||||
if pstate != parser.Utf8State {
|
||||
pstate = state
|
||||
}
|
||||
i++
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if word.Len() != 0 {
|
||||
// Preserve ANSI wrapped spaces at the end of string
|
||||
if curWidth+space.Len() > limit {
|
||||
buf.WriteByte('\n')
|
||||
}
|
||||
addSpace()
|
||||
}
|
||||
buf.Write(word.Bytes())
|
||||
|
||||
return buf.String()
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
func runeContainsAny(r rune, s string) bool {
|
||||
for _, c := range s {
|
||||
if c == r {
|
||||
return true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false
|
||||
}
|
||||
33
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/xterm.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
33
vendor/github.com/charmbracelet/x/ansi/xterm.go
generated
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
package ansi
|
||||
|
||||
// DisableModifyOtherKeys disables the modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 4 ; 0 m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
const DisableModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[>4;0m"
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableModifyOtherKeys1 enables the modifyOtherKeys mode 1.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 4 ; 1 m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
const EnableModifyOtherKeys1 = "\x1b[>4;1m"
|
||||
|
||||
// EnableModifyOtherKeys2 enables the modifyOtherKeys mode 2.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI > 4 ; 2 m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
const EnableModifyOtherKeys2 = "\x1b[>4;2m"
|
||||
|
||||
// RequestModifyOtherKeys requests the modifyOtherKeys mode.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// CSI ? 4 m
|
||||
//
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/ctlseqs/ctlseqs.html#h3-Functions-using-CSI-_-ordered-by-the-final-character_s_
|
||||
// See: https://invisible-island.net/xterm/manpage/xterm.html#VT100-Widget-Resources:modifyOtherKeys
|
||||
const RequestModifyOtherKeys = "\x1b[?4m"
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user